三步问题。有个小孩正在上楼梯,楼梯有n阶台阶,小孩一次可以上1阶、2阶或3阶。实现一种方法,计算小孩有多少种上楼梯的方式。结果可能很大,你需要对结果模1000000007。
+
+
+
+
### 方法二:矩阵快速幂加速递推
我们设 $F(n)$ 表示一个 $1 \times 3$ 的矩阵 $\begin{bmatrix} F_{n - 1} & F_{n - 2} & F_{n - 3} \end{bmatrix}$,其中 $F_{n - 1}$, $F_{n - 2}$ 和 $F_{n - 3}$ 分别表示上第 $n - 1$ 阶、第 $n - 2$ 阶和第 $n - 3$ 阶台阶的方法数。
@@ -171,35 +224,30 @@ $$
+#### Python3
+
```python
-class Solution:
- def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
- mod = 10**9 + 7
+import numpy as np
- def mul(a: List[List[int]], b: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
- m, n = len(a), len(b[0])
- c = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
- for i in range(m):
- for j in range(n):
- for k in range(len(a[0])):
- c[i][j] = (c[i][j] + a[i][k] * b[k][j] % mod) % mod
- return c
-
- def pow(a: List[List[int]], n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- res = [[4, 2, 1]]
- while n:
- if n & 1:
- res = mul(res, a)
- n >>= 1
- a = mul(a, a)
- return res
+class Solution:
+ def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
if n < 4:
return 2 ** (n - 1)
- a = [[1, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0]]
- return sum(pow(a, n - 4)[0]) % mod
+ mod = 10**9 + 7
+ factor = np.asmatrix([(1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0)], np.dtype("O"))
+ res = np.asmatrix([(4, 2, 1)], np.dtype("O"))
+ n -= 4
+ while n:
+ if n & 1:
+ res = res * factor % mod
+ factor = factor * factor % mod
+ n >>= 1
+ return res.sum() % mod
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
private final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
@@ -244,6 +292,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -290,6 +340,8 @@ private:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
const mod = 1e9 + 7
@@ -334,6 +386,8 @@ func pow(a [][]int, n int) [][]int {
}
```
+#### JavaScript
+
```js
/**
* @param {number} n
@@ -388,30 +442,6 @@ function pow(a, n) {
-### 方法三
-
-
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-
-
-class Solution:
- def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
- if n < 4:
- return 2 ** (n - 1)
- mod = 10**9 + 7
- factor = np.mat([(1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0)], np.dtype("O"))
- res = np.mat([(4, 2, 1)], np.dtype("O"))
- n -= 4
- while n:
- if n & 1:
- res = res * factor % mod
- factor = factor * factor % mod
- n >>= 1
- return res.sum() % mod
-```
-
-
+
-
+
diff --git a/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/README_EN.md b/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/README_EN.md
index fbd07e6ed265c..1f10f60a219b3 100644
--- a/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/README_EN.md
+++ b/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/README_EN.md
@@ -1,16 +1,26 @@
+---
+comments: true
+difficulty: Easy
+edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcci/08.01.Three%20Steps%20Problem/README_EN.md
+---
+
+
+
# [08.01. Three Steps Problem](https://leetcode.cn/problems/three-steps-problem-lcci)
[中文文档](/lcci/08.01.Three%20Steps%20Problem/README.md)
## Description
+
+
A child is running up a staircase with n steps and can hop either 1 step, 2 steps, or 3 steps at a time. Implement a method to count how many possible ways the child can run up the stairs. The result may be large, so return it modulo 1000000007.
Example1:
- Input: n = 3
+ Input: n = 3
Output: 4
@@ -30,8 +40,12 @@
1. `1 <= n <= 1000000`
+
+
## Solutions
+
+
### Solution 1: Recursion
We define $f[i]$ as the number of ways to reach the $i$-th step, initially $f[1]=1$, $f[2]=2$, $f[3]=4$. The answer is $f[n]$.
@@ -44,6 +58,8 @@ The time complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the given integer. The space complex
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
@@ -54,6 +70,8 @@ class Solution:
return a
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
public int waysToStep(int n) {
@@ -70,6 +88,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -87,6 +107,8 @@ public:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func waysToStep(n int) int {
const mod int = 1e9 + 7
@@ -98,6 +120,8 @@ func waysToStep(n int) int {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn ways_to_step(n: i32) -> i32 {
@@ -114,6 +138,8 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+#### JavaScript
+
```js
/**
* @param {number} n
@@ -129,6 +155,8 @@ var waysToStep = function (n) {
};
```
+#### C
+
```c
int waysToStep(int n) {
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
@@ -143,8 +171,34 @@ int waysToStep(int n) {
}
```
+#### Swift
+
+```swift
+class Solution {
+ func waysToStep(_ n: Int) -> Int {
+ let mod = Int(1e9) + 7
+ var a = 1, b = 2, c = 4
+ if n == 1 { return a }
+ if n == 2 { return b }
+ if n == 3 { return c }
+
+ for _ in 1..
+
+
+
+
### Solution 2: Matrix Quick Power to Accelerate Recursion
We set $F(n)$ to represent a $1 \times 3$ matrix $\begin{bmatrix} F_{n - 1} & F_{n - 2} & F_{n - 3} \end{bmatrix}$, where $F_{n - 1}$, $F_{n - 2}$ and $F_{n - 3}$ respectively represent the number of ways to reach the $n - 1$-th, $n - 2$-th and $n - 3$-th steps.
@@ -173,35 +227,30 @@ The time complexity is $O(\log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(1)$.
+#### Python3
+
```python
-class Solution:
- def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
- mod = 10**9 + 7
+import numpy as np
- def mul(a: List[List[int]], b: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
- m, n = len(a), len(b[0])
- c = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
- for i in range(m):
- for j in range(n):
- for k in range(len(a[0])):
- c[i][j] = (c[i][j] + a[i][k] * b[k][j] % mod) % mod
- return c
-
- def pow(a: List[List[int]], n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- res = [[4, 2, 1]]
- while n:
- if n & 1:
- res = mul(res, a)
- n >>= 1
- a = mul(a, a)
- return res
+class Solution:
+ def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
if n < 4:
return 2 ** (n - 1)
- a = [[1, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0]]
- return sum(pow(a, n - 4)[0]) % mod
+ mod = 10**9 + 7
+ factor = np.asmatrix([(1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0)], np.dtype("O"))
+ res = np.asmatrix([(4, 2, 1)], np.dtype("O"))
+ n -= 4
+ while n:
+ if n & 1:
+ res = res * factor % mod
+ factor = factor * factor % mod
+ n >>= 1
+ return res.sum() % mod
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
private final int mod = (int) 1e9 + 7;
@@ -246,6 +295,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -292,6 +343,8 @@ private:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
const mod = 1e9 + 7
@@ -336,6 +389,8 @@ func pow(a [][]int, n int) [][]int {
}
```
+#### JavaScript
+
```js
/**
* @param {number} n
@@ -390,30 +445,6 @@ function pow(a, n) {
-### Solution 3
-
-
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-
-
-class Solution:
- def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
- if n < 4:
- return 2 ** (n - 1)
- mod = 10**9 + 7
- factor = np.mat([(1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0)], np.dtype("O"))
- res = np.mat([(4, 2, 1)], np.dtype("O"))
- n -= 4
- while n:
- if n & 1:
- res = res * factor % mod
- factor = factor * factor % mod
- n >>= 1
- return res.sum() % mod
-```
-
-
+
-
+
diff --git a/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/Solution.swift b/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/Solution.swift
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..b7d24920626c5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/Solution.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+class Solution {
+ func waysToStep(_ n: Int) -> Int {
+ let mod = Int(1e9) + 7
+ var a = 1, b = 2, c = 4
+ if n == 1 { return a }
+ if n == 2 { return b }
+ if n == 3 { return c }
+
+ for _ in 1.. int:
- mod = 10**9 + 7
-
- def mul(a: List[List[int]], b: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
- m, n = len(a), len(b[0])
- c = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
- for i in range(m):
- for j in range(n):
- for k in range(len(a[0])):
- c[i][j] = (c[i][j] + a[i][k] * b[k][j] % mod) % mod
- return c
+import numpy as np
- def pow(a: List[List[int]], n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
- res = [[4, 2, 1]]
- while n:
- if n & 1:
- res = mul(res, a)
- n >>= 1
- a = mul(a, a)
- return res
+class Solution:
+ def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
if n < 4:
return 2 ** (n - 1)
- a = [[1, 1, 0], [1, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0]]
- return sum(pow(a, n - 4)[0]) % mod
+ mod = 10**9 + 7
+ factor = np.asmatrix([(1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0)], np.dtype("O"))
+ res = np.asmatrix([(4, 2, 1)], np.dtype("O"))
+ n -= 4
+ while n:
+ if n & 1:
+ res = res * factor % mod
+ factor = factor * factor % mod
+ n >>= 1
+ return res.sum() % mod
diff --git a/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/Solution3.py b/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/Solution3.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 7ee79117fbbaa..0000000000000
--- a/lcci/08.01.Three Steps Problem/Solution3.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
-import numpy as np
-
-
-class Solution:
- def waysToStep(self, n: int) -> int:
- if n < 4:
- return 2 ** (n - 1)
- mod = 10**9 + 7
- factor = np.mat([(1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0)], np.dtype("O"))
- res = np.mat([(4, 2, 1)], np.dtype("O"))
- n -= 4
- while n:
- if n & 1:
- res = res * factor % mod
- factor = factor * factor % mod
- n >>= 1
- return res.sum() % mod
diff --git a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/README.md b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/README.md
index e8626d6dd0ae7..8b60835e73b0c 100644
--- a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/README.md
+++ b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/README.md
@@ -1,12 +1,23 @@
+---
+comments: true
+difficulty: 中等
+edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcci/08.02.Robot%20in%20a%20Grid/README.md
+---
+
+
+
# [面试题 08.02. 迷路的机器人](https://leetcode.cn/problems/robot-in-a-grid-lcci)
[English Version](/lcci/08.02.Robot%20in%20a%20Grid/README_EN.md)
## 题目描述
-
+
+
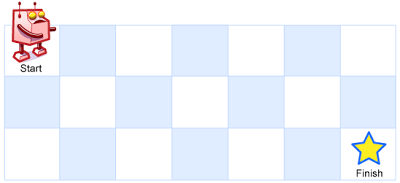
设想有个机器人坐在一个网格的左上角,网格 r 行 c 列。机器人只能向下或向右移动,但不能走到一些被禁止的网格(有障碍物)。设计一种算法,寻找机器人从左上角移动到右下角的路径。
+
+
网格中的障碍物和空位置分别用 1 和 0 来表示。
返回一条可行的路径,路径由经过的网格的行号和列号组成。左上角为 0 行 0 列。
示例 1:
@@ -17,13 +28,17 @@
[0,0,0]
]
输出: [[0,0],[0,1],[0,2],[1,2],[2,2]]
-解释:
+解释:
输入中标粗的位置即为输出表示的路径,即
0行0列(左上角) -> 0行1列 -> 0行2列 -> 1行2列 -> 2行2列(右下角)
说明:r 和 c 的值均不超过 100。
+
+
## 解法
+
+
### 方法一:DFS
我们可以使用深度优先搜索来解决本题。我们从左上角开始,向右或向下移动,直到到达右下角。如果在某一步,我们发现当前位置是障碍物,或者当前位置已经在路径中,那么我们就返回,否则我们将当前位置加入路径中,并且标记当前位置为已经访问过,然后继续向右或向下移动。
@@ -34,6 +49,8 @@
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def pathWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
@@ -52,6 +69,8 @@ class Solution:
return ans if dfs(0, 0) else []
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
private List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
@@ -81,6 +100,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -88,7 +109,7 @@ public:
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector> ans;
- function dfs = [&](int i, int j) -> bool {
+ auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int i, int j) -> bool {
if (i >= m || j >= n || obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {
return false;
}
@@ -105,6 +126,8 @@ public:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func pathWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(obstacleGrid), len(obstacleGrid[0])
@@ -129,6 +152,8 @@ func pathWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) [][]int {
}
```
+#### TypeScript
+
```ts
function pathWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = obstacleGrid.length;
@@ -153,6 +178,8 @@ function pathWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number[][] {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
fn dfs(grid: &mut Vec>, path: &mut Vec>, i: usize, j: usize) -> bool {
@@ -161,10 +188,9 @@ impl Solution {
}
path.push(vec![i as i32, j as i32]);
grid[i as usize][j as usize] = 1;
- if
- (i + 1 == grid.len() && j + 1 == grid[0].len()) ||
- Self::dfs(grid, path, i + 1, j) ||
- Self::dfs(grid, path, i, j + 1)
+ if (i + 1 == grid.len() && j + 1 == grid[0].len())
+ || Self::dfs(grid, path, i + 1, j)
+ || Self::dfs(grid, path, i, j + 1)
{
return true;
}
@@ -182,6 +208,39 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+#### Swift
+
+```swift
+class Solution {
+ private var ans = [[Int]]()
+ private var g: [[Int]] = []
+ private var m: Int = 0
+ private var n: Int = 0
+
+ func pathWithObstacles(_ obstacleGrid: [[Int]]) -> [[Int]] {
+ g = obstacleGrid
+ m = g.count
+ n = g[0].count
+ return dfs(0, 0) ? ans : []
+ }
+
+ private func dfs(_ i: Int, _ j: Int) -> Bool {
+ if i >= m || j >= n || g[i][j] == 1 {
+ return false
+ }
+ ans.append([i, j])
+ g[i][j] = 1
+ if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) || dfs(i + 1, j) || dfs(i, j + 1) {
+ return true
+ }
+ ans.removeLast()
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
+
+
+
diff --git a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/README_EN.md b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/README_EN.md
index 7e3d51ee10130..bb37b1b1bf1d9 100644
--- a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/README_EN.md
+++ b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/README_EN.md
@@ -1,11 +1,23 @@
+---
+comments: true
+difficulty: Medium
+edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcci/08.02.Robot%20in%20a%20Grid/README_EN.md
+---
+
+
+
# [08.02. Robot in a Grid](https://leetcode.cn/problems/robot-in-a-grid-lcci)
[中文文档](/lcci/08.02.Robot%20in%20a%20Grid/README.md)
## Description
+
+
Imagine a robot sitting on the upper left corner of grid with r rows and c columns. The robot can only move in two directions, right and down, but certain cells are "off limits" such that the robot cannot step on them. Design an algorithm to find a path for the robot from the top left to the bottom right.
+

+
"off limits" and empty grid are represented by 1 and 0 respectively.
Return a valid path, consisting of row number and column number of grids in the path.
Example 1:
@@ -30,8 +42,12 @@
r, c <= 100
+
+
## Solutions
+
+
### Solution 1: DFS (Depth-First Search)
We can use depth-first search to solve this problem. We start from the top left corner and move right or down until we reach the bottom right corner. If at some step, we find that the current position is an obstacle, or the current position is already in the path, then we return. Otherwise, we add the current position to the path and mark the current position as visited, then continue to move right or down.
@@ -42,6 +58,8 @@ The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$, and the space complexity is $O(m \times
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def pathWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
@@ -60,6 +78,8 @@ class Solution:
return ans if dfs(0, 0) else []
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
private List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
@@ -89,6 +109,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -96,7 +118,7 @@ public:
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector> ans;
- function dfs = [&](int i, int j) -> bool {
+ auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int i, int j) -> bool {
if (i >= m || j >= n || obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {
return false;
}
@@ -113,6 +135,8 @@ public:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func pathWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(obstacleGrid), len(obstacleGrid[0])
@@ -137,6 +161,8 @@ func pathWithObstacles(obstacleGrid [][]int) [][]int {
}
```
+#### TypeScript
+
```ts
function pathWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = obstacleGrid.length;
@@ -161,6 +187,8 @@ function pathWithObstacles(obstacleGrid: number[][]): number[][] {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
fn dfs(grid: &mut Vec>, path: &mut Vec>, i: usize, j: usize) -> bool {
@@ -169,10 +197,9 @@ impl Solution {
}
path.push(vec![i as i32, j as i32]);
grid[i as usize][j as usize] = 1;
- if
- (i + 1 == grid.len() && j + 1 == grid[0].len()) ||
- Self::dfs(grid, path, i + 1, j) ||
- Self::dfs(grid, path, i, j + 1)
+ if (i + 1 == grid.len() && j + 1 == grid[0].len())
+ || Self::dfs(grid, path, i + 1, j)
+ || Self::dfs(grid, path, i, j + 1)
{
return true;
}
@@ -190,6 +217,39 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+#### Swift
+
+```swift
+class Solution {
+ private var ans = [[Int]]()
+ private var g: [[Int]] = []
+ private var m: Int = 0
+ private var n: Int = 0
+
+ func pathWithObstacles(_ obstacleGrid: [[Int]]) -> [[Int]] {
+ g = obstacleGrid
+ m = g.count
+ n = g[0].count
+ return dfs(0, 0) ? ans : []
+ }
+
+ private func dfs(_ i: Int, _ j: Int) -> Bool {
+ if i >= m || j >= n || g[i][j] == 1 {
+ return false
+ }
+ ans.append([i, j])
+ g[i][j] = 1
+ if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) || dfs(i + 1, j) || dfs(i, j + 1) {
+ return true
+ }
+ ans.removeLast()
+ return false
+ }
+}
+```
+
-
+
+
+
diff --git a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.cpp b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.cpp
index e9657e05ef757..f7daef341d833 100644
--- a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.cpp
+++ b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.cpp
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ class Solution {
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector> ans;
- function dfs = [&](int i, int j) -> bool {
+ auto dfs = [&](this auto&& dfs, int i, int j) -> bool {
if (i >= m || j >= n || obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {
return false;
}
@@ -18,4 +18,4 @@ class Solution {
};
return dfs(0, 0) ? ans : vector>();
}
-};
\ No newline at end of file
+};
diff --git a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.rs b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.rs
index 6c6e7a5d7adad..3f121643bd9ce 100644
--- a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.rs
+++ b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.rs
@@ -5,10 +5,9 @@ impl Solution {
}
path.push(vec![i as i32, j as i32]);
grid[i as usize][j as usize] = 1;
- if
- (i + 1 == grid.len() && j + 1 == grid[0].len()) ||
- Self::dfs(grid, path, i + 1, j) ||
- Self::dfs(grid, path, i, j + 1)
+ if (i + 1 == grid.len() && j + 1 == grid[0].len())
+ || Self::dfs(grid, path, i + 1, j)
+ || Self::dfs(grid, path, i, j + 1)
{
return true;
}
diff --git a/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.swift b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.swift
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..cd7e2c70825de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/lcci/08.02.Robot in a Grid/Solution.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
+class Solution {
+ private var ans = [[Int]]()
+ private var g: [[Int]] = []
+ private var m: Int = 0
+ private var n: Int = 0
+
+ func pathWithObstacles(_ obstacleGrid: [[Int]]) -> [[Int]] {
+ g = obstacleGrid
+ m = g.count
+ n = g[0].count
+ return dfs(0, 0) ? ans : []
+ }
+
+ private func dfs(_ i: Int, _ j: Int) -> Bool {
+ if i >= m || j >= n || g[i][j] == 1 {
+ return false
+ }
+ ans.append([i, j])
+ g[i][j] = 1
+ if (i == m - 1 && j == n - 1) || dfs(i + 1, j) || dfs(i, j + 1) {
+ return true
+ }
+ ans.removeLast()
+ return false
+ }
+}
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/README.md b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/README.md
index 69924ac5de815..cab927034e5ea 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/README.md
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/README.md
@@ -1,10 +1,19 @@
+---
+comments: true
+difficulty: 简单
+edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcci/08.03.Magic%20Index/README.md
+---
+
+
+
# [面试题 08.03. 魔术索引](https://leetcode.cn/problems/magic-index-lcci)
[English Version](/lcci/08.03.Magic%20Index/README_EN.md)
## 题目描述
-
+
+
魔术索引。 在数组A[0...n-1]中,有所谓的魔术索引,满足条件A[i] = i。给定一个有序整数数组,编写一种方法找出魔术索引,若有的话,在数组A中找出一个魔术索引,如果没有,则返回-1。若有多个魔术索引,返回索引值最小的一个。
示例1:
@@ -26,202 +35,218 @@
nums长度在[1, 1000000]之间
+
+
## 解法
-### 方法一
+
+
+### 方法一:二分搜索
+
+我们设计一个函数 $dfs(i, j)$,表示在数组 $nums[i, j]$ 中寻找魔术索引。如果找到了,返回魔术索引的值,否则返回 $-1$。那么答案就是 $dfs(0, n-1)$。
+
+函数 $dfs(i, j)$ 的实现如下:
+
+1. 如果 $i > j$,返回 $-1$。
+2. 否则,我们取中间位置 $mid = (i + j) / 2$,然后递归调用 $dfs(i, mid-1)$,如果返回值不为 $-1$,说明在左半部分找到了魔术索引,直接返回。否则,如果 $nums[mid] = mid$,说明找到了魔术索引,直接返回。否则,递归调用 $dfs(mid+1, j)$ 并返回。
+
+时间复杂度最坏情况下为 $O(n)$,空间复杂度最坏情况下为 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组 $nums$ 的长度。
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def findMagicIndex(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
- def find(nums, left, right):
- if left > right:
+ def dfs(i: int, j: int) -> int:
+ if i > j:
return -1
- mid = (left + right) >> 1
- left_index = find(nums, left, mid - 1)
- if left_index != -1:
- return left_index
+ mid = (i + j) >> 1
+ l = dfs(i, mid - 1)
+ if l != -1:
+ return l
if nums[mid] == mid:
return mid
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right)
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j)
- return find(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
+ return dfs(0, len(nums) - 1)
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
public int findMagicIndex(int[] nums) {
- int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
- return find(nums, left, right);
+ return dfs(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
- private int find(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
- if (left > right) {
+ private int dfs(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
+ if (i > j) {
return -1;
}
- int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
- int leftIndex = find(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) {
- return leftIndex;
+ int mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ int l = dfs(nums, i, mid - 1);
+ if (l != -1) {
+ return l;
}
if (nums[mid] == mid) {
return mid;
}
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right);
+ return dfs(nums, mid + 1, j);
}
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
int findMagicIndex(vector& nums) {
- return find(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
- }
-
- int find(vector& nums, int left, int right) {
- if (left > right) {
- return -1;
- }
- int mid = left + right >> 1;
- int leftIndex = find(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) {
- return leftIndex;
- }
- if (nums[mid] == mid) {
- return mid;
- }
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right);
+ function dfs = [&](int i, int j) {
+ if (i > j) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ int mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ int l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l != -1) {
+ return l;
+ }
+ if (nums[mid] == mid) {
+ return mid;
+ }
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
+ };
+ return dfs(0, nums.size() - 1);
}
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func findMagicIndex(nums []int) int {
- return find(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
-}
-
-func find(nums []int, left, right int) int {
- if left > right {
- return -1
+ var dfs func(i, j int) int
+ dfs = func(i, j int) int {
+ if i > j {
+ return -1
+ }
+ mid := (i + j) >> 1
+ if l := dfs(i, mid-1); l != -1 {
+ return l
+ }
+ if nums[mid] == mid {
+ return mid
+ }
+ return dfs(mid+1, j)
}
- mid := (left + right) >> 1
- leftIndex := find(nums, left, mid-1)
- if leftIndex != -1 {
- return leftIndex
- }
- if nums[mid] == mid {
- return mid
- }
- return find(nums, mid+1, right)
+ return dfs(0, len(nums)-1)
}
```
+#### TypeScript
+
```ts
function findMagicIndex(nums: number[]): number {
- const n = nums.length;
- const find = (l: number, r: number): number => {
- if (l > r || nums[r] < 0) {
+ const dfs = (i: number, j: number): number => {
+ if (i > j) {
return -1;
}
- const mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
- if (nums[mid] >= l) {
- const res = find(l, mid - 1);
- if (res !== -1) {
- return res;
- }
+ const mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ const l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l !== -1) {
+ return l;
}
if (nums[mid] === mid) {
return mid;
}
- return find(mid + 1, r);
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
};
- return find(0, n - 1);
+ return dfs(0, nums.length - 1);
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
- fn find(nums: &Vec, l: usize, r: usize) -> i32 {
- if l >= r || nums[r - 1] < 0 {
+ fn dfs(nums: &Vec, i: usize, j: usize) -> i32 {
+ if i >= j || nums[j - 1] < 0 {
return -1;
}
- let mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
- if nums[mid] >= (l as i32) {
- let res = Self::find(nums, l, mid);
- if res != -1 {
- return res;
+ let mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ if nums[mid] >= (i as i32) {
+ let l = Self::dfs(nums, i, mid);
+ if l != -1 {
+ return l;
}
}
if nums[mid] == (mid as i32) {
return mid as i32;
}
- Self::find(nums, mid + 1, r)
+ Self::dfs(nums, mid + 1, j)
}
pub fn find_magic_index(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- Self::find(&nums, 0, nums.len())
+ Self::dfs(&nums, 0, nums.len())
}
}
```
+#### JavaScript
+
```js
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var findMagicIndex = function (nums) {
- return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
+ const dfs = (i, j) => {
+ if (i > j) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ const mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ const l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l !== -1) {
+ return l;
+ }
+ if (nums[mid] === mid) {
+ return mid;
+ }
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
+ };
+ return dfs(0, nums.length - 1);
};
-
-function helper(nums, left, right) {
- if (left > right) return -1;
- let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
- let leftIndex = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) return leftIndex;
- if (nums[mid] == mid) return mid;
- return helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
-}
```
-
-
-### 方法二
+#### Swift
-
-
-```ts
-function findMagicIndex(nums: number[]): number {
- const n = nums.length;
- let i = 0;
- while (i < n) {
- if (nums[i] === i) {
- return i;
- }
- i = Math.max(nums[i], i + 1);
+```swift
+class Solution {
+ func findMagicIndex(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {
+ return find(nums, 0, nums.count - 1)
}
- return -1;
-}
-```
-```rust
-impl Solution {
- pub fn find_magic_index(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let n = nums.len();
- let mut i = 0 as i32;
- while (i as usize) < n {
- let num = nums[i as usize];
- if num == i {
- return i;
- }
- i = num.max(i + 1);
+ private func find(_ nums: [Int], _ i: Int, _ j: Int) -> Int {
+ if i > j {
+ return -1
}
- -1
+ let mid = (i + j) >> 1
+ let l = find(nums, i, mid - 1)
+ if l != -1 {
+ return l
+ }
+ if nums[mid] == mid {
+ return mid
+ }
+ return find(nums, mid + 1, j)
}
}
```
-
+
+
+
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/README_EN.md b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/README_EN.md
index e303eff8fa259..f2378b50c0365 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/README_EN.md
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/README_EN.md
@@ -1,9 +1,19 @@
+---
+comments: true
+difficulty: Easy
+edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcci/08.03.Magic%20Index/README_EN.md
+---
+
+
+
# [08.03. Magic Index](https://leetcode.cn/problems/magic-index-lcci)
[中文文档](/lcci/08.03.Magic%20Index/README.md)
## Description
+
+
A magic index in an array A[0...n-1] is defined to be an index such that A[i] = i. Given a sorted array of distinct integers, write a method to find a magic index, if one exists, in array A. If not, return -1. If there are more than one magic index, return the smallest one.
Example1:
@@ -32,202 +42,218 @@
1 <= nums.length <= 1000000
+
+
## Solutions
-### Solution 1
+
+
+### Solution 1: Binary Search
+
+We design a function $dfs(i, j)$ to find the magic index in the array $nums[i, j]$. If found, return the value of the magic index, otherwise return $-1$. So the answer is $dfs(0, n-1)$.
+
+The implementation of the function $dfs(i, j)$ is as follows:
+
+1. If $i > j$, return $-1$.
+2. Otherwise, we take the middle position $mid = (i + j) / 2$, then recursively call $dfs(i, mid-1)$. If the return value is not $-1$, it means that the magic index is found in the left half, return it directly. Otherwise, if $nums[mid] = mid$, it means that the magic index is found, return it directly. Otherwise, recursively call $dfs(mid+1, j)$ and return.
+
+In the worst case, the time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. Where $n$ is the length of the array $nums$.
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def findMagicIndex(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
- def find(nums, left, right):
- if left > right:
+ def dfs(i: int, j: int) -> int:
+ if i > j:
return -1
- mid = (left + right) >> 1
- left_index = find(nums, left, mid - 1)
- if left_index != -1:
- return left_index
+ mid = (i + j) >> 1
+ l = dfs(i, mid - 1)
+ if l != -1:
+ return l
if nums[mid] == mid:
return mid
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right)
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j)
- return find(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
+ return dfs(0, len(nums) - 1)
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
public int findMagicIndex(int[] nums) {
- int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
- return find(nums, left, right);
+ return dfs(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
- private int find(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
- if (left > right) {
+ private int dfs(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
+ if (i > j) {
return -1;
}
- int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
- int leftIndex = find(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) {
- return leftIndex;
+ int mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ int l = dfs(nums, i, mid - 1);
+ if (l != -1) {
+ return l;
}
if (nums[mid] == mid) {
return mid;
}
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right);
+ return dfs(nums, mid + 1, j);
}
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
int findMagicIndex(vector& nums) {
- return find(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
- }
-
- int find(vector& nums, int left, int right) {
- if (left > right) {
- return -1;
- }
- int mid = left + right >> 1;
- int leftIndex = find(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) {
- return leftIndex;
- }
- if (nums[mid] == mid) {
- return mid;
- }
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right);
+ function dfs = [&](int i, int j) {
+ if (i > j) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ int mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ int l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l != -1) {
+ return l;
+ }
+ if (nums[mid] == mid) {
+ return mid;
+ }
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
+ };
+ return dfs(0, nums.size() - 1);
}
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func findMagicIndex(nums []int) int {
- return find(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
-}
-
-func find(nums []int, left, right int) int {
- if left > right {
- return -1
+ var dfs func(i, j int) int
+ dfs = func(i, j int) int {
+ if i > j {
+ return -1
+ }
+ mid := (i + j) >> 1
+ if l := dfs(i, mid-1); l != -1 {
+ return l
+ }
+ if nums[mid] == mid {
+ return mid
+ }
+ return dfs(mid+1, j)
}
- mid := (left + right) >> 1
- leftIndex := find(nums, left, mid-1)
- if leftIndex != -1 {
- return leftIndex
- }
- if nums[mid] == mid {
- return mid
- }
- return find(nums, mid+1, right)
+ return dfs(0, len(nums)-1)
}
```
+#### TypeScript
+
```ts
function findMagicIndex(nums: number[]): number {
- const n = nums.length;
- const find = (l: number, r: number): number => {
- if (l > r || nums[r] < 0) {
+ const dfs = (i: number, j: number): number => {
+ if (i > j) {
return -1;
}
- const mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
- if (nums[mid] >= l) {
- const res = find(l, mid - 1);
- if (res !== -1) {
- return res;
- }
+ const mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ const l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l !== -1) {
+ return l;
}
if (nums[mid] === mid) {
return mid;
}
- return find(mid + 1, r);
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
};
- return find(0, n - 1);
+ return dfs(0, nums.length - 1);
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
- fn find(nums: &Vec, l: usize, r: usize) -> i32 {
- if l >= r || nums[r - 1] < 0 {
+ fn dfs(nums: &Vec, i: usize, j: usize) -> i32 {
+ if i >= j || nums[j - 1] < 0 {
return -1;
}
- let mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
- if nums[mid] >= (l as i32) {
- let res = Self::find(nums, l, mid);
- if res != -1 {
- return res;
+ let mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ if nums[mid] >= (i as i32) {
+ let l = Self::dfs(nums, i, mid);
+ if l != -1 {
+ return l;
}
}
if nums[mid] == (mid as i32) {
return mid as i32;
}
- Self::find(nums, mid + 1, r)
+ Self::dfs(nums, mid + 1, j)
}
pub fn find_magic_index(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- Self::find(&nums, 0, nums.len())
+ Self::dfs(&nums, 0, nums.len())
}
}
```
+#### JavaScript
+
```js
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var findMagicIndex = function (nums) {
- return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
+ const dfs = (i, j) => {
+ if (i > j) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ const mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ const l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l !== -1) {
+ return l;
+ }
+ if (nums[mid] === mid) {
+ return mid;
+ }
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
+ };
+ return dfs(0, nums.length - 1);
};
-
-function helper(nums, left, right) {
- if (left > right) return -1;
- let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
- let leftIndex = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) return leftIndex;
- if (nums[mid] == mid) return mid;
- return helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
-}
```
-
-
-### Solution 2
+#### Swift
-
-
-```ts
-function findMagicIndex(nums: number[]): number {
- const n = nums.length;
- let i = 0;
- while (i < n) {
- if (nums[i] === i) {
- return i;
- }
- i = Math.max(nums[i], i + 1);
+```swift
+class Solution {
+ func findMagicIndex(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {
+ return find(nums, 0, nums.count - 1)
}
- return -1;
-}
-```
-```rust
-impl Solution {
- pub fn find_magic_index(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let n = nums.len();
- let mut i = 0 as i32;
- while (i as usize) < n {
- let num = nums[i as usize];
- if num == i {
- return i;
- }
- i = num.max(i + 1);
+ private func find(_ nums: [Int], _ i: Int, _ j: Int) -> Int {
+ if i > j {
+ return -1
}
- -1
+ let mid = (i + j) >> 1
+ let l = find(nums, i, mid - 1)
+ if l != -1 {
+ return l
+ }
+ if nums[mid] == mid {
+ return mid
+ }
+ return find(nums, mid + 1, j)
}
}
```
-
+
+
+
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.cpp b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.cpp
index b86f2690b7ad1..baf2c6cbecb9c 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.cpp
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.cpp
@@ -1,21 +1,20 @@
class Solution {
public:
int findMagicIndex(vector& nums) {
- return find(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
- }
-
- int find(vector& nums, int left, int right) {
- if (left > right) {
- return -1;
- }
- int mid = left + right >> 1;
- int leftIndex = find(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) {
- return leftIndex;
- }
- if (nums[mid] == mid) {
- return mid;
- }
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right);
+ function dfs = [&](int i, int j) {
+ if (i > j) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ int mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ int l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l != -1) {
+ return l;
+ }
+ if (nums[mid] == mid) {
+ return mid;
+ }
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
+ };
+ return dfs(0, nums.size() - 1);
}
};
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.go b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.go
index 2a352c7c3ee7d..dc9ff71759392 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.go
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.go
@@ -1,18 +1,17 @@
func findMagicIndex(nums []int) int {
- return find(nums, 0, len(nums)-1)
-}
-
-func find(nums []int, left, right int) int {
- if left > right {
- return -1
+ var dfs func(i, j int) int
+ dfs = func(i, j int) int {
+ if i > j {
+ return -1
+ }
+ mid := (i + j) >> 1
+ if l := dfs(i, mid-1); l != -1 {
+ return l
+ }
+ if nums[mid] == mid {
+ return mid
+ }
+ return dfs(mid+1, j)
}
- mid := (left + right) >> 1
- leftIndex := find(nums, left, mid-1)
- if leftIndex != -1 {
- return leftIndex
- }
- if nums[mid] == mid {
- return mid
- }
- return find(nums, mid+1, right)
+ return dfs(0, len(nums)-1)
}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.java b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.java
index 3cf55a1a0c701..376fd241e45aa 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.java
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.java
@@ -1,21 +1,20 @@
class Solution {
public int findMagicIndex(int[] nums) {
- int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
- return find(nums, left, right);
+ return dfs(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
- private int find(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
- if (left > right) {
+ private int dfs(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
+ if (i > j) {
return -1;
}
- int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
- int leftIndex = find(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) {
- return leftIndex;
+ int mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ int l = dfs(nums, i, mid - 1);
+ if (l != -1) {
+ return l;
}
if (nums[mid] == mid) {
return mid;
}
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right);
+ return dfs(nums, mid + 1, j);
}
}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.js b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.js
index ec59ca1f61687..04557466a6371 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.js
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.js
@@ -3,14 +3,19 @@
* @return {number}
*/
var findMagicIndex = function (nums) {
- return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
+ const dfs = (i, j) => {
+ if (i > j) {
+ return -1;
+ }
+ const mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ const l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l !== -1) {
+ return l;
+ }
+ if (nums[mid] === mid) {
+ return mid;
+ }
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
+ };
+ return dfs(0, nums.length - 1);
};
-
-function helper(nums, left, right) {
- if (left > right) return -1;
- let mid = Math.floor((left + right) / 2);
- let leftIndex = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
- if (leftIndex != -1) return leftIndex;
- if (nums[mid] == mid) return mid;
- return helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
-}
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.py b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.py
index d82ad883e773c..30a230a53f8a6 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.py
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.py
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
class Solution:
def findMagicIndex(self, nums: List[int]) -> int:
- def find(nums, left, right):
- if left > right:
+ def dfs(i: int, j: int) -> int:
+ if i > j:
return -1
- mid = (left + right) >> 1
- left_index = find(nums, left, mid - 1)
- if left_index != -1:
- return left_index
+ mid = (i + j) >> 1
+ l = dfs(i, mid - 1)
+ if l != -1:
+ return l
if nums[mid] == mid:
return mid
- return find(nums, mid + 1, right)
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j)
- return find(nums, 0, len(nums) - 1)
+ return dfs(0, len(nums) - 1)
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.rs b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.rs
index f5674a654709a..a4b12573d063c 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.rs
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.rs
@@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
impl Solution {
- fn find(nums: &Vec, l: usize, r: usize) -> i32 {
- if l >= r || nums[r - 1] < 0 {
+ fn dfs(nums: &Vec, i: usize, j: usize) -> i32 {
+ if i >= j || nums[j - 1] < 0 {
return -1;
}
- let mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
- if nums[mid] >= (l as i32) {
- let res = Self::find(nums, l, mid);
- if res != -1 {
- return res;
+ let mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ if nums[mid] >= (i as i32) {
+ let l = Self::dfs(nums, i, mid);
+ if l != -1 {
+ return l;
}
}
if nums[mid] == (mid as i32) {
return mid as i32;
}
- Self::find(nums, mid + 1, r)
+ Self::dfs(nums, mid + 1, j)
}
pub fn find_magic_index(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- Self::find(&nums, 0, nums.len())
+ Self::dfs(&nums, 0, nums.len())
}
}
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.swift b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.swift
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..8f04ee244eb8c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.swift
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+class Solution {
+ func findMagicIndex(_ nums: [Int]) -> Int {
+ return find(nums, 0, nums.count - 1)
+ }
+
+ private func find(_ nums: [Int], _ i: Int, _ j: Int) -> Int {
+ if i > j {
+ return -1
+ }
+ let mid = (i + j) >> 1
+ let l = find(nums, i, mid - 1)
+ if l != -1 {
+ return l
+ }
+ if nums[mid] == mid {
+ return mid
+ }
+ return find(nums, mid + 1, j)
+ }
+}
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.ts b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.ts
index 74db52ca16bf0..dfc79eee60109 100644
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.ts
+++ b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution.ts
@@ -1,20 +1,17 @@
function findMagicIndex(nums: number[]): number {
- const n = nums.length;
- const find = (l: number, r: number): number => {
- if (l > r || nums[r] < 0) {
+ const dfs = (i: number, j: number): number => {
+ if (i > j) {
return -1;
}
- const mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2);
- if (nums[mid] >= l) {
- const res = find(l, mid - 1);
- if (res !== -1) {
- return res;
- }
+ const mid = (i + j) >> 1;
+ const l = dfs(i, mid - 1);
+ if (l !== -1) {
+ return l;
}
if (nums[mid] === mid) {
return mid;
}
- return find(mid + 1, r);
+ return dfs(mid + 1, j);
};
- return find(0, n - 1);
+ return dfs(0, nums.length - 1);
}
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution2.rs b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution2.rs
deleted file mode 100644
index cd13572072eff..0000000000000
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution2.rs
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
-impl Solution {
- pub fn find_magic_index(nums: Vec) -> i32 {
- let n = nums.len();
- let mut i = 0 as i32;
- while (i as usize) < n {
- let num = nums[i as usize];
- if num == i {
- return i;
- }
- i = num.max(i + 1);
- }
- -1
- }
-}
diff --git a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution2.ts b/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution2.ts
deleted file mode 100644
index 09a988aa75c36..0000000000000
--- a/lcci/08.03.Magic Index/Solution2.ts
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
-function findMagicIndex(nums: number[]): number {
- const n = nums.length;
- let i = 0;
- while (i < n) {
- if (nums[i] === i) {
- return i;
- }
- i = Math.max(nums[i], i + 1);
- }
- return -1;
-}
diff --git a/lcci/08.04.Power Set/README.md b/lcci/08.04.Power Set/README.md
index 9e6971d61f690..3d158833ea132 100644
--- a/lcci/08.04.Power Set/README.md
+++ b/lcci/08.04.Power Set/README.md
@@ -1,10 +1,19 @@
+---
+comments: true
+difficulty: 中等
+edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcci/08.04.Power%20Set/README.md
+---
+
+
+
# [面试题 08.04. 幂集](https://leetcode.cn/problems/power-set-lcci)
[English Version](/lcci/08.04.Power%20Set/README_EN.md)
## 题目描述
-
+
+
幂集。编写一种方法,返回某集合的所有子集。集合中不包含重复的元素。
说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
@@ -25,8 +34,12 @@
]
+
+
## 解法
+
+
### 方法一:递归枚举
我们设计一个递归函数 $dfs(u, t)$,它的参数为当前枚举到的元素的下标 $u$,以及当前的子集 $t$。
@@ -37,6 +50,8 @@
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
@@ -54,6 +69,8 @@ class Solution:
return ans
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
private List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
@@ -78,6 +95,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -101,6 +120,8 @@ public:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
var ans [][]int
@@ -121,6 +142,8 @@ func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
}
```
+#### TypeScript
+
```ts
function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
const res = [[]];
@@ -133,6 +156,8 @@ function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn subsets(nums: Vec) -> Vec> {
@@ -148,6 +173,8 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+#### JavaScript
+
```js
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
@@ -171,8 +198,38 @@ function dfs(nums, depth, prev, res) {
}
```
+#### Swift
+
+```swift
+class Solution {
+ private var ans = [[Int]]()
+ private var nums: [Int] = []
+
+ func subsets(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
+ self.nums = nums
+ dfs(0, [])
+ return ans.sorted { $0.count < $1.count }
+ }
+
+ private func dfs(_ u: Int, _ t: [Int]) {
+ if u == nums.count {
+ ans.append(t)
+ return
+ }
+ dfs(u + 1, t)
+ var tWithCurrent = t
+ tWithCurrent.append(nums[u])
+ dfs(u + 1, tWithCurrent)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
### 方法二:二进制枚举
我们可以将方法一中的递归过程改写成迭代的形式,即使用二进制枚举的方法来枚举所有的子集。
@@ -183,6 +240,8 @@ function dfs(nums, depth, prev, res) {
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
@@ -196,6 +255,8 @@ class Solution:
return ans
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
public List> subsets(int[] nums) {
@@ -215,6 +276,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -236,6 +299,8 @@ public:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
var ans [][]int
@@ -253,6 +318,8 @@ func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
}
```
+#### TypeScript
+
```ts
function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
const n = nums.length;
@@ -273,6 +340,8 @@ function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
fn dfs(nums: &Vec, i: usize, res: &mut Vec>, list: &mut Vec) {
@@ -296,4 +365,6 @@ impl Solution {
-
+
+
+
diff --git a/lcci/08.04.Power Set/README_EN.md b/lcci/08.04.Power Set/README_EN.md
index 1e361e61be8ba..bce77529749ec 100644
--- a/lcci/08.04.Power Set/README_EN.md
+++ b/lcci/08.04.Power Set/README_EN.md
@@ -1,9 +1,19 @@
+---
+comments: true
+difficulty: Medium
+edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcci/08.04.Power%20Set/README_EN.md
+---
+
+
+
# [08.04. Power Set](https://leetcode.cn/problems/power-set-lcci)
[中文文档](/lcci/08.04.Power%20Set/README.md)
## Description
+
+
Write a method to return all subsets of a set. The elements in a set are pairwise distinct.
Note: The result set should not contain duplicated subsets.
@@ -38,8 +48,12 @@
+
+
## Solutions
+
+
### Solution 1: Recursive Enumeration
We design a recursive function $dfs(u, t)$, where $u$ is the index of the current element being enumerated, and $t$ is the current subset.
@@ -50,6 +64,8 @@ The time complexity is $O(n \times 2^n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. He
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
@@ -67,6 +83,8 @@ class Solution:
return ans
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
private List> ans = new ArrayList<>();
@@ -91,6 +109,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -114,6 +134,8 @@ public:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
var ans [][]int
@@ -134,6 +156,8 @@ func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
}
```
+#### TypeScript
+
```ts
function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
const res = [[]];
@@ -146,6 +170,8 @@ function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
pub fn subsets(nums: Vec) -> Vec> {
@@ -161,6 +187,8 @@ impl Solution {
}
```
+#### JavaScript
+
```js
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
@@ -184,8 +212,38 @@ function dfs(nums, depth, prev, res) {
}
```
+#### Swift
+
+```swift
+class Solution {
+ private var ans = [[Int]]()
+ private var nums: [Int] = []
+
+ func subsets(_ nums: [Int]) -> [[Int]] {
+ self.nums = nums
+ dfs(0, [])
+ return ans.sorted { $0.count < $1.count }
+ }
+
+ private func dfs(_ u: Int, _ t: [Int]) {
+ if u == nums.count {
+ ans.append(t)
+ return
+ }
+ dfs(u + 1, t)
+ var tWithCurrent = t
+ tWithCurrent.append(nums[u])
+ dfs(u + 1, tWithCurrent)
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
### Solution 2: Binary Enumeration
We can rewrite the recursive process in Method 1 into an iterative form, that is, using binary enumeration to enumerate all subsets.
@@ -196,6 +254,8 @@ The time complexity is $O(n \times 2^n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$. He
+#### Python3
+
```python
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
@@ -209,6 +269,8 @@ class Solution:
return ans
```
+#### Java
+
```java
class Solution {
public List> subsets(int[] nums) {
@@ -228,6 +290,8 @@ class Solution {
}
```
+#### C++
+
```cpp
class Solution {
public:
@@ -249,6 +313,8 @@ public:
};
```
+#### Go
+
```go
func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
var ans [][]int
@@ -266,6 +332,8 @@ func subsets(nums []int) [][]int {
}
```
+#### TypeScript
+
```ts
function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
const n = nums.length;
@@ -286,6 +354,8 @@ function subsets(nums: number[]): number[][] {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
```rust
impl Solution {
fn dfs(nums: &Vec, i: usize, res: &mut Vec +
+ 
 +
+ +
+
+
+  +
+  -
## 版权
本项目著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 @yanglbme 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
-## 联系我们
+## 联系我们 & 支持项目
欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
-|
-
## 版权
本项目著作权归 [GitHub 开源社区 Doocs](https://github.com/doocs) 所有,商业转载请联系 @yanglbme 获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
-## 联系我们
+## 联系我们 & 支持项目
欢迎各位小伙伴们添加 @yanglbme 的个人微信(微信号:YLB0109),备注 「**leetcode**」。后续我们会创建算法、技术相关的交流群,大家一起交流学习,分享经验,共同进步。
-|  |
-| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+如果你觉得这个项目对你有帮助,也欢迎通过微信扫码赞赏我们 ☕️~
+
+|
|
-| ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
+如果你觉得这个项目对你有帮助,也欢迎通过微信扫码赞赏我们 ☕️~
+
+|  |
|  |
+| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
## 许可证
diff --git a/README_EN.md b/README_EN.md
index 332de667a3348..3b461059720a9 100644
--- a/README_EN.md
+++ b/README_EN.md
@@ -1,15 +1,16 @@
## Introduction
@@ -18,9 +19,9 @@ This project contains solutions for problems from LeetCode, "Coding Interviews (
[中文文档](/README.md)
-## Sites
+## Site
-https://doocs.github.io/leetcode
+https://leetcode.doocs.org/en
## Solutions
@@ -31,8 +32,8 @@ https://doocs.github.io/leetcode
## JavaScript & Database Practice
-- [JavaScript Practice](/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md)
-- [Database Practice](/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md)
+- [JavaScript](/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md)
+- [Database](/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md)
## Topics
@@ -90,7 +91,7 @@ https://doocs.github.io/leetcode
- [Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes](/solution/0800-0899/0847.Shortest%20Path%20Visiting%20All%20Nodes/README_EN.md) - `BFS`, `Minimum steps model`, `A* search`
- [Cut Off Trees for Golf Event](/solution/0600-0699/0675.Cut%20Off%20Trees%20for%20Golf%20Event/README_EN.md) - `BFS`, `A* search`
- [Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid](/solution/1300-1399/1368.Minimum%20Cost%20to%20Make%20at%20Least%20One%20Valid%20Path%20in%20a%20Grid/README_EN.md) - `BFS using deque`
-- [Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid](/solution/2200-2299/2290.Minimum%20Obstacle%20Removal%20to%20Reach%20Corner/README_EN.md) - `BFS using deque`
+- [Minimum Obstacle Removal to Reach Corner](/solution/2200-2299/2290.Minimum%20Obstacle%20Removal%20to%20Reach%20Corner/README_EN.md) - `BFS using deque`
- [The Maze](/solution/0400-0499/0490.The%20Maze/README_EN.md) - `DFS, Flood fill`
- [Word Search](/solution/0000-0099/0079.Word%20Search/README_EN.md) - `DFS`, `Backtracking`
- [Path with Maximum Gold](/solution/1200-1299/1219.Path%20with%20Maximum%20Gold/README_EN.md) - `DFS`, `Backtracking`
@@ -183,40 +184,38 @@ I'm looking for long-term contributors/partners to this repo! Send me [PRs](http
1. Create a pull request with your changes!
1. See [CONTRIBUTING](https://github.com/doocs/.github/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md) or [GitHub Help](https://help.github.com/en) for more details.
-
+
|
+| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
## 许可证
diff --git a/README_EN.md b/README_EN.md
index 332de667a3348..3b461059720a9 100644
--- a/README_EN.md
+++ b/README_EN.md
@@ -1,15 +1,16 @@
## Introduction
@@ -18,9 +19,9 @@ This project contains solutions for problems from LeetCode, "Coding Interviews (
[中文文档](/README.md)
-## Sites
+## Site
-https://doocs.github.io/leetcode
+https://leetcode.doocs.org/en
## Solutions
@@ -31,8 +32,8 @@ https://doocs.github.io/leetcode
## JavaScript & Database Practice
-- [JavaScript Practice](/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md)
-- [Database Practice](/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md)
+- [JavaScript](/solution/JAVASCRIPT_README_EN.md)
+- [Database](/solution/DATABASE_README_EN.md)
## Topics
@@ -90,7 +91,7 @@ https://doocs.github.io/leetcode
- [Shortest Path Visiting All Nodes](/solution/0800-0899/0847.Shortest%20Path%20Visiting%20All%20Nodes/README_EN.md) - `BFS`, `Minimum steps model`, `A* search`
- [Cut Off Trees for Golf Event](/solution/0600-0699/0675.Cut%20Off%20Trees%20for%20Golf%20Event/README_EN.md) - `BFS`, `A* search`
- [Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid](/solution/1300-1399/1368.Minimum%20Cost%20to%20Make%20at%20Least%20One%20Valid%20Path%20in%20a%20Grid/README_EN.md) - `BFS using deque`
-- [Minimum Cost to Make at Least One Valid Path in a Grid](/solution/2200-2299/2290.Minimum%20Obstacle%20Removal%20to%20Reach%20Corner/README_EN.md) - `BFS using deque`
+- [Minimum Obstacle Removal to Reach Corner](/solution/2200-2299/2290.Minimum%20Obstacle%20Removal%20to%20Reach%20Corner/README_EN.md) - `BFS using deque`
- [The Maze](/solution/0400-0499/0490.The%20Maze/README_EN.md) - `DFS, Flood fill`
- [Word Search](/solution/0000-0099/0079.Word%20Search/README_EN.md) - `DFS`, `Backtracking`
- [Path with Maximum Gold](/solution/1200-1299/1219.Path%20with%20Maximum%20Gold/README_EN.md) - `DFS`, `Backtracking`
@@ -183,40 +184,38 @@ I'm looking for long-term contributors/partners to this repo! Send me [PRs](http
1. Create a pull request with your changes!
1. See [CONTRIBUTING](https://github.com/doocs/.github/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md) or [GitHub Help](https://help.github.com/en) for more details.
-
+ +
+ +
+
+
+  +
+