, k: &mut i32) {
+ if s.len() == n as usize {
+ ans.push(s.clone());
+ return;
+ }
+ if ans.len() >= *k as usize {
+ return;
+ }
+ for c in "abc".chars() {
+ if s.is_empty() || s.chars().last() != Some(c) {
+ s.push(c);
+ dfs(n, s, ans, k);
+ s.pop();
+ }
+ }
+ }
+
+ dfs(n, &mut s, &mut ans, &mut k);
+ if ans.len() < k as usize {
+ "".to_string()
+ } else {
+ ans[(k - 1) as usize].clone()
+ }
+ }
+}
diff --git a/solution/1400-1499/1415.The k-th Lexicographical String of All Happy Strings of Length n/Solution.ts b/solution/1400-1499/1415.The k-th Lexicographical String of All Happy Strings of Length n/Solution.ts
index 8f421ccaf92f4..b676a2f42b60a 100644
--- a/solution/1400-1499/1415.The k-th Lexicographical String of All Happy Strings of Length n/Solution.ts
+++ b/solution/1400-1499/1415.The k-th Lexicographical String of All Happy Strings of Length n/Solution.ts
@@ -1,19 +1,22 @@
function getHappyString(n: number, k: number): string {
const ans: string[] = [];
-
- const dfs = (s = '') => {
+ const s: string[] = [];
+ const dfs = () => {
if (s.length === n) {
- ans.push(s);
+ ans.push(s.join(''));
return;
}
-
- for (const ch of 'abc') {
- if (s.at(-1) === ch) continue;
- dfs(s + ch);
+ if (ans.length >= k) {
+ return;
+ }
+ for (const c of 'abc') {
+ if (!s.length || s.at(-1)! !== c) {
+ s.push(c);
+ dfs();
+ s.pop();
+ }
}
};
-
dfs();
-
return ans[k - 1] ?? '';
}
diff --git a/solution/1400-1499/1418.Display Table of Food Orders in a Restaurant/README_EN.md b/solution/1400-1499/1418.Display Table of Food Orders in a Restaurant/README_EN.md
index 809ec164c6da3..dd6bc86d1a53a 100644
--- a/solution/1400-1499/1418.Display Table of Food Orders in a Restaurant/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1400-1499/1418.Display Table of Food Orders in a Restaurant/README_EN.md
@@ -27,48 +27,77 @@ tags:
Return the restaurant's “display table”. The “display table” is a table whose row entries denote how many of each food item each table ordered. The first column is the table number and the remaining columns correspond to each food item in alphabetical order. The first row should be a header whose first column is “Table”, followed by the names of the food items. Note that the customer names are not part of the table. Additionally, the rows should be sorted in numerically increasing order.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: orders = [["David","3","Ceviche"],["Corina","10","Beef Burrito"],["David","3","Fried Chicken"],["Carla","5","Water"],["Carla","5","Ceviche"],["Rous","3","Ceviche"]]
+
Output: [["Table","Beef Burrito","Ceviche","Fried Chicken","Water"],["3","0","2","1","0"],["5","0","1","0","1"],["10","1","0","0","0"]]
+
Explanation:
+
The displaying table looks like:
+
Table,Beef Burrito,Ceviche,Fried Chicken,Water
+
3 ,0 ,2 ,1 ,0
+
5 ,0 ,1 ,0 ,1
+
10 ,1 ,0 ,0 ,0
+
For the table 3: David orders "Ceviche" and "Fried Chicken", and Rous orders "Ceviche".
+
For the table 5: Carla orders "Water" and "Ceviche".
+
For the table 10: Corina orders "Beef Burrito".
+
Example 2:
+
Input: orders = [["James","12","Fried Chicken"],["Ratesh","12","Fried Chicken"],["Amadeus","12","Fried Chicken"],["Adam","1","Canadian Waffles"],["Brianna","1","Canadian Waffles"]]
+
Output: [["Table","Canadian Waffles","Fried Chicken"],["1","2","0"],["12","0","3"]]
+
Explanation:
+
For the table 1: Adam and Brianna order "Canadian Waffles".
+
For the table 12: James, Ratesh and Amadeus order "Fried Chicken".
+
Example 3:
+
Input: orders = [["Laura","2","Bean Burrito"],["Jhon","2","Beef Burrito"],["Melissa","2","Soda"]]
+
Output: [["Table","Bean Burrito","Beef Burrito","Soda"],["2","1","1","1"]]
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= orders.length <= 5 * 10^4orders[i].length == 31 <= customerNamei.length, foodItemi.length <= 20customerNamei and foodItemi consist of lowercase and uppercase English letters and the space character.tableNumberi is a valid integer between 1 and 500.1 <= orders.length <= 5 * 10^4orders[i].length == 31 <= customerNamei.length, foodItemi.length <= 20customerNamei and foodItemi consist of lowercase and uppercase English letters and the space character.tableNumberi is a valid integer between 1 and 500.
diff --git a/solution/1400-1499/1448.Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree/README_EN.md b/solution/1400-1499/1448.Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree/README_EN.md
index 75f9d52c74990..4a07c72b0b946 100644
--- a/solution/1400-1499/1448.Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1400-1499/1448.Count Good Nodes in Binary Tree/README_EN.md
@@ -26,17 +26,25 @@ tags:
Return the number of good nodes in the binary tree.
+
Example 1:
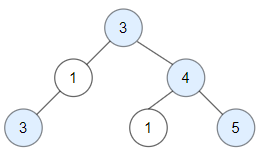
+
Input: root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5]
+
Output: 4
+
Explanation: Nodes in blue are good.
+
Root Node (3) is always a good node.
+
Node 4 -> (3,4) is the maximum value in the path starting from the root.
+
Node 5 -> (3,4,5) is the maximum value in the path
+
Node 3 -> (3,1,3) is the maximum value in the path.
Example 2:
@@ -44,23 +52,33 @@ Node 3 -> (3,1,3) is the maximum value in the path.
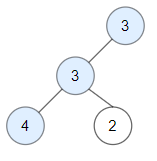
+
Input: root = [3,3,null,4,2]
+
Output: 3
+
Explanation: Node 2 -> (3, 3, 2) is not good, because "3" is higher than it.
Example 3:
+
Input: root = [1]
+
Output: 1
+
Explanation: Root is considered as good.
+
Constraints:
- - The number of nodes in the binary tree is in the range
[1, 10^5].
- - Each node's value is between
[-10^4, 10^4].
+
+ - The number of nodes in the binary tree is in the range
[1, 10^5].
+
+ - Each node's value is between
[-10^4, 10^4].
+
diff --git a/solution/1400-1499/1470.Shuffle the Array/README_EN.md b/solution/1400-1499/1470.Shuffle the Array/README_EN.md
index 9246c35a92d80..8a806cd3fd73d 100644
--- a/solution/1400-1499/1470.Shuffle the Array/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1400-1499/1470.Shuffle the Array/README_EN.md
@@ -23,35 +23,51 @@ tags:
Return the array in the form [x1,y1,x2,y2,...,xn,yn].
+
Example 1:
+
Input: nums = [2,5,1,3,4,7], n = 3
+
Output: [2,3,5,4,1,7]
+
Explanation: Since x1=2, x2=5, x3=1, y1=3, y2=4, y3=7 then the answer is [2,3,5,4,1,7].
+
Example 2:
+
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,4,3,2,1], n = 4
+
Output: [1,4,2,3,3,2,4,1]
+
Example 3:
+
Input: nums = [1,1,2,2], n = 2
+
Output: [1,2,1,2]
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= n <= 500nums.length == 2n1 <= nums[i] <= 10^31 <= n <= 500nums.length == 2n1 <= nums[i] <= 10^3
diff --git a/solution/1400-1499/1481.Least Number of Unique Integers after K Removals/README_EN.md b/solution/1400-1499/1481.Least Number of Unique Integers after K Removals/README_EN.md
index 00dee15fada33..d367cf0458c18 100644
--- a/solution/1400-1499/1481.Least Number of Unique Integers after K Removals/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1400-1499/1481.Least Number of Unique Integers after K Removals/README_EN.md
@@ -25,31 +25,45 @@ tags:
Given an array of integers arr and an integer k. Find the least number of unique integers after removing exactly k elements.
+
+
Example 1:
+
Input: arr = [5,5,4], k = 1
+
Output: 1
+
Explanation: Remove the single 4, only 5 is left.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: arr = [4,3,1,1,3,3,2], k = 3
+
Output: 2
+
Explanation: Remove 4, 2 and either one of the two 1s or three 3s. 1 and 3 will be left.
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= arr.length <= 10^51 <= arr[i] <= 10^90 <= k <= arr.length1 <= arr.length <= 10^51 <= arr[i] <= 10^90 <= k <= arr.length
diff --git a/solution/1500-1599/1523.Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range/README_EN.md b/solution/1500-1599/1523.Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range/README_EN.md
index d1eea923bf055..03cb439cf8dbc 100644
--- a/solution/1500-1599/1523.Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1500-1599/1523.Count Odd Numbers in an Interval Range/README_EN.md
@@ -21,25 +21,35 @@ tags:
Given two non-negative integers low and high. Return the count of odd numbers between low and high (inclusive).
+
Example 1:
+
Input: low = 3, high = 7
+
Output: 3
+
Explanation: The odd numbers between 3 and 7 are [3,5,7].
Example 2:
+
Input: low = 8, high = 10
+
Output: 1
+
Explanation: The odd numbers between 8 and 10 are [9].
+
Constraints:
- 0 <= low <= high <= 10^90 <= low <= high <= 10^9
diff --git a/solution/1500-1599/1534.Count Good Triplets/README_EN.md b/solution/1500-1599/1534.Count Good Triplets/README_EN.md
index cdec96dfb8cd3..1a417e60574bf 100644
--- a/solution/1500-1599/1534.Count Good Triplets/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1500-1599/1534.Count Good Triplets/README_EN.md
@@ -24,10 +24,15 @@ tags:
A triplet (arr[i], arr[j], arr[k]) is good if the following conditions are true:
- 0 <= i < j < k < arr.length|arr[i] - arr[j]| <= a|arr[j] - arr[k]| <= b|arr[i] - arr[k]| <= c0 <= i < j < k < arr.length|arr[i] - arr[j]| <= a|arr[j] - arr[k]| <= b|arr[i] - arr[k]| <= c
Where |x| denotes the absolute value of x.
@@ -35,29 +40,43 @@ tags:
Return the number of good triplets.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: arr = [3,0,1,1,9,7], a = 7, b = 2, c = 3
+
Output: 4
+
Explanation: There are 4 good triplets: [(3,0,1), (3,0,1), (3,1,1), (0,1,1)].
+
Example 2:
+
Input: arr = [1,1,2,2,3], a = 0, b = 0, c = 1
+
Output: 0
+
Explanation: No triplet satisfies all conditions.
+
+
Constraints:
- 3 <= arr.length <= 1000 <= arr[i] <= 10000 <= a, b, c <= 10003 <= arr.length <= 1000 <= arr[i] <= 10000 <= a, b, c <= 1000
diff --git a/solution/1600-1699/1617.Count Subtrees With Max Distance Between Cities/README_EN.md b/solution/1600-1699/1617.Count Subtrees With Max Distance Between Cities/README_EN.md
index 58a5aa233655e..a39d7dd0a4861 100644
--- a/solution/1600-1699/1617.Count Subtrees With Max Distance Between Cities/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1600-1699/1617.Count Subtrees With Max Distance Between Cities/README_EN.md
@@ -33,42 +33,63 @@ tags:
Notice that the distance between the two cities is the number of edges in the path between them.
+
Example 1:
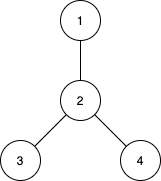
+
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[2,4]]
+
Output: [3,4,0]
+
Explanation:
+
The subtrees with subsets {1,2}, {2,3} and {2,4} have a max distance of 1.
+
The subtrees with subsets {1,2,3}, {1,2,4}, {2,3,4} and {1,2,3,4} have a max distance of 2.
+
No subtree has two nodes where the max distance between them is 3.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: n = 2, edges = [[1,2]]
+
Output: [1]
+
Example 3:
+
Input: n = 3, edges = [[1,2],[2,3]]
+
Output: [2,1]
+
+
Constraints:
- 2 <= n <= 15edges.length == n-1edges[i].length == 21 <= ui, vi <= n- All pairs
(ui, vi) are distinct.
+
+ 2 <= n <= 15edges.length == n-1edges[i].length == 21 <= ui, vi <= n- All pairs
(ui, vi) are distinct.
+
diff --git a/solution/1600-1699/1618.Maximum Font to Fit a Sentence in a Screen/README_EN.md b/solution/1600-1699/1618.Maximum Font to Fit a Sentence in a Screen/README_EN.md
index 637b3531cdded..86b831b8cd79f 100644
--- a/solution/1600-1699/1618.Maximum Font to Fit a Sentence in a Screen/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1600-1699/1618.Maximum Font to Fit a Sentence in a Screen/README_EN.md
@@ -26,14 +26,23 @@ tags:
The FontInfo interface is defined as such:
+
interface FontInfo {
+
// Returns the width of character ch on the screen using font size fontSize.
+
// O(1) per call
+
public int getWidth(int fontSize, char ch);
+
+
// Returns the height of any character on the screen using font size fontSize.
+
// O(1) per call
+
public int getHeight(int fontSize);
+
}
The calculated width of text for some fontSize is the sum of every getWidth(fontSize, text[i]) call for each 0 <= i < text.length (0-indexed). The calculated height of text for some fontSize is getHeight(fontSize). Note that text is displayed on a single line.
@@ -43,45 +52,67 @@ interface FontInfo {
It is also guaranteed that for any font size fontSize and any character ch:
- getHeight(fontSize) <= getHeight(fontSize+1)getWidth(fontSize, ch) <= getWidth(fontSize+1, ch)getHeight(fontSize) <= getHeight(fontSize+1)getWidth(fontSize, ch) <= getWidth(fontSize+1, ch)
Return the maximum font size you can use to display text on the screen. If text cannot fit on the display with any font size, return -1.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: text = "helloworld", w = 80, h = 20, fonts = [6,8,10,12,14,16,18,24,36]
+
Output: 6
+
Example 2:
+
Input: text = "leetcode", w = 1000, h = 50, fonts = [1,2,4]
+
Output: 4
+
Example 3:
+
Input: text = "easyquestion", w = 100, h = 100, fonts = [10,15,20,25]
+
Output: -1
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= text.length <= 50000text contains only lowercase English letters.1 <= w <= 1071 <= h <= 1041 <= fonts.length <= 1051 <= fonts[i] <= 105fonts is sorted in ascending order and does not contain duplicates.1 <= text.length <= 50000text contains only lowercase English letters.1 <= w <= 1071 <= h <= 1041 <= fonts.length <= 1051 <= fonts[i] <= 105fonts is sorted in ascending order and does not contain duplicates.
diff --git a/solution/1600-1699/1634.Add Two Polynomials Represented as Linked Lists/README_EN.md b/solution/1600-1699/1634.Add Two Polynomials Represented as Linked Lists/README_EN.md
index b5a4c41d13436..107929af544fa 100644
--- a/solution/1600-1699/1634.Add Two Polynomials Represented as Linked Lists/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1600-1699/1634.Add Two Polynomials Represented as Linked Lists/README_EN.md
@@ -23,9 +23,13 @@ tags:
Each node has three attributes:
- coefficient: an integer representing the number multiplier of the term. The coefficient of the term 9x4 is 9.power: an integer representing the exponent. The power of the term 9x4 is 4.next: a pointer to the next node in the list, or null if it is the last node of the list.coefficient: an integer representing the number multiplier of the term. The coefficient of the term 9x4 is 9.power: an integer representing the exponent. The power of the term 9x4 is 4.next: a pointer to the next node in the list, or null if it is the last node of the list.
For example, the polynomial 5x3 + 4x - 7 is represented by the polynomial linked list illustrated below:
@@ -41,41 +45,61 @@ tags:
The input/output format is as a list of n nodes, where each node is represented as its [coefficient, power]. For example, the polynomial 5x3 + 4x - 7 would be represented as: [[5,3],[4,1],[-7,0]].
+
Example 1:
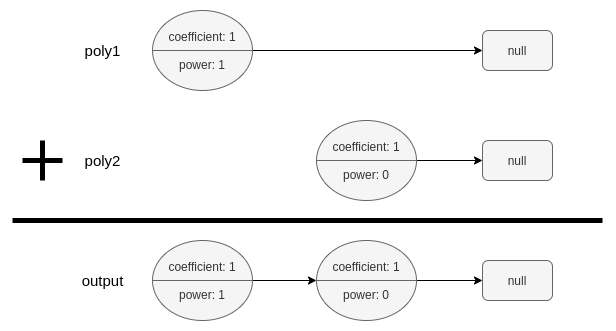
+
Input: poly1 = [[1,1]], poly2 = [[1,0]]
+
Output: [[1,1],[1,0]]
+
Explanation: poly1 = x. poly2 = 1. The sum is x + 1.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: poly1 = [[2,2],[4,1],[3,0]], poly2 = [[3,2],[-4,1],[-1,0]]
+
Output: [[5,2],[2,0]]
+
Explanation: poly1 = 2x2 + 4x + 3. poly2 = 3x2 - 4x - 1. The sum is 5x2 + 2. Notice that we omit the "0x" term.
+
Example 3:
+
Input: poly1 = [[1,2]], poly2 = [[-1,2]]
+
Output: []
+
Explanation: The sum is 0. We return an empty list.
+
+
Constraints:
- 0 <= n <= 104-109 <= PolyNode.coefficient <= 109PolyNode.coefficient != 00 <= PolyNode.power <= 109PolyNode.power > PolyNode.next.power0 <= n <= 104-109 <= PolyNode.coefficient <= 109PolyNode.coefficient != 00 <= PolyNode.power <= 109PolyNode.power > PolyNode.next.power
diff --git a/solution/1600-1699/1649.Create Sorted Array through Instructions/README_EN.md b/solution/1600-1699/1649.Create Sorted Array through Instructions/README_EN.md
index 429cfe2142d4e..d7708d65d82ee 100644
--- a/solution/1600-1699/1649.Create Sorted Array through Instructions/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1600-1699/1649.Create Sorted Array through Instructions/README_EN.md
@@ -27,8 +27,11 @@ tags:
Given an integer array instructions, you are asked to create a sorted array from the elements in instructions. You start with an empty container nums. For each element from left to right in instructions, insert it into nums. The cost of each insertion is the minimum of the following:
- - The number of elements currently in
nums that are strictly less than instructions[i].
- - The number of elements currently in
nums that are strictly greater than instructions[i].
+
+ - The number of elements currently in
nums that are strictly less than instructions[i].
+
+ - The number of elements currently in
nums that are strictly greater than instructions[i].
+
For example, if inserting element 3 into nums = [1,2,3,5], the cost of insertion is min(2, 1) (elements 1 and 2 are less than 3, element 5 is greater than 3) and nums will become [1,2,3,3,5].
@@ -36,57 +39,95 @@ tags:
Return the total cost to insert all elements from instructions into nums. Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 109 + 7
+
Example 1:
+
Input: instructions = [1,5,6,2]
+
Output: 1
+
Explanation: Begin with nums = [].
+
Insert 1 with cost min(0, 0) = 0, now nums = [1].
+
Insert 5 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,5].
+
Insert 6 with cost min(2, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,5,6].
+
Insert 2 with cost min(1, 2) = 1, now nums = [1,2,5,6].
+
The total cost is 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 1.
Example 2:
+
Input: instructions = [1,2,3,6,5,4]
+
Output: 3
+
Explanation: Begin with nums = [].
+
Insert 1 with cost min(0, 0) = 0, now nums = [1].
+
Insert 2 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,2].
+
Insert 3 with cost min(2, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,2,3].
+
Insert 6 with cost min(3, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,2,3,6].
+
Insert 5 with cost min(3, 1) = 1, now nums = [1,2,3,5,6].
+
Insert 4 with cost min(3, 2) = 2, now nums = [1,2,3,4,5,6].
+
The total cost is 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 + 2 = 3.
+
Example 3:
+
Input: instructions = [1,3,3,3,2,4,2,1,2]
+
Output: 4
+
Explanation: Begin with nums = [].
+
Insert 1 with cost min(0, 0) = 0, now nums = [1].
+
Insert 3 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,3].
+
Insert 3 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,3,3].
+
Insert 3 with cost min(1, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,3,3,3].
+
Insert 2 with cost min(1, 3) = 1, now nums = [1,2,3,3,3].
+
Insert 4 with cost min(5, 0) = 0, now nums = [1,2,3,3,3,4].
+
Insert 2 with cost min(1, 4) = 1, now nums = [1,2,2,3,3,3,4].
+
Insert 1 with cost min(0, 6) = 0, now nums = [1,1,2,2,3,3,3,4].
+
Insert 2 with cost min(2, 4) = 2, now nums = [1,1,2,2,2,3,3,3,4].
+
The total cost is 0 + 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 2 = 4.
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= instructions.length <= 1051 <= instructions[i] <= 1051 <= instructions.length <= 1051 <= instructions[i] <= 105
diff --git a/solution/1600-1699/1660.Correct a Binary Tree/README_EN.md b/solution/1600-1699/1660.Correct a Binary Tree/README_EN.md
index 4a5e058ed554d..4c4926392dd0d 100644
--- a/solution/1600-1699/1660.Correct a Binary Tree/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1600-1699/1660.Correct a Binary Tree/README_EN.md
@@ -29,22 +29,31 @@ tags:
The test input is read as 3 lines:
- TreeNode rootint fromNode (not available to correctBinaryTree)int toNode (not available to correctBinaryTree)TreeNode rootint fromNode (not available to correctBinaryTree)int toNode (not available to correctBinaryTree)
After the binary tree rooted at root is parsed, the TreeNode with value of fromNode will have its right child pointer pointing to the TreeNode with a value of toNode. Then, root is passed to correctBinaryTree.
+
Example 1:
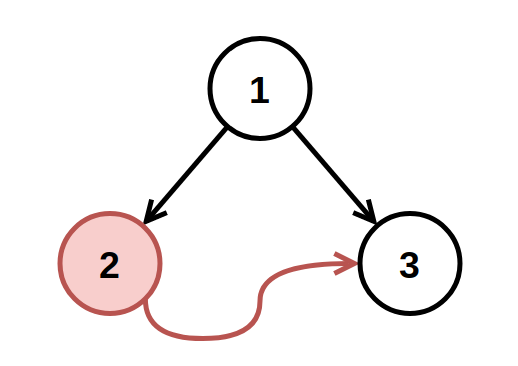
+
Input: root = [1,2,3], fromNode = 2, toNode = 3
+
Output: [1,null,3]
+
Explanation: The node with value 2 is invalid, so remove it.
+
Example 2:
@@ -52,22 +61,35 @@ tags:
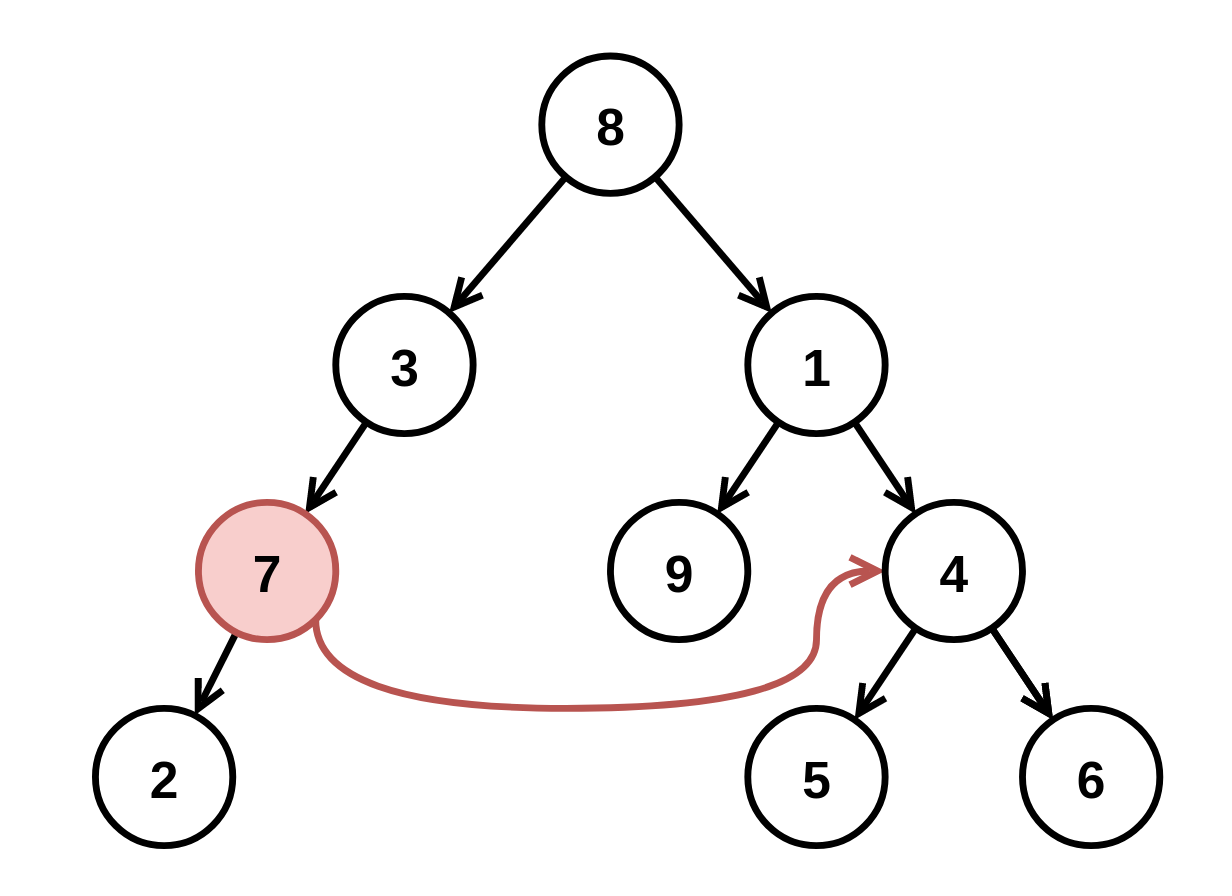
+
Input: root = [8,3,1,7,null,9,4,2,null,null,null,5,6], fromNode = 7, toNode = 4
+
Output: [8,3,1,null,null,9,4,null,null,5,6]
+
Explanation: The node with value 7 is invalid, so remove it and the node underneath it, node 2.
+
+
Constraints:
- - The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[3, 104].
- -109 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.val are unique.
- fromNode != toNodefromNode and toNode will exist in the tree and will be on the same depth.toNode is to the right of fromNode.fromNode.right is null in the initial tree from the test data.- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[3, 104].
+
+ -109 <= Node.val <= 109- All
Node.val are unique.
+
+ fromNode != toNodefromNode and toNode will exist in the tree and will be on the same depth.toNode is to the right of fromNode.fromNode.right is null in the initial tree from the test data.
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/README_EN.md
index cbb623295007f..34f00129f2a96 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1725.Number Of Rectangles That Can Form The Largest Square/README_EN.md
@@ -27,30 +27,45 @@ tags:
Return the number of rectangles that can make a square with a side length of maxLen.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: rectangles = [[5,8],[3,9],[5,12],[16,5]]
+
Output: 3
+
Explanation: The largest squares you can get from each rectangle are of lengths [5,3,5,5].
+
The largest possible square is of length 5, and you can get it out of 3 rectangles.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: rectangles = [[2,3],[3,7],[4,3],[3,7]]
+
Output: 3
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= rectangles.length <= 1000rectangles[i].length == 21 <= li, wi <= 109li != wi1 <= rectangles.length <= 1000rectangles[i].length == 21 <= li, wi <= 109li != wi
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1746.Maximum Subarray Sum After One Operation/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1746.Maximum Subarray Sum After One Operation/README_EN.md
index a96cde7d700f3..2ae33ffa3a49c 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1746.Maximum Subarray Sum After One Operation/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1746.Maximum Subarray Sum After One Operation/README_EN.md
@@ -22,26 +22,37 @@ tags:
Return the maximum possible subarray sum after exactly one operation. The subarray must be non-empty.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: nums = [2,-1,-4,-3]
+
Output: 17
+
Explanation: You can perform the operation on index 2 (0-indexed) to make nums = [2,-1,16,-3]. Now, the maximum subarray sum is 2 + -1 + 16 = 17.
Example 2:
+
Input: nums = [1,-1,1,1,-1,-1,1]
+
Output: 4
+
Explanation: You can perform the operation on index 1 (0-indexed) to make nums = [1,1,1,1,-1,-1,1]. Now, the maximum subarray sum is 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 = 4.
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 1041 <= nums.length <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1768.Merge Strings Alternately/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1768.Merge Strings Alternately/README_EN.md
index 28ec43946435a..23f19bc99a475 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1768.Merge Strings Alternately/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1768.Merge Strings Alternately/README_EN.md
@@ -24,45 +24,71 @@ tags:
Return the merged string.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: word1 = "abc", word2 = "pqr"
+
Output: "apbqcr"
+
Explanation: The merged string will be merged as so:
+
word1: a b c
+
word2: p q r
+
merged: a p b q c r
+
Example 2:
+
Input: word1 = "ab", word2 = "pqrs"
+
Output: "apbqrs"
+
Explanation: Notice that as word2 is longer, "rs" is appended to the end.
+
word1: a b
+
word2: p q r s
+
merged: a p b q r s
+
Example 3:
+
Input: word1 = "abcd", word2 = "pq"
+
Output: "apbqcd"
+
Explanation: Notice that as word1 is longer, "cd" is appended to the end.
+
word1: a b c d
+
word2: p q
+
merged: a p b q c d
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 100word1 and word2 consist of lowercase English letters.1 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 100word1 and word2 consist of lowercase English letters.
diff --git a/solution/1700-1799/1788.Maximize the Beauty of the Garden/README_EN.md b/solution/1700-1799/1788.Maximize the Beauty of the Garden/README_EN.md
index 8060248067a33..08179c3e044b3 100644
--- a/solution/1700-1799/1788.Maximize the Beauty of the Garden/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1700-1799/1788.Maximize the Beauty of the Garden/README_EN.md
@@ -24,8 +24,11 @@ tags:
A garden is valid if it meets these conditions:
- - The garden has at least two flowers.
- - The first and the last flower of the garden have the same beauty value.
+
+ - The garden has at least two flowers.
+
+ - The first and the last flower of the garden have the same beauty value.
+
As the appointed gardener, you have the ability to remove any (possibly none) flowers from the garden. You want to remove flowers in a way that makes the remaining garden valid. The beauty of the garden is the sum of the beauty of all the remaining flowers.
@@ -33,36 +36,53 @@ tags:
Return the maximum possible beauty of some valid garden after you have removed any (possibly none) flowers.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: flowers = [1,2,3,1,2]
+
Output: 8
+
Explanation: You can produce the valid garden [2,3,1,2] to have a total beauty of 2 + 3 + 1 + 2 = 8.
Example 2:
+
Input: flowers = [100,1,1,-3,1]
+
Output: 3
+
Explanation: You can produce the valid garden [1,1,1] to have a total beauty of 1 + 1 + 1 = 3.
+
Example 3:
+
Input: flowers = [-1,-2,0,-1]
+
Output: -2
+
Explanation: You can produce the valid garden [-1,-1] to have a total beauty of -1 + -1 = -2.
+
+
Constraints:
- 2 <= flowers.length <= 105-104 <= flowers[i] <= 104- It is possible to create a valid garden by removing some (possibly none) flowers.
+
+ 2 <= flowers.length <= 105-104 <= flowers[i] <= 104- It is possible to create a valid garden by removing some (possibly none) flowers.
+
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1801.Number of Orders in the Backlog/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1801.Number of Orders in the Backlog/README_EN.md
index 858710a6203f7..fb8b1f0df8967 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1801.Number of Orders in the Backlog/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1801.Number of Orders in the Backlog/README_EN.md
@@ -23,8 +23,11 @@ tags:
You are given a 2D integer array orders, where each orders[i] = [pricei, amounti, orderTypei] denotes that amounti orders have been placed of type orderTypei at the price pricei. The orderTypei is:
- 0 if it is a batch of buy orders, or1 if it is a batch of sell orders.0 if it is a batch of buy orders, or1 if it is a batch of sell orders.
Note that orders[i] represents a batch of amounti independent orders with the same price and order type. All orders represented by orders[i] will be placed before all orders represented by orders[i+1] for all valid i.
@@ -32,47 +35,79 @@ tags:
There is a backlog that consists of orders that have not been executed. The backlog is initially empty. When an order is placed, the following happens:
- - If the order is a
buy order, you look at the sell order with the smallest price in the backlog. If that sell order's price is smaller than or equal to the current buy order's price, they will match and be executed, and that sell order will be removed from the backlog. Else, the buy order is added to the backlog.
- - Vice versa, if the order is a
sell order, you look at the buy order with the largest price in the backlog. If that buy order's price is larger than or equal to the current sell order's price, they will match and be executed, and that buy order will be removed from the backlog. Else, the sell order is added to the backlog.
+
+ - If the order is a
buy order, you look at the sell order with the smallest price in the backlog. If that sell order's price is smaller than or equal to the current buy order's price, they will match and be executed, and that sell order will be removed from the backlog. Else, the buy order is added to the backlog.
+
+ - Vice versa, if the order is a
sell order, you look at the buy order with the largest price in the backlog. If that buy order's price is larger than or equal to the current sell order's price, they will match and be executed, and that buy order will be removed from the backlog. Else, the sell order is added to the backlog.
+
Return the total amount of orders in the backlog after placing all the orders from the input. Since this number can be large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
Example 1:
+
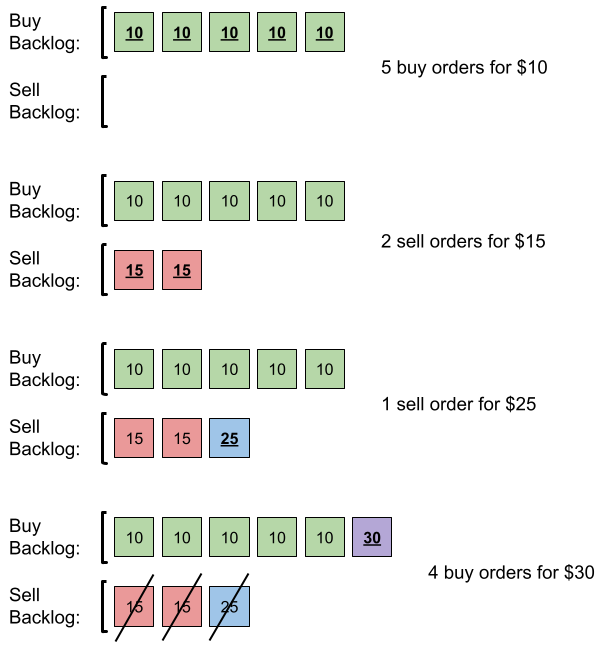 +
+
+
Input: orders = [[10,5,0],[15,2,1],[25,1,1],[30,4,0]]
+
Output: 6
+
Explanation: Here is what happens with the orders:
+
- 5 orders of type buy with price 10 are placed. There are no sell orders, so the 5 orders are added to the backlog.
+
- 2 orders of type sell with price 15 are placed. There are no buy orders with prices larger than or equal to 15, so the 2 orders are added to the backlog.
+
- 1 order of type sell with price 25 is placed. There are no buy orders with prices larger than or equal to 25 in the backlog, so this order is added to the backlog.
+
- 4 orders of type buy with price 30 are placed. The first 2 orders are matched with the 2 sell orders of the least price, which is 15 and these 2 sell orders are removed from the backlog. The 3rd order is matched with the sell order of the least price, which is 25 and this sell order is removed from the backlog. Then, there are no more sell orders in the backlog, so the 4th order is added to the backlog.
+
Finally, the backlog has 5 buy orders with price 10, and 1 buy order with price 30. So the total number of orders in the backlog is 6.
+
Example 2:
+
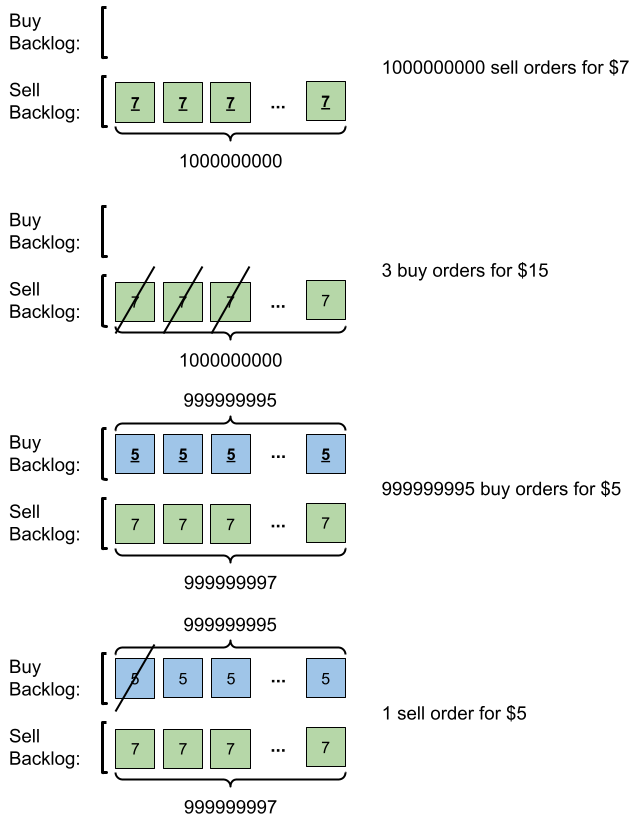 +
+
+
Input: orders = [[7,1000000000,1],[15,3,0],[5,999999995,0],[5,1,1]]
+
Output: 999999984
+
Explanation: Here is what happens with the orders:
+
- 109 orders of type sell with price 7 are placed. There are no buy orders, so the 109 orders are added to the backlog.
+
- 3 orders of type buy with price 15 are placed. They are matched with the 3 sell orders with the least price which is 7, and those 3 sell orders are removed from the backlog.
+
- 999999995 orders of type buy with price 5 are placed. The least price of a sell order is 7, so the 999999995 orders are added to the backlog.
+
- 1 order of type sell with price 5 is placed. It is matched with the buy order of the highest price, which is 5, and that buy order is removed from the backlog.
+
Finally, the backlog has (1000000000-3) sell orders with price 7, and (999999995-1) buy orders with price 5. So the total number of orders = 1999999991, which is equal to 999999984 % (109 + 7).
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= orders.length <= 105orders[i].length == 31 <= pricei, amounti <= 109orderTypei is either 0 or 1.1 <= orders.length <= 105orders[i].length == 31 <= pricei, amounti <= 109orderTypei is either 0 or 1.
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1803.Count Pairs With XOR in a Range/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1803.Count Pairs With XOR in a Range/README_EN.md
index 71d734e8f7114..b2f0cba2a3268 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1803.Count Pairs With XOR in a Range/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1803.Count Pairs With XOR in a Range/README_EN.md
@@ -25,42 +25,69 @@ tags:
A nice pair is a pair (i, j) where 0 <= i < j < nums.length and low <= (nums[i] XOR nums[j]) <= high.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: nums = [1,4,2,7], low = 2, high = 6
+
Output: 6
+
Explanation: All nice pairs (i, j) are as follows:
+
- (0, 1): nums[0] XOR nums[1] = 5
+
- (0, 2): nums[0] XOR nums[2] = 3
+
- (0, 3): nums[0] XOR nums[3] = 6
+
- (1, 2): nums[1] XOR nums[2] = 6
+
- (1, 3): nums[1] XOR nums[3] = 3
+
- (2, 3): nums[2] XOR nums[3] = 5
+
Example 2:
+
Input: nums = [9,8,4,2,1], low = 5, high = 14
+
Output: 8
+
Explanation: All nice pairs (i, j) are as follows:
+
- (0, 2): nums[0] XOR nums[2] = 13
+
- (0, 3): nums[0] XOR nums[3] = 11
+
- (0, 4): nums[0] XOR nums[4] = 8
+
- (1, 2): nums[1] XOR nums[2] = 12
+
- (1, 3): nums[1] XOR nums[3] = 10
+
- (1, 4): nums[1] XOR nums[4] = 9
+
- (2, 3): nums[2] XOR nums[3] = 6
+
- (2, 4): nums[2] XOR nums[4] = 5
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 1041 <= nums[i] <= 2 * 1041 <= low <= high <= 2 * 1041 <= nums.length <= 2 * 1041 <= nums[i] <= 2 * 1041 <= low <= high <= 2 * 104
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1808.Maximize Number of Nice Divisors/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1808.Maximize Number of Nice Divisors/README_EN.md
index 043890fcacd1a..d114a92da494e 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1808.Maximize Number of Nice Divisors/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1808.Maximize Number of Nice Divisors/README_EN.md
@@ -23,8 +23,11 @@ tags:
You are given a positive integer primeFactors. You are asked to construct a positive integer n that satisfies the following conditions:
+
- The number of prime factors of
n (not necessarily distinct) is at most primeFactors.
+
- The number of nice divisors of
n is maximized. Note that a divisor of n is nice if it is divisible by every prime factor of n. For example, if n = 12, then its prime factors are [2,2,3], then 6 and 12 are nice divisors, while 3 and 4 are not.
+
Return the number of nice divisors of n. Since that number can be too large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
@@ -32,28 +35,41 @@ tags:
Note that a prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. The prime factors of a number n is a list of prime numbers such that their product equals n.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: primeFactors = 5
+
Output: 6
+
Explanation: 200 is a valid value of n.
+
It has 5 prime factors: [2,2,2,5,5], and it has 6 nice divisors: [10,20,40,50,100,200].
+
There is not other value of n that has at most 5 prime factors and more nice divisors.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: primeFactors = 8
+
Output: 18
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= primeFactors <= 1091 <= primeFactors <= 109
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1827.Minimum Operations to Make the Array Increasing/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1827.Minimum Operations to Make the Array Increasing/README_EN.md
index af4a7cf20dd88..979e584e8350d 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1827.Minimum Operations to Make the Array Increasing/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1827.Minimum Operations to Make the Array Increasing/README_EN.md
@@ -22,7 +22,9 @@ tags:
You are given an integer array nums (0-indexed). In one operation, you can choose an element of the array and increment it by 1.
- - For example, if
nums = [1,2,3], you can choose to increment nums[1] to make nums = [1,3,3].
+
+ - For example, if
nums = [1,2,3], you can choose to increment nums[1] to make nums = [1,3,3].
+
Return the minimum number of operations needed to make nums strictly increasing.
@@ -30,37 +32,55 @@ tags:
An array nums is strictly increasing if nums[i] < nums[i+1] for all 0 <= i < nums.length - 1. An array of length 1 is trivially strictly increasing.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: nums = [1,1,1]
+
Output: 3
+
Explanation: You can do the following operations:
+
1) Increment nums[2], so nums becomes [1,1,2].
+
2) Increment nums[1], so nums becomes [1,2,2].
+
3) Increment nums[2], so nums becomes [1,2,3].
+
Example 2:
+
Input: nums = [1,5,2,4,1]
+
Output: 14
+
Example 3:
+
Input: nums = [8]
+
Output: 0
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 50001 <= nums[i] <= 1041 <= nums.length <= 50001 <= nums[i] <= 104
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1836.Remove Duplicates From an Unsorted Linked List/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1836.Remove Duplicates From an Unsorted Linked List/README_EN.md
index 22fb099044ee4..e1c623dee2b31 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1836.Remove Duplicates From an Unsorted Linked List/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1836.Remove Duplicates From an Unsorted Linked List/README_EN.md
@@ -22,36 +22,59 @@ tags:
Return the linked list after the deletions.
+
Example 1:
+
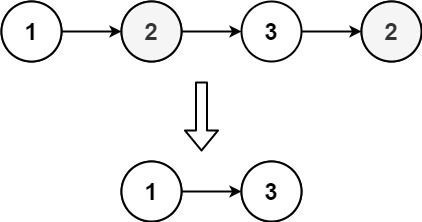 +
+
+
Input: head = [1,2,3,2]
+
Output: [1,3]
+
Explanation: 2 appears twice in the linked list, so all 2's should be deleted. After deleting all 2's, we are left with [1,3].
+
Example 2:
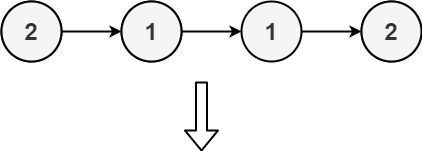
+
 +
+
+
Input: head = [2,1,1,2]
+
Output: []
+
Explanation: 2 and 1 both appear twice. All the elements should be deleted.
+
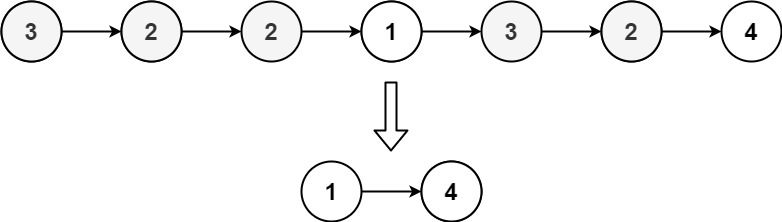
Example 3:
+
 +
+
+
Input: head = [3,2,2,1,3,2,4]
+
Output: [1,4]
+
Explanation: 3 appears twice and 2 appears three times. After deleting all 3's and 2's, we are left with [1,4].
+
+
Constraints:
- - The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 105]
- 1 <= Node.val <= 105- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 105]
+
+ 1 <= Node.val <= 105
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1857.Largest Color Value in a Directed Graph/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1857.Largest Color Value in a Directed Graph/README_EN.md
index 0aba7a5ebe9a4..d90b69df177ce 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1857.Largest Color Value in a Directed Graph/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1857.Largest Color Value in a Directed Graph/README_EN.md
@@ -32,14 +32,19 @@ tags:
Return the largest color value of any valid path in the given graph, or -1 if the graph contains a cycle.
+
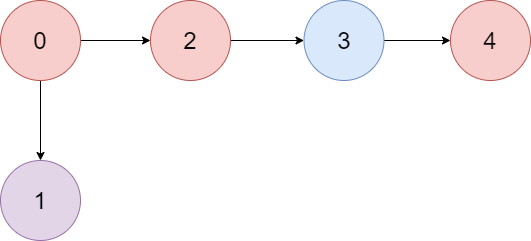
Example 1:
+
Input: colors = "abaca", edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[3,4]]
+
Output: 3
+
Explanation: The path 0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 contains 3 nodes that are colored "a" (red in the above image).
+
Example 2:
@@ -47,21 +52,33 @@ tags:
+
Input: colors = "a", edges = [[0,0]]
+
Output: -1
+
Explanation: There is a cycle from 0 to 0.
+
+
Constraints:
- n == colors.lengthm == edges.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= m <= 105colors consists of lowercase English letters.0 <= aj, bj < nn == colors.lengthm == edges.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= m <= 105colors consists of lowercase English letters.0 <= aj, bj < n
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1872.Stone Game VIII/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1872.Stone Game VIII/README_EN.md
index fc84b32817c0f..db273764cb33b 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1872.Stone Game VIII/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1872.Stone Game VIII/README_EN.md
@@ -27,9 +27,13 @@ tags:
There are n stones arranged in a row. On each player's turn, while the number of stones is more than one, they will do the following:
- - Choose an integer
x > 1, and remove the leftmost x stones from the row.
- - Add the sum of the removed stones' values to the player's score.
- - Place a new stone, whose value is equal to that sum, on the left side of the row.
+
+ - Choose an integer
x > 1, and remove the leftmost x stones from the row.
+
+ - Add the sum of the removed stones' values to the player's score.
+
+ - Place a new stone, whose value is equal to that sum, on the left side of the row.
+
The game stops when only one stone is left in the row.
@@ -39,48 +43,77 @@ tags:
Given an integer array stones of length n where stones[i] represents the value of the ith stone from the left, return the score difference between Alice and Bob if they both play optimally.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: stones = [-1,2,-3,4,-5]
+
Output: 5
+
Explanation:
+
- Alice removes the first 4 stones, adds (-1) + 2 + (-3) + 4 = 2 to her score, and places a stone of
+
value 2 on the left. stones = [2,-5].
+
- Bob removes the first 2 stones, adds 2 + (-5) = -3 to his score, and places a stone of value -3 on
+
the left. stones = [-3].
+
The difference between their scores is 2 - (-3) = 5.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: stones = [7,-6,5,10,5,-2,-6]
+
Output: 13
+
Explanation:
+
- Alice removes all stones, adds 7 + (-6) + 5 + 10 + 5 + (-2) + (-6) = 13 to her score, and places a
+
stone of value 13 on the left. stones = [13].
+
The difference between their scores is 13 - 0 = 13.
+
Example 3:
+
Input: stones = [-10,-12]
+
Output: -22
+
Explanation:
+
- Alice can only make one move, which is to remove both stones. She adds (-10) + (-12) = -22 to her
+
score and places a stone of value -22 on the left. stones = [-22].
+
The difference between their scores is (-22) - 0 = -22.
+
+
Constraints:
- n == stones.length2 <= n <= 105-104 <= stones[i] <= 104n == stones.length2 <= n <= 105-104 <= stones[i] <= 104
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1874.Minimize Product Sum of Two Arrays/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1874.Minimize Product Sum of Two Arrays/README_EN.md
index a072d1144acd3..f4db46805a1ca 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1874.Minimize Product Sum of Two Arrays/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1874.Minimize Product Sum of Two Arrays/README_EN.md
@@ -21,35 +21,51 @@ tags:
The product sum of two equal-length arrays a and b is equal to the sum of a[i] * b[i] for all 0 <= i < a.length (0-indexed).
- - For example, if
a = [1,2,3,4] and b = [5,2,3,1], the product sum would be 1*5 + 2*2 + 3*3 + 4*1 = 22.
+
+ - For example, if
a = [1,2,3,4] and b = [5,2,3,1], the product sum would be 1*5 + 2*2 + 3*3 + 4*1 = 22.
+
Given two arrays nums1 and nums2 of length n, return the minimum product sum if you are allowed to rearrange the order of the elements in nums1.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: nums1 = [5,3,4,2], nums2 = [4,2,2,5]
+
Output: 40
+
Explanation: We can rearrange nums1 to become [3,5,4,2]. The product sum of [3,5,4,2] and [4,2,2,5] is 3*4 + 5*2 + 4*2 + 2*5 = 40.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: nums1 = [2,1,4,5,7], nums2 = [3,2,4,8,6]
+
Output: 65
+
Explanation: We can rearrange nums1 to become [5,7,4,1,2]. The product sum of [5,7,4,1,2] and [3,2,4,8,6] is 5*3 + 7*2 + 4*4 + 1*8 + 2*6 = 65.
+
+
Constraints:
- n == nums1.length == nums2.length1 <= n <= 1051 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 100n == nums1.length == nums2.length1 <= n <= 1051 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 100
diff --git a/solution/1800-1899/1877.Minimize Maximum Pair Sum in Array/README_EN.md b/solution/1800-1899/1877.Minimize Maximum Pair Sum in Array/README_EN.md
index 929c483956728..4e50827246f87 100644
--- a/solution/1800-1899/1877.Minimize Maximum Pair Sum in Array/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1800-1899/1877.Minimize Maximum Pair Sum in Array/README_EN.md
@@ -24,45 +24,67 @@ tags:
The pair sum of a pair (a,b) is equal to a + b. The maximum pair sum is the largest pair sum in a list of pairs.
- - For example, if we have pairs
(1,5), (2,3), and (4,4), the maximum pair sum would be max(1+5, 2+3, 4+4) = max(6, 5, 8) = 8.
+
+ - For example, if we have pairs
(1,5), (2,3), and (4,4), the maximum pair sum would be max(1+5, 2+3, 4+4) = max(6, 5, 8) = 8.
+
Given an array nums of even length n, pair up the elements of nums into n / 2 pairs such that:
- - Each element of
nums is in exactly one pair, and
- - The maximum pair sum is minimized.
+
+ - Each element of
nums is in exactly one pair, and
+
+ - The maximum pair sum is minimized.
+
Return the minimized maximum pair sum after optimally pairing up the elements.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: nums = [3,5,2,3]
+
Output: 7
+
Explanation: The elements can be paired up into pairs (3,3) and (5,2).
+
The maximum pair sum is max(3+3, 5+2) = max(6, 7) = 7.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: nums = [3,5,4,2,4,6]
+
Output: 8
+
Explanation: The elements can be paired up into pairs (3,5), (4,4), and (6,2).
+
The maximum pair sum is max(3+5, 4+4, 6+2) = max(8, 8, 8) = 8.
+
+
Constraints:
- n == nums.length2 <= n <= 105n is even.1 <= nums[i] <= 105n == nums.length2 <= n <= 105n is even.1 <= nums[i] <= 105
diff --git a/solution/1900-1999/1911.Maximum Alternating Subsequence Sum/README_EN.md b/solution/1900-1999/1911.Maximum Alternating Subsequence Sum/README_EN.md
index ecc7532e55269..76cda62341188 100644
--- a/solution/1900-1999/1911.Maximum Alternating Subsequence Sum/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1900-1999/1911.Maximum Alternating Subsequence Sum/README_EN.md
@@ -22,47 +22,67 @@ tags:
The alternating sum of a 0-indexed array is defined as the sum of the elements at even indices minus the sum of the elements at odd indices.
- - For example, the alternating sum of
[4,2,5,3] is (4 + 5) - (2 + 3) = 4.
+
+ - For example, the alternating sum of
[4,2,5,3] is (4 + 5) - (2 + 3) = 4.
+
Given an array nums, return the maximum alternating sum of any subsequence of nums (after reindexing the elements of the subsequence).
A subsequence of an array is a new array generated from the original array by deleting some elements (possibly none) without changing the remaining elements' relative order. For example, [2,7,4] is a subsequence of [4,2,3,7,2,1,4] (the underlined elements), while [2,4,2] is not.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: nums = [4,2,5,3]
+
Output: 7
+
Explanation: It is optimal to choose the subsequence [4,2,5] with alternating sum (4 + 5) - 2 = 7.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: nums = [5,6,7,8]
+
Output: 8
+
Explanation: It is optimal to choose the subsequence [8] with alternating sum 8.
+
Example 3:
+
Input: nums = [6,2,1,2,4,5]
+
Output: 10
+
Explanation: It is optimal to choose the subsequence [6,1,5] with alternating sum (6 + 5) - 1 = 10.
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 1051 <= nums.length <= 1051 <= nums[i] <= 105
diff --git a/solution/1900-1999/1913.Maximum Product Difference Between Two Pairs/README_EN.md b/solution/1900-1999/1913.Maximum Product Difference Between Two Pairs/README_EN.md
index de2987a86b5c6..806f7cb640d4f 100644
--- a/solution/1900-1999/1913.Maximum Product Difference Between Two Pairs/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1900-1999/1913.Maximum Product Difference Between Two Pairs/README_EN.md
@@ -22,7 +22,9 @@ tags:
The product difference between two pairs (a, b) and (c, d) is defined as (a * b) - (c * d).
- - For example, the product difference between
(5, 6) and (2, 7) is (5 * 6) - (2 * 7) = 16.
+
+ - For example, the product difference between
(5, 6) and (2, 7) is (5 * 6) - (2 * 7) = 16.
+
Given an integer array nums, choose four distinct indices w, x, y, and z such that the product difference between pairs (nums[w], nums[x]) and (nums[y], nums[z]) is maximized.
@@ -30,30 +32,45 @@ tags:
Return the maximum such product difference.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: nums = [5,6,2,7,4]
+
Output: 34
+
Explanation: We can choose indices 1 and 3 for the first pair (6, 7) and indices 2 and 4 for the second pair (2, 4).
+
The product difference is (6 * 7) - (2 * 4) = 34.
+
Example 2:
+
Input: nums = [4,2,5,9,7,4,8]
+
Output: 64
+
Explanation: We can choose indices 3 and 6 for the first pair (9, 8) and indices 1 and 5 for the second pair (2, 4).
+
The product difference is (9 * 8) - (2 * 4) = 64.
+
+
Constraints:
- 4 <= nums.length <= 1041 <= nums[i] <= 1044 <= nums.length <= 1041 <= nums[i] <= 104
diff --git a/solution/1900-1999/1914.Cyclically Rotating a Grid/README_EN.md b/solution/1900-1999/1914.Cyclically Rotating a Grid/README_EN.md
index fae78135d2d47..2b5a5d14a34c7 100644
--- a/solution/1900-1999/1914.Cyclically Rotating a Grid/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1900-1999/1914.Cyclically Rotating a Grid/README_EN.md
@@ -27,37 +27,59 @@ tags:
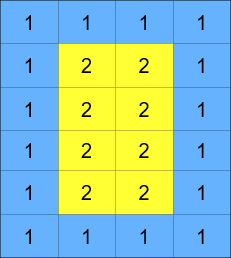
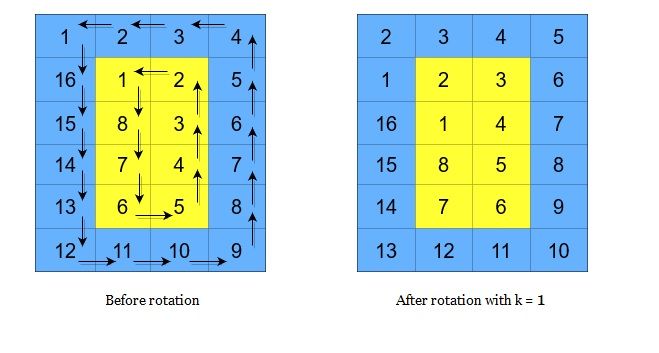
A cyclic rotation of the matrix is done by cyclically rotating each layer in the matrix. To cyclically rotate a layer once, each element in the layer will take the place of the adjacent element in the counter-clockwise direction. An example rotation is shown below:
+
 +
+
Return the matrix after applying k cyclic rotations to it.
+
Example 1:
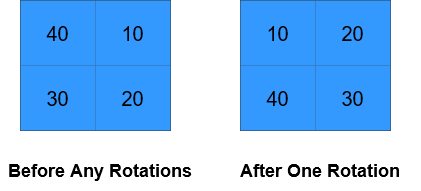
+
 +
+
+
Input: grid = [[40,10],[30,20]], k = 1
+
Output: [[10,20],[40,30]]
+
Explanation: The figures above represent the grid at every state.
+
Example 2:
+
+
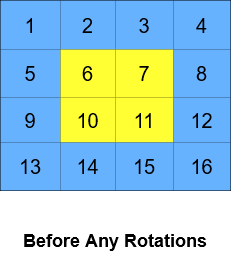
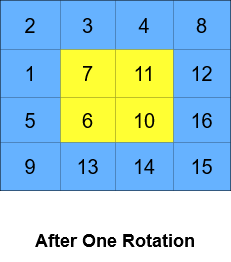
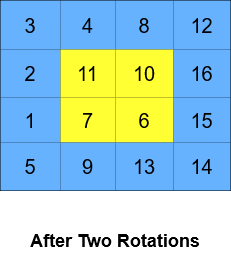
Input: grid = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12],[13,14,15,16]], k = 2
+
Output: [[3,4,8,12],[2,11,10,16],[1,7,6,15],[5,9,13,14]]
+
Explanation: The figures above represent the grid at every state.
+
+
Constraints:
- m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 50- Both
m and n are even integers.
- 1 <= grid[i][j] <= 50001 <= k <= 109m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 50- Both
m and n are even integers.
+
+ 1 <= grid[i][j] <= 50001 <= k <= 109
diff --git a/solution/1900-1999/1915.Number of Wonderful Substrings/README_EN.md b/solution/1900-1999/1915.Number of Wonderful Substrings/README_EN.md
index 1db1ec7914388..e6048268f5cc4 100644
--- a/solution/1900-1999/1915.Number of Wonderful Substrings/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1900-1999/1915.Number of Wonderful Substrings/README_EN.md
@@ -24,7 +24,9 @@ tags:
A wonderful string is a string where at most one letter appears an odd number of times.
- - For example,
"ccjjc" and "abab" are wonderful, but "ab" is not.
+
+ - For example,
"ccjjc" and "abab" are wonderful, but "ab" is not.
+
Given a string word that consists of the first ten lowercase English letters ('a' through 'j'), return the number of wonderful non-empty substrings in word. If the same substring appears multiple times in word, then count each occurrence separately.
@@ -32,51 +34,83 @@ tags:
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
+
Example 1:
+
Input: word = "aba"
+
Output: 4
+
Explanation: The four wonderful substrings are underlined below:
+
- "aba" -> "a"
+
- "aba" -> "b"
+
- "aba" -> "a"
+
- "aba" -> "aba"
+
Example 2:
+
Input: word = "aabb"
+
Output: 9
+
Explanation: The nine wonderful substrings are underlined below:
+
- "aabb" -> "a"
+
- "aabb" -> "aa"
+
- "aabb" -> "aab"
+
- "aabb" -> "aabb"
+
- "aabb" -> "a"
+
- "aabb" -> "abb"
+
- "aabb" -> "b"
+
- "aabb" -> "bb"
+
- "aabb" -> "b"
+
Example 3:
+
Input: word = "he"
+
Output: 2
+
Explanation: The two wonderful substrings are underlined below:
+
- "he" -> "h"
+
- "he" -> "e"
+
+
Constraints:
- 1 <= word.length <= 105word consists of lowercase English letters from 'a' to 'j'.1 <= word.length <= 105word consists of lowercase English letters from 'a' to 'j'.
diff --git a/solution/1900-1999/1916.Count Ways to Build Rooms in an Ant Colony/README_EN.md b/solution/1900-1999/1916.Count Ways to Build Rooms in an Ant Colony/README_EN.md
index 08e8d9fb13bfc..f306ec994eb05 100644
--- a/solution/1900-1999/1916.Count Ways to Build Rooms in an Ant Colony/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/1900-1999/1916.Count Ways to Build Rooms in an Ant Colony/README_EN.md
@@ -30,39 +30,65 @@ tags:
Return the number of different orders you can build all the rooms in. Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
+
Example 1:
+
 +
+
+
Input: prevRoom = [-1,0,1]
+
Output: 1
+
Explanation: There is only one way to build the additional rooms: 0 → 1 → 2
+
Example 2:
+
+
Input: prevRoom = [-1,0,0,1,2]
+
Output: 6
+
Explanation:
+
The 6 ways are:
+
0 → 1 → 3 → 2 → 4
+
0 → 2 → 4 → 1 → 3
+
0 → 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
+
0 → 1 → 2 → 4 → 3
+
0 → 2 → 1 → 3 → 4
+
0 → 2 → 1 → 4 → 3
+
+
Constraints:
- n == prevRoom.length2 <= n <= 105prevRoom[0] == -10 <= prevRoom[i] < n for all 1 <= i < n- Every room is reachable from room
0 once all the rooms are built.
+
+ n == prevRoom.length2 <= n <= 105prevRoom[0] == -10 <= prevRoom[i] < n for all 1 <= i < n- Every room is reachable from room
0 once all the rooms are built.
+
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2612.Minimum Reverse Operations/README.md b/solution/2600-2699/2612.Minimum Reverse Operations/README.md
index 49a46fe26c70a..f2c06d0e2c4ea 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2612.Minimum Reverse Operations/README.md
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2612.Minimum Reverse Operations/README.md
@@ -20,49 +20,60 @@ tags:
-给你一个整数 n 和一个在范围 [0, n - 1] 以内的整数 p ,它们表示一个长度为 n 且下标从 0 开始的数组 arr ,数组中除了下标为 p 处是 1 以外,其他所有数都是 0 。
+给定一个整数 n 和一个整数 p,它们表示一个长度为 n 且除了下标为 p 处是 1 以外,其他所有数都是 0 的数组 arr。同时给定一个整数数组 banned ,它包含数组中的一些限制位置。在 arr 上进行下列操作:
-同时给你一个整数数组 banned ,它包含数组中的一些位置。banned 中第 i 个位置表示 arr[banned[i]] = 0 ,题目保证 banned[i] != p 。
+
+ - 如果单个 1 不在
banned 中的位置上,反转大小为 k 的 子数组。
+
+
+返回一个包含 n 个结果的整数数组 answer,其中第 i 个结果是将 1 放到位置 i 处所需的 最少 翻转操作次数,如果无法放到位置 i 处,此数为 -1 。
+
+
-你可以对 arr 进行 若干次 操作。一次操作中,你选择大小为 k 的一个 子数组 ,并将它 翻转 。在任何一次翻转操作后,你都需要确保 arr 中唯一的 1 不会到达任何 banned 中的位置。换句话说,arr[banned[i]] 始终 保持 0 。
+示例 1:
-请你返回一个数组 ans ,对于 [0, n - 1] 之间的任意下标 i ,ans[i] 是将 1 放到位置 i 处的 最少 翻转操作次数,如果无法放到位置 i 处,此数为 -1 。
+
+
输入:n = 4, p = 0, banned = [1,2], k = 4
+
+
输出:[0,-1,-1,1]
+
+
解释:
- - 子数组 指的是一个数组里一段连续 非空 的元素序列。
- - 对于所有的
i ,ans[i] 相互之间独立计算。
- - 将一个数组中的元素 翻转 指的是将数组中的值变成 相反顺序 。
+ - 一开始 1 位于位置 0,因此我们需要在位置 0 上的操作数是 0。
+ - 我们不能将 1 放置在被禁止的位置上,所以位置 1 和 2 的答案是 -1。
+ - 执行大小为 4 的操作以反转整个数组。
+ - 在一次操作后,1 位于位置 3,因此位置 3 的答案是 1。
+
+示例 2:
+
+
+
输入:n = 5, p = 0, banned = [2,4], k = 3
+
+
输出:[0,-1,-1,-1,-1]
+
+
解释:
+
+
+ - 一开始 1 位于位置 0,因此我们需要在位置 0 上的操作数是 0。
+ - 我们不能在
[0, 2] 的子数组位置上执行操作,因为位置 2 在 banned 中。
+ - 由于 1 不能够放置在位置 2 上,使用更多操作将 1 放置在其它位置上是不可能的。
+
+
示例 3:
+
+
+
输入:n = 4, p = 2, banned = [0,1,3], k = 1
+
+
输出:[-1,-1,0,-1]
+
+
解释:
-
示例 1:
-
-
-输入:n = 4, p = 0, banned = [1,2], k = 4
-输出:[0,-1,-1,1]
-解释:k = 4,所以只有一种可行的翻转操作,就是将整个数组翻转。一开始 1 在位置 0 处,所以将它翻转到位置 0 处需要的操作数为 0 。
-我们不能将 1 翻转到 banned 中的位置,所以位置 1 和 2 处的答案都是 -1 。
-通过一次翻转操作,可以将 1 放到位置 3 处,所以位置 3 的答案是 1 。
-
-
-
示例 2:
-
-
-输入:n = 5, p = 0, banned = [2,4], k = 3
-输出:[0,-1,-1,-1,-1]
-解释:这个例子中 1 一开始在位置 0 处,所以此下标的答案为 0 。
-翻转的子数组长度为 k = 3 ,1 此时在位置 0 处,所以我们可以翻转子数组 [0, 2],但翻转后的下标 2 在 banned 中,所以不能执行此操作。
-由于 1 没法离开位置 0 ,所以其他位置的答案都是 -1 。
-
-
-
示例 3:
-
-
-输入:n = 4, p = 2, banned = [0,1,3], k = 1
-输出:[-1,-1,0,-1]
-解释:这个例子中,我们只能对长度为 1 的子数组执行翻转操作,所以 1 无法离开初始位置。
-
+
执行大小为 1 的操作,且 1 永远不会改变位置。
+
From 2800255f42b310fed0e4c07ee23ed89915403d11 Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: Libin YANG
Date: Fri, 21 Mar 2025 21:46:46 +0800
Subject: [PATCH 006/336] feat: add solutions to lc problem: No.0435 (#4278)
---
.../0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README.md | 156 ++++++------------
.../README_EN.md | 147 ++++++-----------
.../Solution.cpp | 20 ++-
.../Solution.go | 15 +-
.../Solution.java | 17 +-
.../Solution.py | 12 +-
.../Solution.ts | 13 +-
.../Solution2.java | 32 ----
.../Solution2.py | 11 --
9 files changed, 137 insertions(+), 286 deletions(-)
delete mode 100644 solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution2.java
delete mode 100644 solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution2.py
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README.md b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README.md
index d11d9c230875c..239271f1d1323 100644
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README.md
+++ b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README.md
@@ -65,9 +65,18 @@ tags:
-### 方法一:转换为最长上升子序列问题
+### 方法一:排序 + 贪心
-最长上升子序列问题,动态规划的做法,时间复杂度是 $O(n^2)$,这里可以采用贪心优化,将复杂度降至 $O(n\log n)$。
+我们首先将区间按照右边界升序排序,用一个变量 $\textit{pre}$ 记录上一个区间的右边界,用一个变量 $\textit{ans}$ 记录需要移除的区间数量,初始时 $\textit{ans} = \textit{intervals.length}$。
+
+然后遍历区间,对于每一个区间:
+
+- 若当前区间的左边界大于等于 $\textit{pre}$,说明该区间无需移除,直接更新 $\textit{pre}$ 为当前区间的右边界,然后将 $\textit{ans}$ 减一;
+- 否则,说明该区间需要移除,不需要更新 $\textit{pre}$ 和 $\textit{ans}$。
+
+最后返回 $\textit{ans}$ 即可。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(\log n)$。其中 $n$ 为区间的数量。
@@ -77,12 +86,12 @@ tags:
class Solution:
def eraseOverlapIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
intervals.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
- ans, t = 0, intervals[0][1]
- for s, e in intervals[1:]:
- if s >= t:
- t = e
- else:
- ans += 1
+ ans = len(intervals)
+ pre = -inf
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ if pre <= l:
+ ans -= 1
+ pre = r
return ans
```
@@ -91,13 +100,14 @@ class Solution:
```java
class Solution {
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
- Arrays.sort(intervals, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[1]));
- int t = intervals[0][1], ans = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- if (intervals[i][0] >= t) {
- t = intervals[i][1];
- } else {
- ++ans;
+ Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
+ int ans = intervals.length;
+ int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ int l = e[0], r = e[1];
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
}
}
return ans;
@@ -111,13 +121,17 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector>& intervals) {
- sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](const auto& a, const auto& b) { return a[1] < b[1]; });
- int ans = 0, t = intervals[0][1];
- for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i) {
- if (t <= intervals[i][0])
- t = intervals[i][1];
- else
- ++ans;
+ ranges::sort(intervals, [](const vector& a, const vector& b) {
+ return a[1] < b[1];
+ });
+ int ans = intervals.size();
+ int pre = INT_MIN;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ int l = e[0], r = e[1];
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
+ }
}
return ans;
}
@@ -131,12 +145,13 @@ func eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals [][]int) int {
sort.Slice(intervals, func(i, j int) bool {
return intervals[i][1] < intervals[j][1]
})
- t, ans := intervals[0][1], 0
- for i := 1; i < len(intervals); i++ {
- if intervals[i][0] >= t {
- t = intervals[i][1]
- } else {
- ans++
+ ans := len(intervals)
+ pre := math.MinInt32
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ l, r := e[0], e[1]
+ if pre <= l {
+ ans--
+ pre = r
}
}
return ans
@@ -148,14 +163,11 @@ func eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals [][]int) int {
```ts
function eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals: number[][]): number {
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[1] - b[1]);
- let end = intervals[0][1],
- ans = 0;
- for (let i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- let cur = intervals[i];
- if (end > cur[0]) {
- ans++;
- } else {
- end = cur[1];
+ let [ans, pre] = [intervals.length, -Infinity];
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
}
}
return ans;
@@ -166,76 +178,4 @@ function eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals: number[][]): number {
-
-
-### 方法二:排序 + 贪心
-
-先按照区间右边界排序。优先选择最小的区间的右边界作为起始边界。遍历区间:
-
-- 若当前区间左边界大于等于起始右边界,说明该区间无需移除,直接更新起始右边界;
-- 否则说明该区间需要移除,更新移除区间的数量 ans。
-
-最后返回 ans 即可。
-
-时间复杂度 $O(n\log n)$。
-
-
-
-#### Python3
-
-```python
-class Solution:
- def eraseOverlapIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- intervals.sort()
- d = [intervals[0][1]]
- for s, e in intervals[1:]:
- if s >= d[-1]:
- d.append(e)
- else:
- idx = bisect_left(d, s)
- d[idx] = min(d[idx], e)
- return len(intervals) - len(d)
-```
-
-#### Java
-
-```java
-class Solution {
- public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
- Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> {
- if (a[0] != b[0]) {
- return a[0] - b[0];
- }
- return a[1] - b[1];
- });
- int n = intervals.length;
- int[] d = new int[n + 1];
- d[1] = intervals[0][1];
- int size = 1;
- for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
- int s = intervals[i][0], e = intervals[i][1];
- if (s >= d[size]) {
- d[++size] = e;
- } else {
- int left = 1, right = size;
- while (left < right) {
- int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
- if (d[mid] >= s) {
- right = mid;
- } else {
- left = mid + 1;
- }
- }
- d[left] = Math.min(d[left], e);
- }
- }
- return n - size;
- }
-}
-```
-
-
-
-
-
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README_EN.md b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README_EN.md
index d4ea312a3852c..61a99a2fbd245 100644
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/README_EN.md
@@ -63,7 +63,18 @@ tags:
-### Solution 1
+### Solution 1: Sorting + Greedy
+
+We first sort the intervals in ascending order by their right boundary. We use a variable $\textit{pre}$ to record the right boundary of the previous interval and a variable $\textit{ans}$ to record the number of intervals that need to be removed. Initially, $\textit{ans} = \textit{intervals.length}$.
+
+Then we iterate through the intervals. For each interval:
+
+- If the left boundary of the current interval is greater than or equal to $\textit{pre}$, it means that this interval does not need to be removed. We directly update $\textit{pre}$ to the right boundary of the current interval and decrement $\textit{ans}$ by one;
+- Otherwise, it means that this interval needs to be removed, and we do not need to update $\textit{pre}$ and $\textit{ans}$.
+
+Finally, we return $\textit{ans}$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n \times \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(\log n)$, where $n$ is the number of intervals.
@@ -73,12 +84,12 @@ tags:
class Solution:
def eraseOverlapIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
intervals.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
- ans, t = 0, intervals[0][1]
- for s, e in intervals[1:]:
- if s >= t:
- t = e
- else:
- ans += 1
+ ans = len(intervals)
+ pre = -inf
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ if pre <= l:
+ ans -= 1
+ pre = r
return ans
```
@@ -87,13 +98,14 @@ class Solution:
```java
class Solution {
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
- Arrays.sort(intervals, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[1]));
- int t = intervals[0][1], ans = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- if (intervals[i][0] >= t) {
- t = intervals[i][1];
- } else {
- ++ans;
+ Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
+ int ans = intervals.length;
+ int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ int l = e[0], r = e[1];
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
}
}
return ans;
@@ -107,13 +119,17 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector>& intervals) {
- sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](const auto& a, const auto& b) { return a[1] < b[1]; });
- int ans = 0, t = intervals[0][1];
- for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i) {
- if (t <= intervals[i][0])
- t = intervals[i][1];
- else
- ++ans;
+ ranges::sort(intervals, [](const vector& a, const vector& b) {
+ return a[1] < b[1];
+ });
+ int ans = intervals.size();
+ int pre = INT_MIN;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ int l = e[0], r = e[1];
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
+ }
}
return ans;
}
@@ -127,12 +143,13 @@ func eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals [][]int) int {
sort.Slice(intervals, func(i, j int) bool {
return intervals[i][1] < intervals[j][1]
})
- t, ans := intervals[0][1], 0
- for i := 1; i < len(intervals); i++ {
- if intervals[i][0] >= t {
- t = intervals[i][1]
- } else {
- ans++
+ ans := len(intervals)
+ pre := math.MinInt32
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ l, r := e[0], e[1]
+ if pre <= l {
+ ans--
+ pre = r
}
}
return ans
@@ -144,14 +161,11 @@ func eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals [][]int) int {
```ts
function eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals: number[][]): number {
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[1] - b[1]);
- let end = intervals[0][1],
- ans = 0;
- for (let i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- let cur = intervals[i];
- if (end > cur[0]) {
- ans++;
- } else {
- end = cur[1];
+ let [ans, pre] = [intervals.length, -Infinity];
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
}
}
return ans;
@@ -162,67 +176,4 @@ function eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals: number[][]): number {
-
-
-### Solution 2
-
-
-
-#### Python3
-
-```python
-class Solution:
- def eraseOverlapIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- intervals.sort()
- d = [intervals[0][1]]
- for s, e in intervals[1:]:
- if s >= d[-1]:
- d.append(e)
- else:
- idx = bisect_left(d, s)
- d[idx] = min(d[idx], e)
- return len(intervals) - len(d)
-```
-
-#### Java
-
-```java
-class Solution {
- public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
- Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> {
- if (a[0] != b[0]) {
- return a[0] - b[0];
- }
- return a[1] - b[1];
- });
- int n = intervals.length;
- int[] d = new int[n + 1];
- d[1] = intervals[0][1];
- int size = 1;
- for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
- int s = intervals[i][0], e = intervals[i][1];
- if (s >= d[size]) {
- d[++size] = e;
- } else {
- int left = 1, right = size;
- while (left < right) {
- int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
- if (d[mid] >= s) {
- right = mid;
- } else {
- left = mid + 1;
- }
- }
- d[left] = Math.min(d[left], e);
- }
- }
- return n - size;
- }
-}
-```
-
-
-
-
-
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.cpp b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.cpp
index e754f1db36a3a..f362aa4fee404 100644
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.cpp
+++ b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.cpp
@@ -1,14 +1,18 @@
class Solution {
public:
int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector>& intervals) {
- sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](const auto& a, const auto& b) { return a[1] < b[1]; });
- int ans = 0, t = intervals[0][1];
- for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i) {
- if (t <= intervals[i][0])
- t = intervals[i][1];
- else
- ++ans;
+ ranges::sort(intervals, [](const vector& a, const vector& b) {
+ return a[1] < b[1];
+ });
+ int ans = intervals.size();
+ int pre = INT_MIN;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ int l = e[0], r = e[1];
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
+ }
}
return ans;
}
-};
\ No newline at end of file
+};
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.go b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.go
index d40eb5b6378ed..16085cd32cfb7 100644
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.go
+++ b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.go
@@ -2,13 +2,14 @@ func eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals [][]int) int {
sort.Slice(intervals, func(i, j int) bool {
return intervals[i][1] < intervals[j][1]
})
- t, ans := intervals[0][1], 0
- for i := 1; i < len(intervals); i++ {
- if intervals[i][0] >= t {
- t = intervals[i][1]
- } else {
- ans++
+ ans := len(intervals)
+ pre := math.MinInt32
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ l, r := e[0], e[1]
+ if pre <= l {
+ ans--
+ pre = r
}
}
return ans
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.java b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.java
index 06940f1be5f62..907073e547ef1 100644
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.java
+++ b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.java
@@ -1,14 +1,15 @@
class Solution {
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
- Arrays.sort(intervals, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[1]));
- int t = intervals[0][1], ans = 0;
- for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- if (intervals[i][0] >= t) {
- t = intervals[i][1];
- } else {
- ++ans;
+ Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[1] - b[1]);
+ int ans = intervals.length;
+ int pre = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ int l = e[0], r = e[1];
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
}
}
return ans;
}
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.py b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.py
index d599421163958..55d4b26112c33 100644
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.py
+++ b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.py
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
class Solution:
def eraseOverlapIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
intervals.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
- ans, t = 0, intervals[0][1]
- for s, e in intervals[1:]:
- if s >= t:
- t = e
- else:
- ans += 1
+ ans = len(intervals)
+ pre = -inf
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ if pre <= l:
+ ans -= 1
+ pre = r
return ans
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.ts b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.ts
index d10fa2a880de6..9e6ced4c9275e 100644
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.ts
+++ b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution.ts
@@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
function eraseOverlapIntervals(intervals: number[][]): number {
intervals.sort((a, b) => a[1] - b[1]);
- let end = intervals[0][1],
- ans = 0;
- for (let i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- let cur = intervals[i];
- if (end > cur[0]) {
- ans++;
- } else {
- end = cur[1];
+ let [ans, pre] = [intervals.length, -Infinity];
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ if (pre <= l) {
+ --ans;
+ pre = r;
}
}
return ans;
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution2.java b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution2.java
deleted file mode 100644
index 3db74098111b5..0000000000000
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution2.java
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-class Solution {
- public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
- Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> {
- if (a[0] != b[0]) {
- return a[0] - b[0];
- }
- return a[1] - b[1];
- });
- int n = intervals.length;
- int[] d = new int[n + 1];
- d[1] = intervals[0][1];
- int size = 1;
- for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
- int s = intervals[i][0], e = intervals[i][1];
- if (s >= d[size]) {
- d[++size] = e;
- } else {
- int left = 1, right = size;
- while (left < right) {
- int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
- if (d[mid] >= s) {
- right = mid;
- } else {
- left = mid + 1;
- }
- }
- d[left] = Math.min(d[left], e);
- }
- }
- return n - size;
- }
-}
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution2.py b/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution2.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 8b41845673b4f..0000000000000
--- a/solution/0400-0499/0435.Non-overlapping Intervals/Solution2.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
-class Solution:
- def eraseOverlapIntervals(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- intervals.sort()
- d = [intervals[0][1]]
- for s, e in intervals[1:]:
- if s >= d[-1]:
- d.append(e)
- else:
- idx = bisect_left(d, s)
- d[idx] = min(d[idx], e)
- return len(intervals) - len(d)
From 7842612fc202c46203d8e81efc64ebf9244a835d Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: Libin YANG
Date: Sat, 22 Mar 2025 08:38:25 +0800
Subject: [PATCH 007/336] feat: add solutions to lc problem: No.2643 (#4279)
No.2643.Row With Maximum Ones
---
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README.md | 63 +++++++++++--------
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README_EN.md | 63 +++++++++++--------
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cpp | 10 +--
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cs | 12 ++++
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.go | 10 ++-
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.java | 6 +-
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.py | 2 +-
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.rs | 7 +--
.../2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.ts | 4 +-
9 files changed, 102 insertions(+), 75 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cs
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README.md b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README.md
index d29d5170fab3a..1d6d883d7d79f 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README.md
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README.md
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ tags:
输入:mat = [[0,1],[1,0]]
输出:[0,1]
-解释:两行中 1 的数量相同。所以返回下标最小的行,下标为 0 。该行 1 的数量为 1 。所以,答案为 [0,1] 。
+解释:两行中 1 的数量相同。所以返回下标最小的行,下标为 0 。该行 1 的数量为 1 。所以,答案为 [0,1] 。
示例 2:
@@ -69,9 +69,16 @@ tags:
### 方法一:模拟
-我们直接遍历矩阵,统计每一行中 $1$ 的个数,更新最大值和对应的行下标。注意,如果当前行的 $1$ 的个数与最大值相等,我们需要选择行下标较小的那一行。
+我们初始化一个数组 $\textit{ans} = [0, 0]$,用于记录最多 $1$ 的行的下标和 $1$ 的数量。
-时间复杂度 $(m \times n)$,其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别为矩阵的行数和列数。空间复杂度 $O(1)$。
+然后遍历矩阵的每一行,对于每一行:
+
+- 计算该行 $1$ 的数量 $\textit{cnt}$(由于矩阵中只包含 $0$ 和 $1$,我们可以直接对该行求和);
+- 如果 $\textit{ans}[1] < \textit{cnt}$,则更新 $\textit{ans} = [i, \textit{cnt}]$。
+
+遍历结束后,返回 $\textit{ans}$。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(m \times n)$,其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别是矩阵的行数和列数。空间复杂度 $O(1)$。
@@ -82,7 +89,7 @@ class Solution:
def rowAndMaximumOnes(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
ans = [0, 0]
for i, row in enumerate(mat):
- cnt = row.count(1)
+ cnt = sum(row)
if ans[1] < cnt:
ans = [i, cnt]
return ans
@@ -97,9 +104,7 @@ class Solution {
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; ++i) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int x : mat[i]) {
- if (x == 1) {
- ++cnt;
- }
+ cnt += x;
}
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
ans[0] = i;
@@ -119,13 +124,9 @@ public:
vector rowAndMaximumOnes(vector>& mat) {
vector ans(2);
for (int i = 0; i < mat.size(); ++i) {
- int cnt = 0;
- for (auto& x : mat[i]) {
- cnt += x == 1;
- }
+ int cnt = accumulate(mat[i].begin(), mat[i].end(), 0);
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
- ans[0] = i;
- ans[1] = cnt;
+ ans = {i, cnt};
}
}
return ans;
@@ -137,16 +138,14 @@ public:
```go
func rowAndMaximumOnes(mat [][]int) []int {
- ans := make([]int, 2)
+ ans := []int{0, 0}
for i, row := range mat {
cnt := 0
for _, x := range row {
- if x == 1 {
- cnt++
- }
+ cnt += x
}
if ans[1] < cnt {
- ans[0], ans[1] = i, cnt
+ ans = []int{i, cnt}
}
}
return ans
@@ -158,8 +157,8 @@ func rowAndMaximumOnes(mat [][]int) []int {
```ts
function rowAndMaximumOnes(mat: number[][]): number[] {
const ans: number[] = [0, 0];
- for (let i = 0; i < mat.length; ++i) {
- const cnt = mat[i].reduce((a, b) => a + b);
+ for (let i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
+ const cnt = mat[i].reduce((sum, num) => sum + num, 0);
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
ans[0] = i;
ans[1] = cnt;
@@ -175,20 +174,34 @@ function rowAndMaximumOnes(mat: number[][]): number[] {
impl Solution {
pub fn row_and_maximum_ones(mat: Vec>) -> Vec {
let mut ans = vec![0, 0];
-
for (i, row) in mat.iter().enumerate() {
- let cnt = row.iter().filter(|&v| *v == 1).count() as i32;
+ let cnt = row.iter().sum();
if ans[1] < cnt {
- ans[0] = i as i32;
- ans[1] = cnt;
+ ans = vec![i as i32, cnt];
}
}
-
ans
}
}
```
+#### C#
+
+```cs
+public class Solution {
+ public int[] RowAndMaximumOnes(int[][] mat) {
+ int[] ans = new int[2];
+ for (int i = 0; i < mat.Length; i++) {
+ int cnt = mat[i].Sum();
+ if (ans[1] < cnt) {
+ ans = new int[] { i, cnt };
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README_EN.md b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README_EN.md
index 236220b1491cd..f6b88dcb4e3eb 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/README_EN.md
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ tags:
Input: mat = [[0,1],[1,0]]
Output: [0,1]
-Explanation: Both rows have the same number of 1's. So we return the index of the smaller row, 0, and the maximum count of ones (1). So, the answer is [0,1].
+Explanation: Both rows have the same number of 1's. So we return the index of the smaller row, 0, and the maximum count of ones (1). So, the answer is [0,1].
Example 2:
@@ -68,9 +68,16 @@ tags:
### Solution 1: Simulation
-We directly traverse the matrix, count the number of $1$s in each row, and update the maximum value and the corresponding row index. Note that if the number of $1$s in the current row is equal to the maximum value, we need to choose the row with the smaller index.
+We initialize an array $\textit{ans} = [0, 0]$ to store the index of the row with the most $1$s and the count of $1$s.
-The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns of the matrix, respectively. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
+Then, we iterate through each row of the matrix:
+
+- Compute the number of $1$s in the current row, denoted as $\textit{cnt}$ (since the matrix contains only $0$s and $1$s, we can directly sum up the row).
+- If $\textit{ans}[1] < \textit{cnt}$, update $\textit{ans} = [i, \textit{cnt}]$.
+
+After finishing the iteration, we return $\textit{ans}$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(m \times n)$, where $m$ and $n$ are the number of rows and columns in the matrix, respectively. The space complexity is $O(1)$.
@@ -81,7 +88,7 @@ class Solution:
def rowAndMaximumOnes(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
ans = [0, 0]
for i, row in enumerate(mat):
- cnt = row.count(1)
+ cnt = sum(row)
if ans[1] < cnt:
ans = [i, cnt]
return ans
@@ -96,9 +103,7 @@ class Solution {
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; ++i) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int x : mat[i]) {
- if (x == 1) {
- ++cnt;
- }
+ cnt += x;
}
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
ans[0] = i;
@@ -118,13 +123,9 @@ public:
vector rowAndMaximumOnes(vector>& mat) {
vector ans(2);
for (int i = 0; i < mat.size(); ++i) {
- int cnt = 0;
- for (auto& x : mat[i]) {
- cnt += x == 1;
- }
+ int cnt = accumulate(mat[i].begin(), mat[i].end(), 0);
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
- ans[0] = i;
- ans[1] = cnt;
+ ans = {i, cnt};
}
}
return ans;
@@ -136,16 +137,14 @@ public:
```go
func rowAndMaximumOnes(mat [][]int) []int {
- ans := make([]int, 2)
+ ans := []int{0, 0}
for i, row := range mat {
cnt := 0
for _, x := range row {
- if x == 1 {
- cnt++
- }
+ cnt += x
}
if ans[1] < cnt {
- ans[0], ans[1] = i, cnt
+ ans = []int{i, cnt}
}
}
return ans
@@ -157,8 +156,8 @@ func rowAndMaximumOnes(mat [][]int) []int {
```ts
function rowAndMaximumOnes(mat: number[][]): number[] {
const ans: number[] = [0, 0];
- for (let i = 0; i < mat.length; ++i) {
- const cnt = mat[i].reduce((a, b) => a + b);
+ for (let i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
+ const cnt = mat[i].reduce((sum, num) => sum + num, 0);
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
ans[0] = i;
ans[1] = cnt;
@@ -174,20 +173,34 @@ function rowAndMaximumOnes(mat: number[][]): number[] {
impl Solution {
pub fn row_and_maximum_ones(mat: Vec>) -> Vec {
let mut ans = vec![0, 0];
-
for (i, row) in mat.iter().enumerate() {
- let cnt = row.iter().filter(|&v| *v == 1).count() as i32;
+ let cnt = row.iter().sum();
if ans[1] < cnt {
- ans[0] = i as i32;
- ans[1] = cnt;
+ ans = vec![i as i32, cnt];
}
}
-
ans
}
}
```
+#### C#
+
+```cs
+public class Solution {
+ public int[] RowAndMaximumOnes(int[][] mat) {
+ int[] ans = new int[2];
+ for (int i = 0; i < mat.Length; i++) {
+ int cnt = mat[i].Sum();
+ if (ans[1] < cnt) {
+ ans = new int[] { i, cnt };
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cpp b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cpp
index 79bcbe90b4e44..5df58522c7b0a 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cpp
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cpp
@@ -3,15 +3,11 @@ class Solution {
vector rowAndMaximumOnes(vector>& mat) {
vector ans(2);
for (int i = 0; i < mat.size(); ++i) {
- int cnt = 0;
- for (auto& x : mat[i]) {
- cnt += x == 1;
- }
+ int cnt = accumulate(mat[i].begin(), mat[i].end(), 0);
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
- ans[0] = i;
- ans[1] = cnt;
+ ans = {i, cnt};
}
}
return ans;
}
-};
\ No newline at end of file
+};
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cs b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cs
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..1b3b9999f632a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.cs
@@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
+public class Solution {
+ public int[] RowAndMaximumOnes(int[][] mat) {
+ int[] ans = new int[2];
+ for (int i = 0; i < mat.Length; i++) {
+ int cnt = mat[i].Sum();
+ if (ans[1] < cnt) {
+ ans = new int[] { i, cnt };
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.go b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.go
index e3b9d532c6c55..8951c9e9b1aa4 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.go
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.go
@@ -1,15 +1,13 @@
func rowAndMaximumOnes(mat [][]int) []int {
- ans := make([]int, 2)
+ ans := []int{0, 0}
for i, row := range mat {
cnt := 0
for _, x := range row {
- if x == 1 {
- cnt++
- }
+ cnt += x
}
if ans[1] < cnt {
- ans[0], ans[1] = i, cnt
+ ans = []int{i, cnt}
}
}
return ans
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.java b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.java
index 1658ecd1f784d..0c3880cb7020a 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.java
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.java
@@ -4,9 +4,7 @@ public int[] rowAndMaximumOnes(int[][] mat) {
for (int i = 0; i < mat.length; ++i) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int x : mat[i]) {
- if (x == 1) {
- ++cnt;
- }
+ cnt += x;
}
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
ans[0] = i;
@@ -15,4 +13,4 @@ public int[] rowAndMaximumOnes(int[][] mat) {
}
return ans;
}
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.py b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.py
index af13862cc0378..860faeeac4ce2 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.py
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.py
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ class Solution:
def rowAndMaximumOnes(self, mat: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
ans = [0, 0]
for i, row in enumerate(mat):
- cnt = row.count(1)
+ cnt = sum(row)
if ans[1] < cnt:
ans = [i, cnt]
return ans
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.rs b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.rs
index da124bf28e74f..9f88929a8d6fa 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.rs
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.rs
@@ -1,15 +1,12 @@
impl Solution {
pub fn row_and_maximum_ones(mat: Vec>) -> Vec {
let mut ans = vec![0, 0];
-
for (i, row) in mat.iter().enumerate() {
- let cnt = row.iter().filter(|&v| *v == 1).count() as i32;
+ let cnt = row.iter().sum();
if ans[1] < cnt {
- ans[0] = i as i32;
- ans[1] = cnt;
+ ans = vec![i as i32, cnt];
}
}
-
ans
}
}
diff --git a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.ts b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.ts
index 879c1afd9b73a..2d8f1513c806e 100644
--- a/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.ts
+++ b/solution/2600-2699/2643.Row With Maximum Ones/Solution.ts
@@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
function rowAndMaximumOnes(mat: number[][]): number[] {
const ans: number[] = [0, 0];
- for (let i = 0; i < mat.length; ++i) {
- const cnt = mat[i].reduce((a, b) => a + b);
+ for (let i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
+ const cnt = mat[i].reduce((sum, num) => sum + num, 0);
if (ans[1] < cnt) {
ans[0] = i;
ans[1] = cnt;
From 9ce6b20c6cf68f3486db868a50d54e18ba8ef34d Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: Libin YANG
Date: Sat, 22 Mar 2025 10:27:18 +0800
Subject: [PATCH 008/336] feat: add solutions to lc problems: No.0252,0253
(#4280)
* No.0252.Meeting Rooms
* No.0253.Meeting Rooms II
---
.../0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README.md | 39 +--
.../0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README_EN.md | 43 +--
.../0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.cpp | 6 +-
.../0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.java | 6 +-
.../0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.rs | 27 +-
.../0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README.md | 304 +++++++++++++----
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/README_EN.md | 306 ++++++++++++++----
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.cpp | 23 +-
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.go | 25 +-
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.java | 25 +-
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.py | 15 +-
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.rs | 42 +--
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.ts | 14 +
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.cpp | 16 +
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.go | 20 ++
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.java | 15 +
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.py | 11 +
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.rs | 24 ++
.../0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.ts | 17 +
19 files changed, 709 insertions(+), 269 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.ts
create mode 100644 solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.cpp
create mode 100644 solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.go
create mode 100644 solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.java
create mode 100644 solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.py
create mode 100644 solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.rs
create mode 100644 solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.ts
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README.md b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README.md
index db5c3a47d17bf..6b44b73110318 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README.md
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README.md
@@ -53,9 +53,9 @@ tags:
### 方法一:排序
-我们将会议按照开始时间进行排序,然后遍历排序后的会议,如果当前会议的开始时间小于前一个会议的结束时间,则说明两个会议有重叠,返回 `false` 即可。
+我们将会议按照开始时间进行排序,然后遍历排序后的会议,如果当前会议的开始时间小于前一个会议的结束时间,则说明两个会议有重叠,返回 $\text{false}$,否则继续遍历。
-遍历结束后,返回 `true`。
+如果遍历结束都没有发现重叠的会议,则返回 $\text{true}$。
时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(\log n)$。其中 $n$ 为会议数量。
@@ -77,9 +77,7 @@ class Solution {
public boolean canAttendMeetings(int[][] intervals) {
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- var a = intervals[i - 1];
- var b = intervals[i];
- if (a[1] > b[0]) {
+ if (intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0]) {
return false;
}
}
@@ -94,11 +92,11 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
bool canAttendMeetings(vector>& intervals) {
- sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](const vector& a, const vector& b) {
+ ranges::sort(intervals, [](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return a[0] < b[0];
});
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i) {
- if (intervals[i][0] < intervals[i - 1][1]) {
+ if (intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0]) {
return false;
}
}
@@ -141,32 +139,13 @@ function canAttendMeetings(intervals: number[][]): boolean {
```rust
impl Solution {
- #[allow(dead_code)]
- pub fn can_attend_meetings(intervals: Vec>) -> bool {
- if intervals.len() == 1 {
- return true;
- }
-
- let mut intervals = intervals;
-
- // Sort the intervals vector
- intervals.sort_by(|lhs, rhs| lhs[0].cmp(&rhs[0]));
-
- let mut end = -1;
-
- // Begin traverse
- for p in &intervals {
- if end == -1 {
- // This is the first pair
- end = p[1];
- continue;
- }
- if p[0] < end {
+ pub fn can_attend_meetings(mut intervals: Vec>) -> bool {
+ intervals.sort_by(|a, b| a[0].cmp(&b[0]));
+ for i in 1..intervals.len() {
+ if intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0] {
return false;
}
- end = p[1];
}
-
true
}
}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README_EN.md b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README_EN.md
index e052d217a0a34..3553a9ea56eee 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/README_EN.md
@@ -42,7 +42,13 @@ tags:
-### Solution 1
+### Solution 1: Sorting
+
+We sort the meetings based on their start times, and then iterate through the sorted meetings. If the start time of the current meeting is less than the end time of the previous meeting, it indicates that there is an overlap between the two meetings, and we return `false`. Otherwise, we continue iterating.
+
+If no overlap is found by the end of the iteration, we return `true`.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n \times \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(\log n)$, where $n$ is the number of meetings.
@@ -62,9 +68,7 @@ class Solution {
public boolean canAttendMeetings(int[][] intervals) {
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- var a = intervals[i - 1];
- var b = intervals[i];
- if (a[1] > b[0]) {
+ if (intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0]) {
return false;
}
}
@@ -79,11 +83,11 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
bool canAttendMeetings(vector>& intervals) {
- sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](const vector& a, const vector& b) {
+ ranges::sort(intervals, [](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return a[0] < b[0];
});
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i) {
- if (intervals[i][0] < intervals[i - 1][1]) {
+ if (intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0]) {
return false;
}
}
@@ -126,32 +130,13 @@ function canAttendMeetings(intervals: number[][]): boolean {
```rust
impl Solution {
- #[allow(dead_code)]
- pub fn can_attend_meetings(intervals: Vec>) -> bool {
- if intervals.len() == 1 {
- return true;
- }
-
- let mut intervals = intervals;
-
- // Sort the intervals vector
- intervals.sort_by(|lhs, rhs| lhs[0].cmp(&rhs[0]));
-
- let mut end = -1;
-
- // Begin traverse
- for p in &intervals {
- if end == -1 {
- // This is the first pair
- end = p[1];
- continue;
- }
- if p[0] < end {
+ pub fn can_attend_meetings(mut intervals: Vec>) -> bool {
+ intervals.sort_by(|a, b| a[0].cmp(&b[0]));
+ for i in 1..intervals.len() {
+ if intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0] {
return false;
}
- end = p[1];
}
-
true
}
}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.cpp b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.cpp
index 7e6b6657fe2e5..9fca6aeed42e3 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.cpp
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.cpp
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
class Solution {
public:
bool canAttendMeetings(vector>& intervals) {
- sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end(), [](const vector& a, const vector& b) {
+ ranges::sort(intervals, [](const auto& a, const auto& b) {
return a[0] < b[0];
});
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.size(); ++i) {
- if (intervals[i][0] < intervals[i - 1][1]) {
+ if (intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
-};
\ No newline at end of file
+};
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.java b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.java
index 565b05b05f2f8..008f531dfad17 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.java
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.java
@@ -2,12 +2,10 @@ class Solution {
public boolean canAttendMeetings(int[][] intervals) {
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
for (int i = 1; i < intervals.length; ++i) {
- var a = intervals[i - 1];
- var b = intervals[i];
- if (a[1] > b[0]) {
+ if (intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.rs b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.rs
index 1ee4bd2d2cc4a..a81f3d2fc39a5 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.rs
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0252.Meeting Rooms/Solution.rs
@@ -1,30 +1,11 @@
impl Solution {
- #[allow(dead_code)]
- pub fn can_attend_meetings(intervals: Vec>) -> bool {
- if intervals.len() == 1 {
- return true;
- }
-
- let mut intervals = intervals;
-
- // Sort the intervals vector
- intervals.sort_by(|lhs, rhs| lhs[0].cmp(&rhs[0]));
-
- let mut end = -1;
-
- // Begin traverse
- for p in &intervals {
- if end == -1 {
- // This is the first pair
- end = p[1];
- continue;
- }
- if p[0] < end {
+ pub fn can_attend_meetings(mut intervals: Vec>) -> bool {
+ intervals.sort_by(|a, b| a[0].cmp(&b[0]));
+ for i in 1..intervals.len() {
+ if intervals[i - 1][1] > intervals[i][0] {
return false;
}
- end = p[1];
}
-
true
}
}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README.md b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README.md
index c330c2024b93d..72e3b0353c53f 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README.md
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README.md
@@ -56,6 +56,169 @@ tags:
### 方法一:差分数组
+我们可以用差分数组来实现。
+
+我们首先找到所有会议的最大结束时间,记为 $m$,然后创建一个长度为 $m + 1$ 的差分数组 $d$,将每个会议的开始时间和结束时间分别加到差分数组的对应位置上,即 $d[l] = d[l] + 1$,而 $d[r] = d[r] - 1$。
+
+然后,我们计算差分数组的前缀和,找出前缀和的最大值,即为所需会议室的最小数量。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n + m)$,空间复杂度 $O(m)$。其中 $n$ 和 $m$ 分别为会议数量和最大结束时间。
+
+
+
+#### Python3
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def minMeetingRooms(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
+ m = max(e[1] for e in intervals)
+ d = [0] * (m + 1)
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ d[l] += 1
+ d[r] -= 1
+ ans = s = 0
+ for v in d:
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ return ans
+```
+
+#### Java
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int minMeetingRooms(int[][] intervals) {
+ int m = 0;
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ m = Math.max(m, e[1]);
+ }
+ int[] d = new int[m + 1];
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ ++d[e[0]];
+ --d[e[1]];
+ }
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (int v : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### C++
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int minMeetingRooms(vector>& intervals) {
+ int m = 0;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ m = max(m, e[1]);
+ }
+ vector d(m + 1);
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ d[e[0]]++;
+ d[e[1]]--;
+ }
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (int v : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+#### Go
+
+```go
+func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) (ans int) {
+ m := 0
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ m = max(m, e[1])
+ }
+
+ d := make([]int, m+1)
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ d[e[0]]++
+ d[e[1]]--
+ }
+
+ s := 0
+ for _, v := range d {
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ }
+ return
+}
+```
+
+#### TypeScript
+
+```ts
+function minMeetingRooms(intervals: number[][]): number {
+ const m = Math.max(...intervals.map(([_, r]) => r));
+ const d: number[] = Array(m + 1).fill(0);
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ d[l]++;
+ d[r]--;
+ }
+ let [ans, s] = [0, 0];
+ for (const v of d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
+```
+
+#### Rust
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_meeting_rooms(intervals: Vec>) -> i32 {
+ let mut m = 0;
+ for e in &intervals {
+ m = m.max(e[1]);
+ }
+
+ let mut d = vec![0; (m + 1) as usize];
+ for e in intervals {
+ d[e[0] as usize] += 1;
+ d[e[1] as usize] -= 1;
+ }
+
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+ for v in d {
+ s += v;
+ ans = ans.max(s);
+ }
+
+ ans
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### 方法二:差分(哈希表)
+
+如果题目中的会议时间跨度很大,那么我们可以使用哈希表来代替差分数组。
+
+我们首先创建一个哈希表 $d$,将每个会议的开始时间和结束时间分别加到哈希表的对应位置上,即 $d[l] = d[l] + 1$,而 $d[r] = d[r] - 1$。
+
+然后,我们将哈希表按照键进行排序,计算哈希表的前缀和,找出前缀和的最大值,即为所需会议室的最小数量。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 为会议数量。
+
#### Python3
@@ -63,11 +226,15 @@ tags:
```python
class Solution:
def minMeetingRooms(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- delta = [0] * 1000010
- for start, end in intervals:
- delta[start] += 1
- delta[end] -= 1
- return max(accumulate(delta))
+ d = defaultdict(int)
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ d[l] += 1
+ d[r] -= 1
+ ans = s = 0
+ for _, v in sorted(d.items()):
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ return ans
```
#### Java
@@ -75,18 +242,17 @@ class Solution:
```java
class Solution {
public int minMeetingRooms(int[][] intervals) {
- int n = 1000010;
- int[] delta = new int[n];
- for (int[] e : intervals) {
- ++delta[e[0]];
- --delta[e[1]];
+ Map d = new TreeMap<>();
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ d.merge(e[0], 1, Integer::sum);
+ d.merge(e[1], -1, Integer::sum);
}
- int res = delta[0];
- for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
- delta[i] += delta[i - 1];
- res = Math.max(res, delta[i]);
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (var e : d.values()) {
+ s += e;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
}
- return res;
+ return ans;
}
}
```
@@ -97,16 +263,17 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
int minMeetingRooms(vector>& intervals) {
- int n = 1000010;
- vector delta(n);
- for (auto e : intervals) {
- ++delta[e[0]];
- --delta[e[1]];
+ map d;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ d[e[0]]++;
+ d[e[1]]--;
}
- for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
- delta[i + 1] += delta[i];
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (auto& [_, v] : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = max(ans, s);
}
- return *max_element(delta.begin(), delta.end());
+ return ans;
}
};
```
@@ -114,56 +281,75 @@ public:
#### Go
```go
-func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) int {
- n := 1000010
- delta := make([]int, n)
+func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) (ans int) {
+ d := make(map[int]int)
for _, e := range intervals {
- delta[e[0]]++
- delta[e[1]]--
+ d[e[0]]++
+ d[e[1]]--
+ }
+
+ keys := make([]int, 0, len(d))
+ for k := range d {
+ keys = append(keys, k)
}
- for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
- delta[i] += delta[i-1]
+ sort.Ints(keys)
+
+ s := 0
+ for _, k := range keys {
+ s += d[k]
+ ans = max(ans, s)
}
- return slices.Max(delta)
+ return
+}
+```
+
+#### TypeScript
+
+```ts
+function minMeetingRooms(intervals: number[][]): number {
+ const d: { [key: number]: number } = {};
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ d[l] = (d[l] || 0) + 1;
+ d[r] = (d[r] || 0) - 1;
+ }
+
+ let [ans, s] = [0, 0];
+ const keys = Object.keys(d)
+ .map(Number)
+ .sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ for (const k of keys) {
+ s += d[k];
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
}
```
#### Rust
```rust
-use std::{cmp::Reverse, collections::BinaryHeap};
+use std::collections::HashMap;
impl Solution {
- #[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn min_meeting_rooms(intervals: Vec>) -> i32 {
- // The min heap that stores the earliest ending time among all meeting rooms
- let mut pq = BinaryHeap::new();
- let mut intervals = intervals;
- let n = intervals.len();
-
- // Let's first sort the intervals vector
- intervals.sort_by(|lhs, rhs| lhs[0].cmp(&rhs[0]));
-
- // Push the first end time to the heap
- pq.push(Reverse(intervals[0][1]));
-
- // Traverse the intervals vector
- for i in 1..n {
- // Get the current top element from the heap
- if let Some(Reverse(end_time)) = pq.pop() {
- if end_time <= intervals[i][0] {
- // If the end time is early than the current begin time
- let new_end_time = intervals[i][1];
- pq.push(Reverse(new_end_time));
- } else {
- // Otherwise, push the end time back and we also need a new room
- pq.push(Reverse(end_time));
- pq.push(Reverse(intervals[i][1]));
- }
- }
+ let mut d: HashMap = HashMap::new();
+ for interval in intervals {
+ let (l, r) = (interval[0], interval[1]);
+ *d.entry(l).or_insert(0) += 1;
+ *d.entry(r).or_insert(0) -= 1;
+ }
+
+ let mut times: Vec = d.keys().cloned().collect();
+ times.sort();
+
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+ for time in times {
+ s += d[&time];
+ ans = ans.max(s);
}
- pq.len() as i32
+ ans
}
}
```
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README_EN.md b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README_EN.md
index 819e7009ce22e..9065c37a97deb 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/README_EN.md
@@ -45,7 +45,170 @@ tags:
-### Solution 1
+### Solution 1: Difference Array
+
+We can implement this using a difference array.
+
+First, we find the maximum end time of all the meetings, denoted as $m$. Then, we create a difference array $d$ of length $m + 1$. For each meeting, we add to the corresponding positions in the difference array: $d[l] = d[l] + 1$ for the start time, and $d[r] = d[r] - 1$ for the end time.
+
+Next, we calculate the prefix sum of the difference array and find the maximum value of the prefix sum, which represents the minimum number of meeting rooms required.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n + m)$ and the space complexity is $O(m)$, where $n$ is the number of meetings and $m$ is the maximum end time.
+
+
+
+#### Python3
+
+```python
+class Solution:
+ def minMeetingRooms(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
+ m = max(e[1] for e in intervals)
+ d = [0] * (m + 1)
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ d[l] += 1
+ d[r] -= 1
+ ans = s = 0
+ for v in d:
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ return ans
+```
+
+#### Java
+
+```java
+class Solution {
+ public int minMeetingRooms(int[][] intervals) {
+ int m = 0;
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ m = Math.max(m, e[1]);
+ }
+ int[] d = new int[m + 1];
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ ++d[e[0]];
+ --d[e[1]];
+ }
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (int v : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### C++
+
+```cpp
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int minMeetingRooms(vector>& intervals) {
+ int m = 0;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ m = max(m, e[1]);
+ }
+ vector d(m + 1);
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ d[e[0]]++;
+ d[e[1]]--;
+ }
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (int v : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
+```
+
+#### Go
+
+```go
+func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) (ans int) {
+ m := 0
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ m = max(m, e[1])
+ }
+
+ d := make([]int, m+1)
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ d[e[0]]++
+ d[e[1]]--
+ }
+
+ s := 0
+ for _, v := range d {
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ }
+ return
+}
+```
+
+#### TypeScript
+
+```ts
+function minMeetingRooms(intervals: number[][]): number {
+ const m = Math.max(...intervals.map(([_, r]) => r));
+ const d: number[] = Array(m + 1).fill(0);
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ d[l]++;
+ d[r]--;
+ }
+ let [ans, s] = [0, 0];
+ for (const v of d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
+```
+
+#### Rust
+
+```rust
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_meeting_rooms(intervals: Vec>) -> i32 {
+ let mut m = 0;
+ for e in &intervals {
+ m = m.max(e[1]);
+ }
+
+ let mut d = vec![0; (m + 1) as usize];
+ for e in intervals {
+ d[e[0] as usize] += 1;
+ d[e[1] as usize] -= 1;
+ }
+
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+ for v in d {
+ s += v;
+ ans = ans.max(s);
+ }
+
+ ans
+ }
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+### Solution 2: Difference (Hash Map)
+
+If the meeting times span a large range, we can use a hash map instead of a difference array.
+
+First, we create a hash map $d$, where we add to the corresponding positions for each meeting's start time and end time: $d[l] = d[l] + 1$ for the start time, and $d[r] = d[r] - 1$ for the end time.
+
+Then, we sort the hash map by its keys, calculate the prefix sum of the hash map, and find the maximum value of the prefix sum, which represents the minimum number of meeting rooms required.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n \times \log n)$ and the space complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the number of meetings.
@@ -54,11 +217,15 @@ tags:
```python
class Solution:
def minMeetingRooms(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- delta = [0] * 1000010
- for start, end in intervals:
- delta[start] += 1
- delta[end] -= 1
- return max(accumulate(delta))
+ d = defaultdict(int)
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ d[l] += 1
+ d[r] -= 1
+ ans = s = 0
+ for _, v in sorted(d.items()):
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ return ans
```
#### Java
@@ -66,18 +233,17 @@ class Solution:
```java
class Solution {
public int minMeetingRooms(int[][] intervals) {
- int n = 1000010;
- int[] delta = new int[n];
- for (int[] e : intervals) {
- ++delta[e[0]];
- --delta[e[1]];
+ Map d = new TreeMap<>();
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ d.merge(e[0], 1, Integer::sum);
+ d.merge(e[1], -1, Integer::sum);
}
- int res = delta[0];
- for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
- delta[i] += delta[i - 1];
- res = Math.max(res, delta[i]);
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (var e : d.values()) {
+ s += e;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
}
- return res;
+ return ans;
}
}
```
@@ -88,16 +254,17 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
int minMeetingRooms(vector>& intervals) {
- int n = 1000010;
- vector delta(n);
- for (auto e : intervals) {
- ++delta[e[0]];
- --delta[e[1]];
+ map d;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ d[e[0]]++;
+ d[e[1]]--;
}
- for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
- delta[i + 1] += delta[i];
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (auto& [_, v] : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = max(ans, s);
}
- return *max_element(delta.begin(), delta.end());
+ return ans;
}
};
```
@@ -105,56 +272,75 @@ public:
#### Go
```go
-func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) int {
- n := 1000010
- delta := make([]int, n)
+func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) (ans int) {
+ d := make(map[int]int)
for _, e := range intervals {
- delta[e[0]]++
- delta[e[1]]--
+ d[e[0]]++
+ d[e[1]]--
+ }
+
+ keys := make([]int, 0, len(d))
+ for k := range d {
+ keys = append(keys, k)
}
- for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
- delta[i] += delta[i-1]
+ sort.Ints(keys)
+
+ s := 0
+ for _, k := range keys {
+ s += d[k]
+ ans = max(ans, s)
}
- return slices.Max(delta)
+ return
+}
+```
+
+#### TypeScript
+
+```ts
+function minMeetingRooms(intervals: number[][]): number {
+ const d: { [key: number]: number } = {};
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ d[l] = (d[l] || 0) + 1;
+ d[r] = (d[r] || 0) - 1;
+ }
+
+ let [ans, s] = [0, 0];
+ const keys = Object.keys(d)
+ .map(Number)
+ .sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ for (const k of keys) {
+ s += d[k];
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
}
```
#### Rust
```rust
-use std::{cmp::Reverse, collections::BinaryHeap};
+use std::collections::HashMap;
impl Solution {
- #[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn min_meeting_rooms(intervals: Vec>) -> i32 {
- // The min heap that stores the earliest ending time among all meeting rooms
- let mut pq = BinaryHeap::new();
- let mut intervals = intervals;
- let n = intervals.len();
-
- // Let's first sort the intervals vector
- intervals.sort_by(|lhs, rhs| lhs[0].cmp(&rhs[0]));
-
- // Push the first end time to the heap
- pq.push(Reverse(intervals[0][1]));
-
- // Traverse the intervals vector
- for i in 1..n {
- // Get the current top element from the heap
- if let Some(Reverse(end_time)) = pq.pop() {
- if end_time <= intervals[i][0] {
- // If the end time is early than the current begin time
- let new_end_time = intervals[i][1];
- pq.push(Reverse(new_end_time));
- } else {
- // Otherwise, push the end time back and we also need a new room
- pq.push(Reverse(end_time));
- pq.push(Reverse(intervals[i][1]));
- }
- }
+ let mut d: HashMap = HashMap::new();
+ for interval in intervals {
+ let (l, r) = (interval[0], interval[1]);
+ *d.entry(l).or_insert(0) += 1;
+ *d.entry(r).or_insert(0) -= 1;
+ }
+
+ let mut times: Vec = d.keys().cloned().collect();
+ times.sort();
+
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+ for time in times {
+ s += d[&time];
+ ans = ans.max(s);
}
- pq.len() as i32
+ ans
}
}
```
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.cpp b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.cpp
index 2971b1431905a..0242f8d5e1651 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.cpp
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.cpp
@@ -1,15 +1,20 @@
class Solution {
public:
int minMeetingRooms(vector>& intervals) {
- int n = 1000010;
- vector delta(n);
- for (auto e : intervals) {
- ++delta[e[0]];
- --delta[e[1]];
+ int m = 0;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ m = max(m, e[1]);
}
- for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i) {
- delta[i + 1] += delta[i];
+ vector d(m + 1);
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ d[e[0]]++;
+ d[e[1]]--;
}
- return *max_element(delta.begin(), delta.end());
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (int v : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
}
-};
\ No newline at end of file
+};
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.go b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.go
index 88f25a7a1410a..61bd1ca79a537 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.go
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.go
@@ -1,12 +1,19 @@
-func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) int {
- n := 1000010
- delta := make([]int, n)
+func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) (ans int) {
+ m := 0
for _, e := range intervals {
- delta[e[0]]++
- delta[e[1]]--
+ m = max(m, e[1])
}
- for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
- delta[i] += delta[i-1]
+
+ d := make([]int, m+1)
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ d[e[0]]++
+ d[e[1]]--
+ }
+
+ s := 0
+ for _, v := range d {
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
}
- return slices.Max(delta)
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+ return
+}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.java b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.java
index 42db9201e47d7..bfdb5285ced20 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.java
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.java
@@ -1,16 +1,19 @@
class Solution {
public int minMeetingRooms(int[][] intervals) {
- int n = 1000010;
- int[] delta = new int[n];
- for (int[] e : intervals) {
- ++delta[e[0]];
- --delta[e[1]];
+ int m = 0;
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ m = Math.max(m, e[1]);
}
- int res = delta[0];
- for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
- delta[i] += delta[i - 1];
- res = Math.max(res, delta[i]);
+ int[] d = new int[m + 1];
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ ++d[e[0]];
+ --d[e[1]];
}
- return res;
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (int v : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
}
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.py b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.py
index 787a096dd3852..63ed57b18f5f4 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.py
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.py
@@ -1,7 +1,12 @@
class Solution:
def minMeetingRooms(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
- delta = [0] * 1000010
- for start, end in intervals:
- delta[start] += 1
- delta[end] -= 1
- return max(accumulate(delta))
+ m = max(e[1] for e in intervals)
+ d = [0] * (m + 1)
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ d[l] += 1
+ d[r] -= 1
+ ans = s = 0
+ for v in d:
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ return ans
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.rs b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.rs
index ad9cd0a9b24ec..a11e467a2ada7 100644
--- a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.rs
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.rs
@@ -1,35 +1,23 @@
-use std::{cmp::Reverse, collections::BinaryHeap};
-
impl Solution {
- #[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn min_meeting_rooms(intervals: Vec>) -> i32 {
- // The min heap that stores the earliest ending time among all meeting rooms
- let mut pq = BinaryHeap::new();
- let mut intervals = intervals;
- let n = intervals.len();
-
- // Let's first sort the intervals vector
- intervals.sort_by(|lhs, rhs| lhs[0].cmp(&rhs[0]));
+ let mut m = 0;
+ for e in &intervals {
+ m = m.max(e[1]);
+ }
- // Push the first end time to the heap
- pq.push(Reverse(intervals[0][1]));
+ let mut d = vec![0; (m + 1) as usize];
+ for e in intervals {
+ d[e[0] as usize] += 1;
+ d[e[1] as usize] -= 1;
+ }
- // Traverse the intervals vector
- for i in 1..n {
- // Get the current top element from the heap
- if let Some(Reverse(end_time)) = pq.pop() {
- if end_time <= intervals[i][0] {
- // If the end time is early than the current begin time
- let new_end_time = intervals[i][1];
- pq.push(Reverse(new_end_time));
- } else {
- // Otherwise, push the end time back and we also need a new room
- pq.push(Reverse(end_time));
- pq.push(Reverse(intervals[i][1]));
- }
- }
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+ for v in d {
+ s += v;
+ ans = ans.max(s);
}
- pq.len() as i32
+ ans
}
}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.ts b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..5a9811e8693c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
+function minMeetingRooms(intervals: number[][]): number {
+ const m = Math.max(...intervals.map(([_, r]) => r));
+ const d: number[] = Array(m + 1).fill(0);
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ d[l]++;
+ d[r]--;
+ }
+ let [ans, s] = [0, 0];
+ for (const v of d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.cpp b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.cpp
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..b7b455ebaf024
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.cpp
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+class Solution {
+public:
+ int minMeetingRooms(vector>& intervals) {
+ map d;
+ for (const auto& e : intervals) {
+ d[e[0]]++;
+ d[e[1]]--;
+ }
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (auto& [_, v] : d) {
+ s += v;
+ ans = max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+};
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.go b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.go
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..55278187da34e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.go
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+func minMeetingRooms(intervals [][]int) (ans int) {
+ d := make(map[int]int)
+ for _, e := range intervals {
+ d[e[0]]++
+ d[e[1]]--
+ }
+
+ keys := make([]int, 0, len(d))
+ for k := range d {
+ keys = append(keys, k)
+ }
+ sort.Ints(keys)
+
+ s := 0
+ for _, k := range keys {
+ s += d[k]
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ }
+ return
+}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.java b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.java
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..64b95cef08d44
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.java
@@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
+class Solution {
+ public int minMeetingRooms(int[][] intervals) {
+ Map d = new TreeMap<>();
+ for (var e : intervals) {
+ d.merge(e[0], 1, Integer::sum);
+ d.merge(e[1], -1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ int ans = 0, s = 0;
+ for (var e : d.values()) {
+ s += e;
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.py b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.py
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..0db564338d7ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.py
@@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
+class Solution:
+ def minMeetingRooms(self, intervals: List[List[int]]) -> int:
+ d = defaultdict(int)
+ for l, r in intervals:
+ d[l] += 1
+ d[r] -= 1
+ ans = s = 0
+ for _, v in sorted(d.items()):
+ s += v
+ ans = max(ans, s)
+ return ans
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.rs b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.rs
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..e35197162e2e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.rs
@@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
+use std::collections::HashMap;
+
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn min_meeting_rooms(intervals: Vec>) -> i32 {
+ let mut d: HashMap = HashMap::new();
+ for interval in intervals {
+ let (l, r) = (interval[0], interval[1]);
+ *d.entry(l).or_insert(0) += 1;
+ *d.entry(r).or_insert(0) -= 1;
+ }
+
+ let mut times: Vec = d.keys().cloned().collect();
+ times.sort();
+
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+ for time in times {
+ s += d[&time];
+ ans = ans.max(s);
+ }
+
+ ans
+ }
+}
diff --git a/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.ts b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.ts
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..90a204cead1cc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0200-0299/0253.Meeting Rooms II/Solution2.ts
@@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
+function minMeetingRooms(intervals: number[][]): number {
+ const d: { [key: number]: number } = {};
+ for (const [l, r] of intervals) {
+ d[l] = (d[l] || 0) + 1;
+ d[r] = (d[r] || 0) - 1;
+ }
+
+ let [ans, s] = [0, 0];
+ const keys = Object.keys(d)
+ .map(Number)
+ .sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ for (const k of keys) {
+ s += d[k];
+ ans = Math.max(ans, s);
+ }
+ return ans;
+}
From a76908b16b404f116f192f019dcef0524e6f8328 Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: Libin YANG
Date: Sat, 22 Mar 2025 11:53:45 +0800
Subject: [PATCH 009/336] feat: add solutions to lc problem: No.0325 (#4281)
No.0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k
---
.../README.md | 84 +++++++++++++++++--
.../README_EN.md | 84 ++++++++++++++++++-
.../Solution.cs | 18 ++++
.../Solution.js | 21 +++++
.../Solution.rs | 20 +++++
5 files changed, 221 insertions(+), 6 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.cs
create mode 100644 solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.js
create mode 100644 solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.rs
diff --git a/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/README.md b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/README.md
index 128bebe51d7b5..ab2116885424a 100644
--- a/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/README.md
+++ b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/README.md
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ tags:
输入: nums = [1,-1,5,-2,3], k = 3
-输出: 4
+输出: 4
解释: 子数组 [1, -1, 5, -2] 和等于 3,且长度最长。
@@ -55,13 +55,13 @@ tags:
### 方法一:哈希表 + 前缀和
-我们可以用一个哈希表 $d$ 记录数组 $nums$ 中每个前缀和第一次出现的下标,初始时 $d[0] = -1$。另外定义一个变量 $s$ 记录前缀和。
+我们可以用一个哈希表 $\textit{d}$ 记录数组 $\textit{nums}$ 中每个前缀和第一次出现的下标,初始时 $\textit{d}[0] = -1$。另外定义一个变量 $\textit{s}$ 记录前缀和。
-接下来,遍历数组 $nums$,对于当前遍历到的数字 $nums[i]$,我们更新前缀和 $s = s + nums[i]$,如果 $s-k$ 在哈希表 $d$ 中存在,不妨记 $j = d[s - k]$,那么以 $nums[i]$ 结尾的符合条件的子数组的长度为 $i - j$,我们使用一个变量 $ans$ 来维护最长的符合条件的子数组的长度。然后,如果 $s$ 在哈希表中不存在,我们记录 $s$ 和对应的下标 $i$,即 $d[s] = i$,否则我们不更新 $d[s]$。需要注意的是,可能会有多个位置 $i$ 都满足 $s$ 的值,因此我们只记录最小的 $i$,这样就能保证子数组的长度最长。
+接下来,遍历数组 $\textit{nums}$,对于当前遍历到的数字 $\textit{nums}[i]$,我们更新前缀和 $\textit{s} = \textit{s} + \textit{nums}[i]$,如果 $\textit{s}-k$ 在哈希表 $\textit{d}$ 中存在,不妨记 $j = \textit{d}[\textit{s} - k]$,那么以 $\textit{nums}[i]$ 结尾的符合条件的子数组的长度为 $i - j$,我们使用一个变量 $\textit{ans}$ 来维护最长的符合条件的子数组的长度。然后,如果 $\textit{s}$ 在哈希表中不存在,我们记录 $\textit{s}$ 和对应的下标 $i$,即 $\textit{d}[\textit{s}] = i$,否则我们不更新 $\textit{d}[\textit{s}]$。需要注意的是,可能会有多个位置 $i$ 都满足 $\textit{s}$ 的值,因此我们只记录最小的 $i$,这样就能保证子数组的长度最长。
-遍历结束之后,我们返回 $ans$ 即可。
+遍历结束之后,我们返回 $\textit{ans}$ 即可。
-时间复杂度 $O(n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组 $nums$ 的长度。
+时间复杂度 $O(n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组 $\textit{nums}$ 的长度。
@@ -163,6 +163,80 @@ function maxSubArrayLen(nums: number[], k: number): number {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
+```rust
+use std::collections::HashMap;
+
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_sub_array_len(nums: Vec, k: i32) -> i32 {
+ let mut d = HashMap::new();
+ d.insert(0, -1);
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+
+ for (i, &x) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
+ s += x;
+ if let Some(&j) = d.get(&(s - k)) {
+ ans = ans.max((i as i32) - j);
+ }
+ d.entry(s).or_insert(i as i32);
+ }
+
+ ans
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript
+
+```js
+/**
+ * @param {number[]} nums
+ * @param {number} k
+ * @return {number}
+ */
+var maxSubArrayLen = function (nums, k) {
+ const d = new Map();
+ d.set(0, -1);
+ let ans = 0;
+ let s = 0;
+ for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
+ s += nums[i];
+ if (d.has(s - k)) {
+ ans = Math.max(ans, i - d.get(s - k));
+ }
+ if (!d.has(s)) {
+ d.set(s, i);
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+};
+```
+
+#### C#
+
+```cs
+public class Solution {
+ public int MaxSubArrayLen(int[] nums, int k) {
+ var d = new Dictionary();
+ d[0] = -1;
+ int ans = 0;
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++) {
+ s += nums[i];
+ if (d.ContainsKey(s - k)) {
+ ans = Math.Max(ans, i - d[s - k]);
+ }
+ if (!d.ContainsKey(s)) {
+ d[s] = i;
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git a/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/README_EN.md b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/README_EN.md
index faa73742e4b73..6c708b0a1b002 100644
--- a/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/README_EN.md
@@ -52,7 +52,15 @@ tags:
-### Solution 1
+### Solution 1: Hash Table + Prefix Sum
+
+We can use a hash table $\textit{d}$ to record the first occurrence index of each prefix sum in the array $\textit{nums}$, initializing $\textit{d}[0] = -1$. Additionally, we define a variable $\textit{s}$ to keep track of the current prefix sum.
+
+Next, we iterate through the array $\textit{nums}$. For the current number $\textit{nums}[i]$, we update the prefix sum $\textit{s} = \textit{s} + \textit{nums}[i]$. If $\textit{s} - k$ exists in the hash table $\textit{d}$, let $\textit{j} = \textit{d}[\textit{s} - k]$, then the length of the subarray that ends at $\textit{nums}[i]$ and satisfies the condition is $i - j$. We use a variable $\textit{ans}$ to maintain the length of the longest subarray that satisfies the condition. After that, if $\textit{s}$ does not exist in the hash table, we record $\textit{s}$ and its corresponding index $i$ by setting $\textit{d}[\textit{s}] = i$. Otherwise, we do not update $\textit{d}[\textit{s}]$. It is important to note that there may be multiple positions $i$ with the same value of $\textit{s}$, so we only record the smallest $i$ to ensure the subarray length is the longest.
+
+After the iteration ends, we return $\textit{ans}$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the array $\textit{nums}$.
@@ -154,6 +162,80 @@ function maxSubArrayLen(nums: number[], k: number): number {
}
```
+#### Rust
+
+```rust
+use std::collections::HashMap;
+
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_sub_array_len(nums: Vec, k: i32) -> i32 {
+ let mut d = HashMap::new();
+ d.insert(0, -1);
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+
+ for (i, &x) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
+ s += x;
+ if let Some(&j) = d.get(&(s - k)) {
+ ans = ans.max((i as i32) - j);
+ }
+ d.entry(s).or_insert(i as i32);
+ }
+
+ ans
+ }
+}
+```
+
+#### JavaScript
+
+```js
+/**
+ * @param {number[]} nums
+ * @param {number} k
+ * @return {number}
+ */
+var maxSubArrayLen = function (nums, k) {
+ const d = new Map();
+ d.set(0, -1);
+ let ans = 0;
+ let s = 0;
+ for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
+ s += nums[i];
+ if (d.has(s - k)) {
+ ans = Math.max(ans, i - d.get(s - k));
+ }
+ if (!d.has(s)) {
+ d.set(s, i);
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+};
+```
+
+#### C#
+
+```cs
+public class Solution {
+ public int MaxSubArrayLen(int[] nums, int k) {
+ var d = new Dictionary();
+ d[0] = -1;
+ int ans = 0;
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++) {
+ s += nums[i];
+ if (d.ContainsKey(s - k)) {
+ ans = Math.Max(ans, i - d[s - k]);
+ }
+ if (!d.ContainsKey(s)) {
+ d[s] = i;
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
+```
+
diff --git a/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.cs b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.cs
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..209eabe2162d3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.cs
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
+public class Solution {
+ public int MaxSubArrayLen(int[] nums, int k) {
+ var d = new Dictionary();
+ d[0] = -1;
+ int ans = 0;
+ int s = 0;
+ for (int i = 0; i < nums.Length; i++) {
+ s += nums[i];
+ if (d.ContainsKey(s - k)) {
+ ans = Math.Max(ans, i - d[s - k]);
+ }
+ if (!d.ContainsKey(s)) {
+ d[s] = i;
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+ }
+}
diff --git a/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.js b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.js
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..dc542c5d2fa24
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.js
@@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
+/**
+ * @param {number[]} nums
+ * @param {number} k
+ * @return {number}
+ */
+var maxSubArrayLen = function (nums, k) {
+ const d = new Map();
+ d.set(0, -1);
+ let ans = 0;
+ let s = 0;
+ for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
+ s += nums[i];
+ if (d.has(s - k)) {
+ ans = Math.max(ans, i - d.get(s - k));
+ }
+ if (!d.has(s)) {
+ d.set(s, i);
+ }
+ }
+ return ans;
+};
diff --git a/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.rs b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.rs
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000000..e011cb1e1c458
--- /dev/null
+++ b/solution/0300-0399/0325.Maximum Size Subarray Sum Equals k/Solution.rs
@@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
+use std::collections::HashMap;
+
+impl Solution {
+ pub fn max_sub_array_len(nums: Vec, k: i32) -> i32 {
+ let mut d = HashMap::new();
+ d.insert(0, -1);
+ let mut ans = 0;
+ let mut s = 0;
+
+ for (i, &x) in nums.iter().enumerate() {
+ s += x;
+ if let Some(&j) = d.get(&(s - k)) {
+ ans = ans.max((i as i32) - j);
+ }
+ d.entry(s).or_insert(i as i32);
+ }
+
+ ans
+ }
+}
From d89865f179cb09ba9c077ffc5f8246ad46a9c1c9 Mon Sep 17 00:00:00 2001
From: Libin YANG
Date: Sat, 22 Mar 2025 16:10:41 +0800
Subject: [PATCH 010/336] feat: add solutions to lc problems: No.0846,1296
(#4282)
---
.../0846.Hand of Straights/README.md | 718 ++++++++++++++---
.../0846.Hand of Straights/README_EN.md | 722 +++++++++++++++---
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.cpp | 23 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.go | 24 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.java | 23 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.py | 14 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.ts | 25 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.cpp | 25 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.go | 31 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.java | 19 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.py | 22 +-
.../0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.ts | 506 +++++++++++-
.../README.md | 709 +++++++++++++++--
.../README_EN.md | 713 +++++++++++++++--
.../Solution.cpp | 23 +-
.../Solution.go | 24 +-
.../Solution.java | 20 +-
.../Solution.py | 14 +-
.../Solution.ts | 21 +
.../Solution2.cpp | 14 +-
.../Solution2.go | 31 +-
.../Solution2.java | 15 +-
.../Solution2.py | 22 +-
.../Solution2.ts | 507 ++++++++++++
24 files changed, 3684 insertions(+), 581 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 solution/1200-1299/1296.Divide Array in Sets of K Consecutive Numbers/Solution.ts
create mode 100644 solution/1200-1299/1296.Divide Array in Sets of K Consecutive Numbers/Solution2.ts
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/README.md b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/README.md
index 42532a8a87d77..e3f2a87a9d75a 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/README.md
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/README.md
@@ -64,11 +64,15 @@ tags:
### 方法一:哈希表 + 排序
-我们先用哈希表 `cnt` 统计数组 `hand` 中每个数字出现的次数,然后对数组 `hand` 进行排序。
+我们首先判断数组 $\textit{hand}$ 的长度是否能被 $\textit{groupSize}$ 整除,如果不能整除,说明无法将数组划分成若干个长度为 $\textit{groupSize}$ 的子数组,直接返回 $\text{false}$。
-接下来,我们遍历数组 `hand`,对于数组中的每个数字 $v$,如果 $v$ 在哈希表 `cnt` 中出现的次数不为 $0$,则我们枚举 $v$ 到 $v+groupSize-1$ 的每个数字,如果这些数字在哈希表 `cnt` 中出现的次数都不为 $0$,则我们将这些数字的出现次数减 $1$,如果减 $1$ 后这些数字的出现次数为 $0$,则我们在哈希表 `cnt` 中删除这些数字。否则说明无法将数组划分成若干个长度为 $groupSize$ 的子数组,返回 `false`。如果可以将数组划分成若干个长度为 $groupSize$ 的子数组,则遍历结束后返回 `true`。
+接下来,我们用一个哈希表 $\textit{cnt}$ 统计数组 $\textit{hand}$ 中每个数字出现的次数,然后对数组 $\textit{hand}$ 进行排序。
-时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组 `hand` 的长度。
+然后,我们遍历排序后的数组 $\textit{hand}$,对于每个数字 $x$,如果 $\textit{cnt}[x]$ 不为 $0$,我们枚举 $x$ 到 $x+\textit{groupSize}-1$ 的每个数字 $y$,如果 $\textit{cnt}[y]$ 为 $0$,说明无法将数组划分成若干个长度为 $\textit{groupSize}$ 的子数组,直接返回 $\text{false}$。否则,我们将 $\textit{cnt}[y]$ 减 $1$。
+
+遍历结束后,说明可以将数组划分成若干个长度为 $\textit{groupSize}$ 的子数组,返回 $\text{true}$。
+
+时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组 $\textit{hand}$ 的长度。
@@ -77,15 +81,15 @@ tags:
```python
class Solution:
def isNStraightHand(self, hand: List[int], groupSize: int) -> bool:
+ if len(hand) % groupSize:
+ return False
cnt = Counter(hand)
- for v in sorted(hand):
- if cnt[v]:
- for x in range(v, v + groupSize):
- if cnt[x] == 0:
+ for x in sorted(hand):
+ if cnt[x]:
+ for y in range(x, x + groupSize):
+ if cnt[y] == 0:
return False
- cnt[x] -= 1
- if cnt[x] == 0:
- cnt.pop(x)
+ cnt[y] -= 1
return True
```
@@ -94,21 +98,20 @@ class Solution:
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isNStraightHand(int[] hand, int groupSize) {
- Map cnt = new HashMap<>();
- for (int v : hand) {
- cnt.put(v, cnt.getOrDefault(v, 0) + 1);
+ if (hand.length % groupSize != 0) {
+ return false;
}
Arrays.sort(hand);
- for (int v : hand) {
- if (cnt.containsKey(v)) {
- for (int x = v; x < v + groupSize; ++x) {
- if (!cnt.containsKey(x)) {
+ Map cnt = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ cnt.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ if (cnt.getOrDefault(x, 0) > 0) {
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (cnt.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum) < 0) {
return false;
}
- cnt.put(x, cnt.get(x) - 1);
- if (cnt.get(x) == 0) {
- cnt.remove(x);
- }
}
}
}
@@ -123,17 +126,22 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
bool isNStraightHand(vector& hand, int groupSize) {
+ if (hand.size() % groupSize) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ ranges::sort(hand);
unordered_map cnt;
- for (int& v : hand) ++cnt[v];
- sort(hand.begin(), hand.end());
- for (int& v : hand) {
- if (cnt.count(v)) {
- for (int x = v; x < v + groupSize; ++x) {
- if (!cnt.count(x)) {
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ ++cnt[x];
+ }
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ if (cnt.contains(x)) {
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!cnt.contains(y)) {
return false;
}
- if (--cnt[x] == 0) {
- cnt.erase(x);
+ if (--cnt[y] == 0) {
+ cnt.erase(y);
}
}
}
@@ -147,21 +155,21 @@ public:
```go
func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
- cnt := map[int]int{}
- for _, v := range hand {
- cnt[v]++
+ if len(hand)%groupSize != 0 {
+ return false
}
sort.Ints(hand)
- for _, v := range hand {
- if _, ok := cnt[v]; ok {
- for x := v; x < v+groupSize; x++ {
- if _, ok := cnt[x]; !ok {
+ cnt := map[int]int{}
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ cnt[x]++
+ }
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ if cnt[x] > 0 {
+ for y := x; y < x+groupSize; y++ {
+ if cnt[y] == 0 {
return false
}
- cnt[x]--
- if cnt[x] == 0 {
- delete(cnt, x)
- }
+ cnt[y]--
}
}
}
@@ -172,24 +180,25 @@ func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
#### TypeScript
```ts
-function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number) {
- const cnt: Record = {};
- for (const i of hand) {
- cnt[i] = (cnt[i] ?? 0) + 1;
+function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number): boolean {
+ if (hand.length % groupSize !== 0) {
+ return false;
}
-
- const keys = Object.keys(cnt).map(Number);
- for (const i of keys) {
- while (cnt[i]) {
- for (let j = i; j < groupSize + i; j++) {
- if (!cnt[j]) {
+ const cnt = new Map();
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ cnt.set(x, (cnt.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ hand.sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ if (cnt.get(x)! > 0) {
+ for (let y = x; y < x + groupSize; y++) {
+ if ((cnt.get(y) || 0) === 0) {
return false;
}
- cnt[j]--;
+ cnt.set(y, cnt.get(y)! - 1);
}
}
}
-
return true;
}
```
@@ -202,11 +211,13 @@ function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number) {
### 方法二:有序集合
-我们也可以使用有序集合统计数组 `hand` 中每个数字出现的次数。
+与方法一类似,我们首先判断数组 $\textit{hand}$ 的长度是否能被 $\textit{groupSize}$ 整除,如果不能整除,说明无法将数组划分成若干个长度为 $\textit{groupSize}$ 的子数组,直接返回 $\text{false}$。
+
+接下来,我们用一个有序集合 $\textit{sd}$ 统计数组 $\textit{hand}$ 中每个数字出现的次数。
-接下来,循环取出有序集合中的最小值 $v$,然后枚举 $v$ 到 $v+groupSize-1$ 的每个数字,如果这些数字在有序集合中出现的次数都不为 $0$,则我们将这些数字的出现次数减 $1$,如果出现次数减 $1$ 后为 $0$,则将该数字从有序集合中删除,否则说明无法将数组划分成若干个长度为 $groupSize$ 的子数组,返回 `false`。如果可以将数组划分成若干个长度为 $groupSize$ 的子数组,则遍历结束后返回 `true`。
+然后,我们循环取出有序集合中的最小值 $x$,然后枚举 $x$ 到 $x+\textit{groupSize}-1$ 的每个数字 $y$,如果这些数字在有序集合中出现的次数都不为 $0$,则我们将这些数字的出现次数减 $1$,如果出现次数减 $1$ 后为 $0$,则将该数字从有序集合中删除,否则说明无法将数组划分成若干个长度为 $\textit{groupSize}$ 的子数组,返回 $\text{false}$。如果可以将数组划分成若干个长度为 $\textit{groupSize}$ 的子数组,则遍历结束后返回 $\text{true}$。
-时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组 `hand` 的长度。
+时间复杂度 $O(n \times \log n)$,空间复杂度 $O(n)$。其中 $n$ 是数组 $\textit{hand}$ 的长度。
@@ -215,23 +226,19 @@ function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number) {
```python
class Solution:
def isNStraightHand(self, hand: List[int], groupSize: int) -> bool:
- if len(hand) % groupSize != 0:
+ if len(hand) % groupSize:
return False
- sd = SortedDict()
- for h in hand:
- if h in sd:
- sd[h] += 1
- else:
- sd[h] = 1
+ cnt = Counter(hand)
+ sd = SortedDict(cnt)
while sd:
- v = sd.peekitem(0)[0]
- for i in range(v, v + groupSize):
- if i not in sd:
+ x = next(iter(sd))
+ for y in range(x, x + groupSize):
+ if y not in sd:
return False
- if sd[i] == 1:
- sd.pop(i)
+ if sd[y] == 1:
+ del sd[y]
else:
- sd[i] -= 1
+ sd[y] -= 1
return True
```
@@ -244,19 +251,18 @@ class Solution {
return false;
}
TreeMap tm = new TreeMap<>();
- for (int h : hand) {
- tm.put(h, tm.getOrDefault(h, 0) + 1);
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ tm.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
}
while (!tm.isEmpty()) {
- int v = tm.firstKey();
- for (int i = v; i < v + groupSize; ++i) {
- if (!tm.containsKey(i)) {
+ int x = tm.firstKey();
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ int t = tm.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum);
+ if (t < 0) {
return false;
}
- if (tm.get(i) == 1) {
- tm.remove(i);
- } else {
- tm.put(i, tm.get(i) - 1);
+ if (t == 0) {
+ tm.remove(y);
}
}
}
@@ -271,17 +277,22 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
bool isNStraightHand(vector& hand, int groupSize) {
- if (hand.size() % groupSize != 0) return false;
+ if (hand.size() % groupSize) {
+ return false;
+ }
map mp;
- for (int& h : hand) mp[h] += 1;
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ ++mp[x];
+ }
while (!mp.empty()) {
- int v = mp.begin()->first;
- for (int i = v; i < v + groupSize; ++i) {
- if (!mp.count(i)) return false;
- if (mp[i] == 1)
- mp.erase(i);
- else
- mp[i] -= 1;
+ int x = mp.begin()->first;
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!mp.contains(y)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ if (--mp[y] == 0) {
+ mp.erase(y);
+ }
}
}
return true;
@@ -296,24 +307,25 @@ func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
if len(hand)%groupSize != 0 {
return false
}
- m := treemap.NewWithIntComparator()
- for _, h := range hand {
- if v, ok := m.Get(h); ok {
- m.Put(h, v.(int)+1)
+ tm := treemap.NewWithIntComparator()
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ if v, ok := tm.Get(x); ok {
+ tm.Put(x, v.(int)+1)
} else {
- m.Put(h, 1)
+ tm.Put(x, 1)
}
}
- for !m.Empty() {
- v, _ := m.Min()
- for i := v.(int); i < v.(int)+groupSize; i++ {
- if _, ok := m.Get(i); !ok {
- return false
- }
- if v, _ := m.Get(i); v.(int) == 1 {
- m.Remove(i)
+ for !tm.Empty() {
+ x, _ := tm.Min()
+ for y := x.(int); y < x.(int)+groupSize; y++ {
+ if v, ok := tm.Get(y); ok {
+ if v.(int) == 1 {
+ tm.Remove(y)
+ } else {
+ tm.Put(y, v.(int)-1)
+ }
} else {
- m.Put(i, v.(int)-1)
+ return false
}
}
}
@@ -325,33 +337,511 @@ func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
```ts
function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number): boolean {
- const n = hand.length;
- if (n % groupSize) {
+ if (hand.length % groupSize !== 0) {
return false;
}
+ const tm = new TreeMap();
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ tm.set(x, (tm.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ while (tm.size()) {
+ const x = tm.first()![0];
+ for (let y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!tm.has(y)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ if (tm.get(y)! === 1) {
+ tm.delete(y);
+ } else {
+ tm.set(y, tm.get(y)! - 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+}
- const groups: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n / groupSize }, () => []);
- hand.sort((a, b) => a - b);
+type Compare = (lhs: T, rhs: T) => number;
+
+class RBTreeNode {
+ data: T;
+ count: number;
+ left: RBTreeNode | null;
+ right: RBTreeNode | null;
+ parent: RBTreeNode | null;
+ color: number;
+ constructor(data: T) {
+ this.data = data;
+ this.left = this.right = this.parent = null;
+ this.color = 0;
+ this.count = 1;
+ }
+
+ sibling(): RBTreeNode | null {
+ if (!this.parent) return null; // sibling null if no parent
+ return this.isOnLeft() ? this.parent.right : this.parent.left;
+ }
+
+ isOnLeft(): boolean {
+ return this === this.parent!.left;
+ }
+
+ hasRedChild(): boolean {
+ return (
+ Boolean(this.left && this.left.color === 0) ||
+ Boolean(this.right && this.right.color === 0)
+ );
+ }
+}
+
+class RBTree {
+ root: RBTreeNode | null;
+ lt: (l: T, r: T) => boolean;
+ constructor(compare: Compare = (l: T, r: T) => (l < r ? -1 : l > r ? 1 : 0)) {
+ this.root = null;
+ this.lt = (l: T, r: T) => compare(l, r) < 0;
+ }
+
+ rotateLeft(pt: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const right = pt.right!;
+ pt.right = right.left;
+
+ if (pt.right) pt.right.parent = pt;
+ right.parent = pt.parent;
+
+ if (!pt.parent) this.root = right;
+ else if (pt === pt.parent.left) pt.parent.left = right;
+ else pt.parent.right = right;
+
+ right.left = pt;
+ pt.parent = right;
+ }
+
+ rotateRight(pt: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const left = pt.left!;
+ pt.left = left.right;
+
+ if (pt.left) pt.left.parent = pt;
+ left.parent = pt.parent;
+
+ if (!pt.parent) this.root = left;
+ else if (pt === pt.parent.left) pt.parent.left = left;
+ else pt.parent.right = left;
+
+ left.right = pt;
+ pt.parent = left;
+ }
+
+ swapColor(p1: RBTreeNode, p2: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const tmp = p1.color;
+ p1.color = p2.color;
+ p2.color = tmp;
+ }
+
+ swapData(p1: RBTreeNode, p2: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const tmp = p1.data;
+ p1.data = p2.data;
+ p2.data = tmp;
+ }
+
+ fixAfterInsert(pt: RBTreeNode): void {
+ let parent = null;
+ let grandParent = null;
+
+ while (pt !== this.root && pt.color !== 1 && pt.parent?.color === 0) {
+ parent = pt.parent;
+ grandParent = pt.parent.parent;
+
+ /* Case : A
+ Parent of pt is left child of Grand-parent of pt */
+ if (parent === grandParent?.left) {
+ const uncle = grandParent.right;
+
+ /* Case : 1
+ The uncle of pt is also red
+ Only Recoloring required */
+ if (uncle && uncle.color === 0) {
+ grandParent.color = 0;
+ parent.color = 1;
+ uncle.color = 1;
+ pt = grandParent;
+ } else {
+ /* Case : 2
+ pt is right child of its parent
+ Left-rotation required */
+ if (pt === parent.right) {
+ this.rotateLeft(parent);
+ pt = parent;
+ parent = pt.parent;
+ }
+
+ /* Case : 3
+ pt is left child of its parent
+ Right-rotation required */
+ this.rotateRight(grandParent);
+ this.swapColor(parent!, grandParent);
+ pt = parent!;
+ }
+ } else {
+ /* Case : B
+ Parent of pt is right child of Grand-parent of pt */
+ const uncle = grandParent!.left;
+
+ /* Case : 1
+ The uncle of pt is also red
+ Only Recoloring required */
+ if (uncle != null && uncle.color === 0) {
+ grandParent!.color = 0;
+ parent.color = 1;
+ uncle.color = 1;
+ pt = grandParent!;
+ } else {
+ /* Case : 2
+ pt is left child of its parent
+ Right-rotation required */
+ if (pt === parent.left) {
+ this.rotateRight(parent);
+ pt = parent;
+ parent = pt.parent;
+ }
+
+ /* Case : 3
+ pt is right child of its parent
+ Left-rotation required */
+ this.rotateLeft(grandParent!);
+ this.swapColor(parent!, grandParent!);
+ pt = parent!;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ this.root!.color = 1;
+ }
+
+ delete(val: T): boolean {
+ const node = this.find(val);
+ if (!node) return false;
+ node.count--;
+ if (!node.count) this.deleteNode(node);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ deleteAll(val: T): boolean {
+ const node = this.find(val);
+ if (!node) return false;
+ this.deleteNode(node);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ deleteNode(v: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const u = BSTreplace(v);
+
+ // True when u and v are both black
+ const uvBlack = (u === null || u.color === 1) && v.color === 1;
+ const parent = v.parent!;
+
+ if (!u) {
+ // u is null therefore v is leaf
+ if (v === this.root) this.root = null;
+ // v is root, making root null
+ else {
+ if (uvBlack) {
+ // u and v both black
+ // v is leaf, fix double black at v
+ this.fixDoubleBlack(v);
+ } else {
+ // u or v is red
+ if (v.sibling()) {
+ // sibling is not null, make it red"
+ v.sibling()!.color = 0;
+ }
+ }
+ // delete v from the tree
+ if (v.isOnLeft()) parent.left = null;
+ else parent.right = null;
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+
+ if (!v.left || !v.right) {
+ // v has 1 child
+ if (v === this.root) {
+ // v is root, assign the value of u to v, and delete u
+ v.data = u.data;
+ v.left = v.right = null;
+ } else {
+ // Detach v from tree and move u up
+ if (v.isOnLeft()) parent.left = u;
+ else parent.right = u;
+ u.parent = parent;
+ if (uvBlack) this.fixDoubleBlack(u);
+ // u and v both black, fix double black at u
+ else u.color = 1; // u or v red, color u black
+ }
+ return;
+ }
- for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- let isPushed = false;
+ // v has 2 children, swap data with successor and recurse
+ this.swapData(u, v);
+ this.deleteNode(u);
+
+ // find node that replaces a deleted node in BST
+ function BSTreplace(x: RBTreeNode): RBTreeNode | null {
+ // when node have 2 children
+ if (x.left && x.right) return successor(x.right);
+ // when leaf
+ if (!x.left && !x.right) return null;
+ // when single child
+ return x.left ?? x.right;
+ }
+ // find node that do not have a left child
+ // in the subtree of the given node
+ function successor(x: RBTreeNode): RBTreeNode {
+ let temp = x;
+ while (temp.left) temp = temp.left;
+ return temp;
+ }
+ }
- for (const g of groups) {
- if (g.length === groupSize || (g.length && hand[i] - g.at(-1)! !== 1)) {
- continue;
+ fixDoubleBlack(x: RBTreeNode): void {
+ if (x === this.root) return; // Reached root
+
+ const sibling = x.sibling();
+ const parent = x.parent!;
+ if (!sibling) {
+ // No sibiling, double black pushed up
+ this.fixDoubleBlack(parent);
+ } else {
+ if (sibling.color === 0) {
+ // Sibling red
+ parent.color = 0;
+ sibling.color = 1;
+ if (sibling.isOnLeft()) this.rotateRight(parent);
+ // left case
+ else this.rotateLeft(parent); // right case
+ this.fixDoubleBlack(x);
+ } else {
+ // Sibling black
+ if (sibling.hasRedChild()) {
+ // at least 1 red children
+ if (sibling.left && sibling.left.color === 0) {
+ if (sibling.isOnLeft()) {
+ // left left
+ sibling.left.color = sibling.color;
+ sibling.color = parent.color;
+ this.rotateRight(parent);
+ } else {
+ // right left
+ sibling.left.color = parent.color;
+ this.rotateRight(sibling);
+ this.rotateLeft(parent);
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (sibling.isOnLeft()) {
+ // left right
+ sibling.right!.color = parent.color;
+ this.rotateLeft(sibling);
+ this.rotateRight(parent);
+ } else {
+ // right right
+ sibling.right!.color = sibling.color;
+ sibling.color = parent.color;
+ this.rotateLeft(parent);
+ }
+ }
+ parent.color = 1;
+ } else {
+ // 2 black children
+ sibling.color = 0;
+ if (parent.color === 1) this.fixDoubleBlack(parent);
+ else parent.color = 1;
+ }
}
+ }
+ }
- g.push(hand[i]);
- isPushed = true;
- break;
+ insert(data: T): boolean {
+ // search for a position to insert
+ let parent = this.root;
+ while (parent) {
+ if (this.lt(data, parent.data)) {
+ if (!parent.left) break;
+ else parent = parent.left;
+ } else if (this.lt(parent.data, data)) {
+ if (!parent.right) break;
+ else parent = parent.right;
+ } else break;
}
- if (!isPushed) {
+ // insert node into parent
+ const node = new RBTreeNode(data);
+ if (!parent) this.root = node;
+ else if (this.lt(node.data, parent.data)) parent.left = node;
+ else if (this.lt(parent.data, node.data)) parent.right = node;
+ else {
+ parent.count++;
return false;
}
+ node.parent = parent;
+ this.fixAfterInsert(node);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ search(predicate: (val: T) => boolean, direction: 'left' | 'right'): T | undefined {
+ let p = this.root;
+ let result = null;
+ while (p) {
+ if (predicate(p.data)) {
+ result = p;
+ p = p[direction];
+ } else {
+ p = p[direction === 'left' ? 'right' : 'left'];
+ }
+ }
+ return result?.data;
}
- return true;
+ find(data: T): RBTreeNode | null {
+ let p = this.root;
+ while (p) {
+ if (this.lt(data, p.data)) {
+ p = p.left;
+ } else if (this.lt(p.data, data)) {
+ p = p.right;
+ } else break;
+ }
+ return p ?? null;
+ }
+
+ count(data: T): number {
+ const node = this.find(data);
+ return node ? node.count : 0;
+ }
+
+ *inOrder(root: RBTreeNode = this.root!): Generator {
+ if (!root) return;
+ for (const v of this.inOrder(root.left!)) yield v;
+ yield root.data;
+ for (const v of this.inOrder(root.right!)) yield v;
+ }
+
+ *reverseInOrder(root: RBTreeNode = this.root!): Generator {
+ if (!root) return;
+ for (const v of this.reverseInOrder(root.right!)) yield v;
+ yield root.data;
+ for (const v of this.reverseInOrder(root.left!)) yield v;
+ }
+}
+
+class TreeMap {
+ _size: number;
+ tree: RBTree;
+ map: Map = new Map();
+ compare: Compare;
+ constructor(
+ collection: Array<[K, V]> | Compare = [],
+ compare: Compare = (l: K, r: K) => (l < r ? -1 : l > r ? 1 : 0),
+ ) {
+ if (typeof collection === 'function') {
+ compare = collection;
+ collection = [];
+ }
+ this._size = 0;
+ this.compare = compare;
+ this.tree = new RBTree(compare);
+ for (const [key, val] of collection) this.set(key, val);
+ }
+
+ size(): number {
+ return this._size;
+ }
+
+ has(key: K): boolean {
+ return !!this.tree.find(key);
+ }
+
+ get(key: K): V | undefined {
+ return this.map.get(key);
+ }
+
+ set(key: K, val: V): boolean {
+ const successful = this.tree.insert(key);
+ this._size += successful ? 1 : 0;
+ this.map.set(key, val);
+ return successful;
+ }
+
+ delete(key: K): boolean {
+ const deleted = this.tree.deleteAll(key);
+ this._size -= deleted ? 1 : 0;
+ return deleted;
+ }
+
+ ceil(target: K): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.search(key => this.compare(key, target) >= 0, 'left'));
+ }
+
+ floor(target: K): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.search(key => this.compare(key, target) <= 0, 'right'));
+ }
+
+ higher(target: K): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.search(key => this.compare(key, target) > 0, 'left'));
+ }
+
+ lower(target: K): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.search(key => this.compare(key, target) < 0, 'right'));
+ }
+
+ first(): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.inOrder().next().value);
+ }
+
+ last(): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.reverseInOrder().next().value);
+ }
+
+ shift(): [K, V] | undefined {
+ const first = this.first();
+ if (first === undefined) return undefined;
+ this.delete(first[0]);
+ return first;
+ }
+
+ pop(): [K, V] | undefined {
+ const last = this.last();
+ if (last === undefined) return undefined;
+ this.delete(last[0]);
+ return last;
+ }
+
+ toKeyValue(key: K): [K, V];
+ toKeyValue(key: undefined): undefined;
+ toKeyValue(key: K | undefined): [K, V] | undefined;
+ toKeyValue(key: K | undefined): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return key != null ? [key, this.map.get(key)!] : undefined;
+ }
+
+ *[Symbol.iterator](): Generator<[K, V], void, void> {
+ for (const key of this.keys()) yield this.toKeyValue(key);
+ }
+
+ *keys(): Generator {
+ for (const key of this.tree.inOrder()) yield key;
+ }
+
+ *values(): Generator {
+ for (const key of this.keys()) yield this.map.get(key)!;
+ return undefined;
+ }
+
+ *rkeys(): Generator {
+ for (const key of this.tree.reverseInOrder()) yield key;
+ return undefined;
+ }
+
+ *rvalues(): Generator {
+ for (const key of this.rkeys()) yield this.map.get(key)!;
+ return undefined;
+ }
}
```
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/README_EN.md b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/README_EN.md
index e8eef656750af..a0efb8f95ece4 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/README_EN.md
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/README_EN.md
@@ -59,7 +59,17 @@ tags:
-### Solution 1
+### Solution 1: Hash Table + Sorting
+
+We first check whether the length of the array $\textit{hand}$ is divisible by $\textit{groupSize}$. If it is not, this means that the array cannot be partitioned into multiple subarrays of length $\textit{groupSize}$, so we return $\text{false}$.
+
+Next, we use a hash table $\textit{cnt}$ to count the occurrences of each number in the array $\textit{hand}$, and then we sort the array $\textit{hand}$.
+
+After that, we iterate over the sorted array $\textit{hand}$. For each number $x$, if $\textit{cnt}[x] \neq 0$, we enumerate every number $y$ from $x$ to $x + \textit{groupSize} - 1$. If $\textit{cnt}[y] = 0$, it means that we cannot partition the array into multiple subarrays of length $\textit{groupSize}$, so we return $\text{false}$. Otherwise, we decrement $\textit{cnt}[y]$ by $1$.
+
+If the iteration completes successfully, it means that the array can be partitioned into multiple valid subarrays, so we return $\text{true}$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n \times \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the array $\textit{hand}$.
@@ -68,15 +78,15 @@ tags:
```python
class Solution:
def isNStraightHand(self, hand: List[int], groupSize: int) -> bool:
+ if len(hand) % groupSize:
+ return False
cnt = Counter(hand)
- for v in sorted(hand):
- if cnt[v]:
- for x in range(v, v + groupSize):
- if cnt[x] == 0:
+ for x in sorted(hand):
+ if cnt[x]:
+ for y in range(x, x + groupSize):
+ if cnt[y] == 0:
return False
- cnt[x] -= 1
- if cnt[x] == 0:
- cnt.pop(x)
+ cnt[y] -= 1
return True
```
@@ -85,21 +95,20 @@ class Solution:
```java
class Solution {
public boolean isNStraightHand(int[] hand, int groupSize) {
- Map cnt = new HashMap<>();
- for (int v : hand) {
- cnt.put(v, cnt.getOrDefault(v, 0) + 1);
+ if (hand.length % groupSize != 0) {
+ return false;
}
Arrays.sort(hand);
- for (int v : hand) {
- if (cnt.containsKey(v)) {
- for (int x = v; x < v + groupSize; ++x) {
- if (!cnt.containsKey(x)) {
+ Map cnt = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ cnt.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ if (cnt.getOrDefault(x, 0) > 0) {
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (cnt.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum) < 0) {
return false;
}
- cnt.put(x, cnt.get(x) - 1);
- if (cnt.get(x) == 0) {
- cnt.remove(x);
- }
}
}
}
@@ -114,17 +123,22 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
bool isNStraightHand(vector& hand, int groupSize) {
+ if (hand.size() % groupSize) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ ranges::sort(hand);
unordered_map cnt;
- for (int& v : hand) ++cnt[v];
- sort(hand.begin(), hand.end());
- for (int& v : hand) {
- if (cnt.count(v)) {
- for (int x = v; x < v + groupSize; ++x) {
- if (!cnt.count(x)) {
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ ++cnt[x];
+ }
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ if (cnt.contains(x)) {
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!cnt.contains(y)) {
return false;
}
- if (--cnt[x] == 0) {
- cnt.erase(x);
+ if (--cnt[y] == 0) {
+ cnt.erase(y);
}
}
}
@@ -138,21 +152,21 @@ public:
```go
func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
- cnt := map[int]int{}
- for _, v := range hand {
- cnt[v]++
+ if len(hand)%groupSize != 0 {
+ return false
}
sort.Ints(hand)
- for _, v := range hand {
- if _, ok := cnt[v]; ok {
- for x := v; x < v+groupSize; x++ {
- if _, ok := cnt[x]; !ok {
+ cnt := map[int]int{}
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ cnt[x]++
+ }
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ if cnt[x] > 0 {
+ for y := x; y < x+groupSize; y++ {
+ if cnt[y] == 0 {
return false
}
- cnt[x]--
- if cnt[x] == 0 {
- delete(cnt, x)
- }
+ cnt[y]--
}
}
}
@@ -163,24 +177,25 @@ func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
#### TypeScript
```ts
-function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number) {
- const cnt: Record = {};
- for (const i of hand) {
- cnt[i] = (cnt[i] ?? 0) + 1;
+function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number): boolean {
+ if (hand.length % groupSize !== 0) {
+ return false;
}
-
- const keys = Object.keys(cnt).map(Number);
- for (const i of keys) {
- while (cnt[i]) {
- for (let j = i; j < groupSize + i; j++) {
- if (!cnt[j]) {
+ const cnt = new Map();
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ cnt.set(x, (cnt.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ hand.sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ if (cnt.get(x)! > 0) {
+ for (let y = x; y < x + groupSize; y++) {
+ if ((cnt.get(y) || 0) === 0) {
return false;
}
- cnt[j]--;
+ cnt.set(y, cnt.get(y)! - 1);
}
}
}
-
return true;
}
```
@@ -191,7 +206,15 @@ function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number) {
-### Solution 2
+### Solution 2: Ordered Set
+
+Similar to Solution 1, we first check whether the length of the array $\textit{hand}$ is divisible by $\textit{groupSize}$. If it is not, this means that the array cannot be partitioned into multiple subarrays of length $\textit{groupSize}$, so we return $\text{false}$.
+
+Next, we use an ordered set $\textit{sd}$ to count the occurrences of each number in the array $\textit{hand}$.
+
+Then, we repeatedly take the smallest value $x$ from the ordered set and enumerate each number $y$ from $x$ to $x + \textit{groupSize} - 1$. If all these numbers appear at least once in the ordered set, we decrement their occurrence count by $1$. If any count reaches $0$, we remove that number from the ordered set. Otherwise, if we encounter a number that does not exist in the ordered set, it means that the array cannot be partitioned into valid subarrays, so we return $\text{false}$. If the iteration completes successfully, it means that the array can be partitioned into multiple valid subarrays, so we return $\text{true}$.
+
+The time complexity is $O(n \times \log n)$, and the space complexity is $O(n)$, where $n$ is the length of the array $\textit{hand}$.
@@ -200,23 +223,19 @@ function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number) {
```python
class Solution:
def isNStraightHand(self, hand: List[int], groupSize: int) -> bool:
- if len(hand) % groupSize != 0:
+ if len(hand) % groupSize:
return False
- sd = SortedDict()
- for h in hand:
- if h in sd:
- sd[h] += 1
- else:
- sd[h] = 1
+ cnt = Counter(hand)
+ sd = SortedDict(cnt)
while sd:
- v = sd.peekitem(0)[0]
- for i in range(v, v + groupSize):
- if i not in sd:
+ x = next(iter(sd))
+ for y in range(x, x + groupSize):
+ if y not in sd:
return False
- if sd[i] == 1:
- sd.pop(i)
+ if sd[y] == 1:
+ del sd[y]
else:
- sd[i] -= 1
+ sd[y] -= 1
return True
```
@@ -229,19 +248,18 @@ class Solution {
return false;
}
TreeMap tm = new TreeMap<>();
- for (int h : hand) {
- tm.put(h, tm.getOrDefault(h, 0) + 1);
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ tm.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
}
while (!tm.isEmpty()) {
- int v = tm.firstKey();
- for (int i = v; i < v + groupSize; ++i) {
- if (!tm.containsKey(i)) {
+ int x = tm.firstKey();
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ int t = tm.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum);
+ if (t < 0) {
return false;
}
- if (tm.get(i) == 1) {
- tm.remove(i);
- } else {
- tm.put(i, tm.get(i) - 1);
+ if (t == 0) {
+ tm.remove(y);
}
}
}
@@ -256,17 +274,22 @@ class Solution {
class Solution {
public:
bool isNStraightHand(vector& hand, int groupSize) {
- if (hand.size() % groupSize != 0) return false;
+ if (hand.size() % groupSize) {
+ return false;
+ }
map mp;
- for (int& h : hand) mp[h] += 1;
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ ++mp[x];
+ }
while (!mp.empty()) {
- int v = mp.begin()->first;
- for (int i = v; i < v + groupSize; ++i) {
- if (!mp.count(i)) return false;
- if (mp[i] == 1)
- mp.erase(i);
- else
- mp[i] -= 1;
+ int x = mp.begin()->first;
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!mp.contains(y)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ if (--mp[y] == 0) {
+ mp.erase(y);
+ }
}
}
return true;
@@ -281,24 +304,25 @@ func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
if len(hand)%groupSize != 0 {
return false
}
- m := treemap.NewWithIntComparator()
- for _, h := range hand {
- if v, ok := m.Get(h); ok {
- m.Put(h, v.(int)+1)
+ tm := treemap.NewWithIntComparator()
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ if v, ok := tm.Get(x); ok {
+ tm.Put(x, v.(int)+1)
} else {
- m.Put(h, 1)
+ tm.Put(x, 1)
}
}
- for !m.Empty() {
- v, _ := m.Min()
- for i := v.(int); i < v.(int)+groupSize; i++ {
- if _, ok := m.Get(i); !ok {
- return false
- }
- if v, _ := m.Get(i); v.(int) == 1 {
- m.Remove(i)
+ for !tm.Empty() {
+ x, _ := tm.Min()
+ for y := x.(int); y < x.(int)+groupSize; y++ {
+ if v, ok := tm.Get(y); ok {
+ if v.(int) == 1 {
+ tm.Remove(y)
+ } else {
+ tm.Put(y, v.(int)-1)
+ }
} else {
- m.Put(i, v.(int)-1)
+ return false
}
}
}
@@ -310,33 +334,511 @@ func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
```ts
function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number): boolean {
- const n = hand.length;
- if (n % groupSize) {
+ if (hand.length % groupSize !== 0) {
return false;
}
+ const tm = new TreeMap();
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ tm.set(x, (tm.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ while (tm.size()) {
+ const x = tm.first()![0];
+ for (let y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!tm.has(y)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ if (tm.get(y)! === 1) {
+ tm.delete(y);
+ } else {
+ tm.set(y, tm.get(y)! - 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+}
- const groups: number[][] = Array.from({ length: n / groupSize }, () => []);
- hand.sort((a, b) => a - b);
+type Compare = (lhs: T, rhs: T) => number;
+
+class RBTreeNode {
+ data: T;
+ count: number;
+ left: RBTreeNode | null;
+ right: RBTreeNode | null;
+ parent: RBTreeNode | null;
+ color: number;
+ constructor(data: T) {
+ this.data = data;
+ this.left = this.right = this.parent = null;
+ this.color = 0;
+ this.count = 1;
+ }
+
+ sibling(): RBTreeNode | null {
+ if (!this.parent) return null; // sibling null if no parent
+ return this.isOnLeft() ? this.parent.right : this.parent.left;
+ }
+
+ isOnLeft(): boolean {
+ return this === this.parent!.left;
+ }
+
+ hasRedChild(): boolean {
+ return (
+ Boolean(this.left && this.left.color === 0) ||
+ Boolean(this.right && this.right.color === 0)
+ );
+ }
+}
+
+class RBTree {
+ root: RBTreeNode | null;
+ lt: (l: T, r: T) => boolean;
+ constructor(compare: Compare = (l: T, r: T) => (l < r ? -1 : l > r ? 1 : 0)) {
+ this.root = null;
+ this.lt = (l: T, r: T) => compare(l, r) < 0;
+ }
+
+ rotateLeft(pt: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const right = pt.right!;
+ pt.right = right.left;
+
+ if (pt.right) pt.right.parent = pt;
+ right.parent = pt.parent;
+
+ if (!pt.parent) this.root = right;
+ else if (pt === pt.parent.left) pt.parent.left = right;
+ else pt.parent.right = right;
+
+ right.left = pt;
+ pt.parent = right;
+ }
+
+ rotateRight(pt: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const left = pt.left!;
+ pt.left = left.right;
+
+ if (pt.left) pt.left.parent = pt;
+ left.parent = pt.parent;
+
+ if (!pt.parent) this.root = left;
+ else if (pt === pt.parent.left) pt.parent.left = left;
+ else pt.parent.right = left;
+
+ left.right = pt;
+ pt.parent = left;
+ }
+
+ swapColor(p1: RBTreeNode, p2: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const tmp = p1.color;
+ p1.color = p2.color;
+ p2.color = tmp;
+ }
+
+ swapData(p1: RBTreeNode, p2: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const tmp = p1.data;
+ p1.data = p2.data;
+ p2.data = tmp;
+ }
+
+ fixAfterInsert(pt: RBTreeNode): void {
+ let parent = null;
+ let grandParent = null;
+
+ while (pt !== this.root && pt.color !== 1 && pt.parent?.color === 0) {
+ parent = pt.parent;
+ grandParent = pt.parent.parent;
+
+ /* Case : A
+ Parent of pt is left child of Grand-parent of pt */
+ if (parent === grandParent?.left) {
+ const uncle = grandParent.right;
+
+ /* Case : 1
+ The uncle of pt is also red
+ Only Recoloring required */
+ if (uncle && uncle.color === 0) {
+ grandParent.color = 0;
+ parent.color = 1;
+ uncle.color = 1;
+ pt = grandParent;
+ } else {
+ /* Case : 2
+ pt is right child of its parent
+ Left-rotation required */
+ if (pt === parent.right) {
+ this.rotateLeft(parent);
+ pt = parent;
+ parent = pt.parent;
+ }
+
+ /* Case : 3
+ pt is left child of its parent
+ Right-rotation required */
+ this.rotateRight(grandParent);
+ this.swapColor(parent!, grandParent);
+ pt = parent!;
+ }
+ } else {
+ /* Case : B
+ Parent of pt is right child of Grand-parent of pt */
+ const uncle = grandParent!.left;
+
+ /* Case : 1
+ The uncle of pt is also red
+ Only Recoloring required */
+ if (uncle != null && uncle.color === 0) {
+ grandParent!.color = 0;
+ parent.color = 1;
+ uncle.color = 1;
+ pt = grandParent!;
+ } else {
+ /* Case : 2
+ pt is left child of its parent
+ Right-rotation required */
+ if (pt === parent.left) {
+ this.rotateRight(parent);
+ pt = parent;
+ parent = pt.parent;
+ }
+
+ /* Case : 3
+ pt is right child of its parent
+ Left-rotation required */
+ this.rotateLeft(grandParent!);
+ this.swapColor(parent!, grandParent!);
+ pt = parent!;
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ this.root!.color = 1;
+ }
- for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
- let isPushed = false;
+ delete(val: T): boolean {
+ const node = this.find(val);
+ if (!node) return false;
+ node.count--;
+ if (!node.count) this.deleteNode(node);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ deleteAll(val: T): boolean {
+ const node = this.find(val);
+ if (!node) return false;
+ this.deleteNode(node);
+ return true;
+ }
+
+ deleteNode(v: RBTreeNode): void {
+ const u = BSTreplace(v);
+
+ // True when u and v are both black
+ const uvBlack = (u === null || u.color === 1) && v.color === 1;
+ const parent = v.parent!;
+
+ if (!u) {
+ // u is null therefore v is leaf
+ if (v === this.root) this.root = null;
+ // v is root, making root null
+ else {
+ if (uvBlack) {
+ // u and v both black
+ // v is leaf, fix double black at v
+ this.fixDoubleBlack(v);
+ } else {
+ // u or v is red
+ if (v.sibling()) {
+ // sibling is not null, make it red"
+ v.sibling()!.color = 0;
+ }
+ }
+ // delete v from the tree
+ if (v.isOnLeft()) parent.left = null;
+ else parent.right = null;
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+
+ if (!v.left || !v.right) {
+ // v has 1 child
+ if (v === this.root) {
+ // v is root, assign the value of u to v, and delete u
+ v.data = u.data;
+ v.left = v.right = null;
+ } else {
+ // Detach v from tree and move u up
+ if (v.isOnLeft()) parent.left = u;
+ else parent.right = u;
+ u.parent = parent;
+ if (uvBlack) this.fixDoubleBlack(u);
+ // u and v both black, fix double black at u
+ else u.color = 1; // u or v red, color u black
+ }
+ return;
+ }
+
+ // v has 2 children, swap data with successor and recurse
+ this.swapData(u, v);
+ this.deleteNode(u);
+
+ // find node that replaces a deleted node in BST
+ function BSTreplace(x: RBTreeNode): RBTreeNode | null {
+ // when node have 2 children
+ if (x.left && x.right) return successor(x.right);
+ // when leaf
+ if (!x.left && !x.right) return null;
+ // when single child
+ return x.left ?? x.right;
+ }
+ // find node that do not have a left child
+ // in the subtree of the given node
+ function successor(x: RBTreeNode): RBTreeNode {
+ let temp = x;
+ while (temp.left) temp = temp.left;
+ return temp;
+ }
+ }
- for (const g of groups) {
- if (g.length === groupSize || (g.length && hand[i] - g.at(-1)! !== 1)) {
- continue;
+ fixDoubleBlack(x: RBTreeNode): void {
+ if (x === this.root) return; // Reached root
+
+ const sibling = x.sibling();
+ const parent = x.parent!;
+ if (!sibling) {
+ // No sibiling, double black pushed up
+ this.fixDoubleBlack(parent);
+ } else {
+ if (sibling.color === 0) {
+ // Sibling red
+ parent.color = 0;
+ sibling.color = 1;
+ if (sibling.isOnLeft()) this.rotateRight(parent);
+ // left case
+ else this.rotateLeft(parent); // right case
+ this.fixDoubleBlack(x);
+ } else {
+ // Sibling black
+ if (sibling.hasRedChild()) {
+ // at least 1 red children
+ if (sibling.left && sibling.left.color === 0) {
+ if (sibling.isOnLeft()) {
+ // left left
+ sibling.left.color = sibling.color;
+ sibling.color = parent.color;
+ this.rotateRight(parent);
+ } else {
+ // right left
+ sibling.left.color = parent.color;
+ this.rotateRight(sibling);
+ this.rotateLeft(parent);
+ }
+ } else {
+ if (sibling.isOnLeft()) {
+ // left right
+ sibling.right!.color = parent.color;
+ this.rotateLeft(sibling);
+ this.rotateRight(parent);
+ } else {
+ // right right
+ sibling.right!.color = sibling.color;
+ sibling.color = parent.color;
+ this.rotateLeft(parent);
+ }
+ }
+ parent.color = 1;
+ } else {
+ // 2 black children
+ sibling.color = 0;
+ if (parent.color === 1) this.fixDoubleBlack(parent);
+ else parent.color = 1;
+ }
}
+ }
+ }
- g.push(hand[i]);
- isPushed = true;
- break;
+ insert(data: T): boolean {
+ // search for a position to insert
+ let parent = this.root;
+ while (parent) {
+ if (this.lt(data, parent.data)) {
+ if (!parent.left) break;
+ else parent = parent.left;
+ } else if (this.lt(parent.data, data)) {
+ if (!parent.right) break;
+ else parent = parent.right;
+ } else break;
}
- if (!isPushed) {
+ // insert node into parent
+ const node = new RBTreeNode(data);
+ if (!parent) this.root = node;
+ else if (this.lt(node.data, parent.data)) parent.left = node;
+ else if (this.lt(parent.data, node.data)) parent.right = node;
+ else {
+ parent.count++;
return false;
}
+ node.parent = parent;
+ this.fixAfterInsert(node);
+ return true;
}
- return true;
+ search(predicate: (val: T) => boolean, direction: 'left' | 'right'): T | undefined {
+ let p = this.root;
+ let result = null;
+ while (p) {
+ if (predicate(p.data)) {
+ result = p;
+ p = p[direction];
+ } else {
+ p = p[direction === 'left' ? 'right' : 'left'];
+ }
+ }
+ return result?.data;
+ }
+
+ find(data: T): RBTreeNode | null {
+ let p = this.root;
+ while (p) {
+ if (this.lt(data, p.data)) {
+ p = p.left;
+ } else if (this.lt(p.data, data)) {
+ p = p.right;
+ } else break;
+ }
+ return p ?? null;
+ }
+
+ count(data: T): number {
+ const node = this.find(data);
+ return node ? node.count : 0;
+ }
+
+ *inOrder(root: RBTreeNode = this.root!): Generator {
+ if (!root) return;
+ for (const v of this.inOrder(root.left!)) yield v;
+ yield root.data;
+ for (const v of this.inOrder(root.right!)) yield v;
+ }
+
+ *reverseInOrder(root: RBTreeNode = this.root!): Generator {
+ if (!root) return;
+ for (const v of this.reverseInOrder(root.right!)) yield v;
+ yield root.data;
+ for (const v of this.reverseInOrder(root.left!)) yield v;
+ }
+}
+
+class TreeMap {
+ _size: number;
+ tree: RBTree;
+ map: Map = new Map();
+ compare: Compare;
+ constructor(
+ collection: Array<[K, V]> | Compare = [],
+ compare: Compare = (l: K, r: K) => (l < r ? -1 : l > r ? 1 : 0),
+ ) {
+ if (typeof collection === 'function') {
+ compare = collection;
+ collection = [];
+ }
+ this._size = 0;
+ this.compare = compare;
+ this.tree = new RBTree(compare);
+ for (const [key, val] of collection) this.set(key, val);
+ }
+
+ size(): number {
+ return this._size;
+ }
+
+ has(key: K): boolean {
+ return !!this.tree.find(key);
+ }
+
+ get(key: K): V | undefined {
+ return this.map.get(key);
+ }
+
+ set(key: K, val: V): boolean {
+ const successful = this.tree.insert(key);
+ this._size += successful ? 1 : 0;
+ this.map.set(key, val);
+ return successful;
+ }
+
+ delete(key: K): boolean {
+ const deleted = this.tree.deleteAll(key);
+ this._size -= deleted ? 1 : 0;
+ return deleted;
+ }
+
+ ceil(target: K): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.search(key => this.compare(key, target) >= 0, 'left'));
+ }
+
+ floor(target: K): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.search(key => this.compare(key, target) <= 0, 'right'));
+ }
+
+ higher(target: K): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.search(key => this.compare(key, target) > 0, 'left'));
+ }
+
+ lower(target: K): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.search(key => this.compare(key, target) < 0, 'right'));
+ }
+
+ first(): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.inOrder().next().value);
+ }
+
+ last(): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return this.toKeyValue(this.tree.reverseInOrder().next().value);
+ }
+
+ shift(): [K, V] | undefined {
+ const first = this.first();
+ if (first === undefined) return undefined;
+ this.delete(first[0]);
+ return first;
+ }
+
+ pop(): [K, V] | undefined {
+ const last = this.last();
+ if (last === undefined) return undefined;
+ this.delete(last[0]);
+ return last;
+ }
+
+ toKeyValue(key: K): [K, V];
+ toKeyValue(key: undefined): undefined;
+ toKeyValue(key: K | undefined): [K, V] | undefined;
+ toKeyValue(key: K | undefined): [K, V] | undefined {
+ return key != null ? [key, this.map.get(key)!] : undefined;
+ }
+
+ *[Symbol.iterator](): Generator<[K, V], void, void> {
+ for (const key of this.keys()) yield this.toKeyValue(key);
+ }
+
+ *keys(): Generator {
+ for (const key of this.tree.inOrder()) yield key;
+ }
+
+ *values(): Generator {
+ for (const key of this.keys()) yield this.map.get(key)!;
+ return undefined;
+ }
+
+ *rkeys(): Generator {
+ for (const key of this.tree.reverseInOrder()) yield key;
+ return undefined;
+ }
+
+ *rvalues(): Generator {
+ for (const key of this.rkeys()) yield this.map.get(key)!;
+ return undefined;
+ }
}
```
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.cpp b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.cpp
index 343ee6d466449..4d9fdeb7f9ba6 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.cpp
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.cpp
@@ -1,21 +1,26 @@
class Solution {
public:
bool isNStraightHand(vector& hand, int groupSize) {
+ if (hand.size() % groupSize) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ ranges::sort(hand);
unordered_map cnt;
- for (int& v : hand) ++cnt[v];
- sort(hand.begin(), hand.end());
- for (int& v : hand) {
- if (cnt.count(v)) {
- for (int x = v; x < v + groupSize; ++x) {
- if (!cnt.count(x)) {
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ ++cnt[x];
+ }
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ if (cnt.contains(x)) {
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!cnt.contains(y)) {
return false;
}
- if (--cnt[x] == 0) {
- cnt.erase(x);
+ if (--cnt[y] == 0) {
+ cnt.erase(y);
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
-};
\ No newline at end of file
+};
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.go b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.go
index 052092ae3469c..022bb6de7e2c0 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.go
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.go
@@ -1,21 +1,21 @@
func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
- cnt := map[int]int{}
- for _, v := range hand {
- cnt[v]++
+ if len(hand)%groupSize != 0 {
+ return false
}
sort.Ints(hand)
- for _, v := range hand {
- if _, ok := cnt[v]; ok {
- for x := v; x < v+groupSize; x++ {
- if _, ok := cnt[x]; !ok {
+ cnt := map[int]int{}
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ cnt[x]++
+ }
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ if cnt[x] > 0 {
+ for y := x; y < x+groupSize; y++ {
+ if cnt[y] == 0 {
return false
}
- cnt[x]--
- if cnt[x] == 0 {
- delete(cnt, x)
- }
+ cnt[y]--
}
}
}
return true
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.java b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.java
index 736d0922e891b..69354d24442cf 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.java
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.java
@@ -1,23 +1,22 @@
class Solution {
public boolean isNStraightHand(int[] hand, int groupSize) {
- Map cnt = new HashMap<>();
- for (int v : hand) {
- cnt.put(v, cnt.getOrDefault(v, 0) + 1);
+ if (hand.length % groupSize != 0) {
+ return false;
}
Arrays.sort(hand);
- for (int v : hand) {
- if (cnt.containsKey(v)) {
- for (int x = v; x < v + groupSize; ++x) {
- if (!cnt.containsKey(x)) {
+ Map cnt = new HashMap<>();
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ cnt.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
+ }
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ if (cnt.getOrDefault(x, 0) > 0) {
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (cnt.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum) < 0) {
return false;
}
- cnt.put(x, cnt.get(x) - 1);
- if (cnt.get(x) == 0) {
- cnt.remove(x);
- }
}
}
}
return true;
}
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.py b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.py
index 025af0a82f294..c7eccc1a5a41f 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.py
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.py
@@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
class Solution:
def isNStraightHand(self, hand: List[int], groupSize: int) -> bool:
+ if len(hand) % groupSize:
+ return False
cnt = Counter(hand)
- for v in sorted(hand):
- if cnt[v]:
- for x in range(v, v + groupSize):
- if cnt[x] == 0:
+ for x in sorted(hand):
+ if cnt[x]:
+ for y in range(x, x + groupSize):
+ if cnt[y] == 0:
return False
- cnt[x] -= 1
- if cnt[x] == 0:
- cnt.pop(x)
+ cnt[y] -= 1
return True
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.ts b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.ts
index 0396d0bf50443..562559046c37c 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.ts
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution.ts
@@ -1,20 +1,21 @@
-function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number) {
- const cnt: Record = {};
- for (const i of hand) {
- cnt[i] = (cnt[i] ?? 0) + 1;
+function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number): boolean {
+ if (hand.length % groupSize !== 0) {
+ return false;
}
-
- const keys = Object.keys(cnt).map(Number);
- for (const i of keys) {
- while (cnt[i]) {
- for (let j = i; j < groupSize + i; j++) {
- if (!cnt[j]) {
+ const cnt = new Map();
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ cnt.set(x, (cnt.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ hand.sort((a, b) => a - b);
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ if (cnt.get(x)! > 0) {
+ for (let y = x; y < x + groupSize; y++) {
+ if ((cnt.get(y) || 0) === 0) {
return false;
}
- cnt[j]--;
+ cnt.set(y, cnt.get(y)! - 1);
}
}
}
-
return true;
}
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.cpp b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.cpp
index d36a24b98490c..b670ab8f5e47a 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.cpp
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.cpp
@@ -1,19 +1,24 @@
class Solution {
public:
bool isNStraightHand(vector& hand, int groupSize) {
- if (hand.size() % groupSize != 0) return false;
+ if (hand.size() % groupSize) {
+ return false;
+ }
map mp;
- for (int& h : hand) mp[h] += 1;
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ ++mp[x];
+ }
while (!mp.empty()) {
- int v = mp.begin()->first;
- for (int i = v; i < v + groupSize; ++i) {
- if (!mp.count(i)) return false;
- if (mp[i] == 1)
- mp.erase(i);
- else
- mp[i] -= 1;
+ int x = mp.begin()->first;
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!mp.contains(y)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ if (--mp[y] == 0) {
+ mp.erase(y);
+ }
}
}
return true;
}
-};
\ No newline at end of file
+};
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.go b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.go
index d364408ceb4c5..83b10d62e3d13 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.go
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.go
@@ -2,26 +2,27 @@ func isNStraightHand(hand []int, groupSize int) bool {
if len(hand)%groupSize != 0 {
return false
}
- m := treemap.NewWithIntComparator()
- for _, h := range hand {
- if v, ok := m.Get(h); ok {
- m.Put(h, v.(int)+1)
+ tm := treemap.NewWithIntComparator()
+ for _, x := range hand {
+ if v, ok := tm.Get(x); ok {
+ tm.Put(x, v.(int)+1)
} else {
- m.Put(h, 1)
+ tm.Put(x, 1)
}
}
- for !m.Empty() {
- v, _ := m.Min()
- for i := v.(int); i < v.(int)+groupSize; i++ {
- if _, ok := m.Get(i); !ok {
- return false
- }
- if v, _ := m.Get(i); v.(int) == 1 {
- m.Remove(i)
+ for !tm.Empty() {
+ x, _ := tm.Min()
+ for y := x.(int); y < x.(int)+groupSize; y++ {
+ if v, ok := tm.Get(y); ok {
+ if v.(int) == 1 {
+ tm.Remove(y)
+ } else {
+ tm.Put(y, v.(int)-1)
+ }
} else {
- m.Put(i, v.(int)-1)
+ return false
}
}
}
return true
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.java b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.java
index 5f8bcca97a56c..e875f280dae90 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.java
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.java
@@ -4,22 +4,21 @@ public boolean isNStraightHand(int[] hand, int groupSize) {
return false;
}
TreeMap tm = new TreeMap<>();
- for (int h : hand) {
- tm.put(h, tm.getOrDefault(h, 0) + 1);
+ for (int x : hand) {
+ tm.merge(x, 1, Integer::sum);
}
while (!tm.isEmpty()) {
- int v = tm.firstKey();
- for (int i = v; i < v + groupSize; ++i) {
- if (!tm.containsKey(i)) {
+ int x = tm.firstKey();
+ for (int y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ int t = tm.merge(y, -1, Integer::sum);
+ if (t < 0) {
return false;
}
- if (tm.get(i) == 1) {
- tm.remove(i);
- } else {
- tm.put(i, tm.get(i) - 1);
+ if (t == 0) {
+ tm.remove(y);
}
}
}
return true;
}
-}
\ No newline at end of file
+}
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.py b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.py
index 60cc15f201b41..3e193822d7b4f 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.py
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.py
@@ -1,20 +1,16 @@
class Solution:
def isNStraightHand(self, hand: List[int], groupSize: int) -> bool:
- if len(hand) % groupSize != 0:
+ if len(hand) % groupSize:
return False
- sd = SortedDict()
- for h in hand:
- if h in sd:
- sd[h] += 1
- else:
- sd[h] = 1
+ cnt = Counter(hand)
+ sd = SortedDict(cnt)
while sd:
- v = sd.peekitem(0)[0]
- for i in range(v, v + groupSize):
- if i not in sd:
+ x = next(iter(sd))
+ for y in range(x, x + groupSize):
+ if y not in sd:
return False
- if sd[i] == 1:
- sd.pop(i)
+ if sd[y] == 1:
+ del sd[y]
else:
- sd[i] -= 1
+ sd[y] -= 1
return True
diff --git a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.ts b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.ts
index 5cd2d00b224b8..10e86ac07d79d 100644
--- a/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.ts
+++ b/solution/0800-0899/0846.Hand of Straights/Solution2.ts
@@ -1,29 +1,507 @@
function isNStraightHand(hand: number[], groupSize: number): boolean {
- const n = hand.length;
- if (n % groupSize) {
+ if (hand.length % groupSize !== 0) {
return false;
}
+ const tm = new TreeMap();
+ for (const x of hand) {
+ tm.set(x, (tm.get(x) || 0) + 1);
+ }
+ while (tm.size()) {
+ const x = tm.first()![0];
+ for (let y = x; y < x + groupSize; ++y) {
+ if (!tm.has(y)) {
+ return false;
+ }
+ if (tm.get(y)! === 1) {
+ tm.delete(y);
+ } else {
+ tm.set(y, tm.get(y)! - 1);
+ }
+ }
+ }
+ return true;
+}
+
+type Compare = (lhs: T, rhs: T) => number;
+
+class RBTreeNode {
+ data: T;
+ count: number;
+ left: RBTreeNode | null;
+ right: RBTreeNode
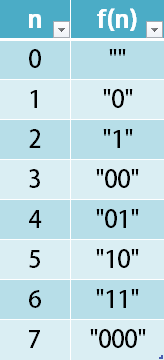
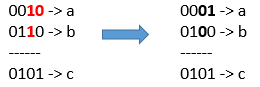






 +
+
 +
+
 +
+
 +
+
 +
+



 +
+
 +
+



 +
+
